Everyone Needs a Repair Crew: Elizabethkingia anophelis R26
... across the United States in the past several years. E. anophelis is found in the gut of certain mosquitos as well as a human pathogen (5, 10). The danger of the bacteria to humans is its resistance to multiple antibiotics. E. anophelis has a circular genome of over 4 million base pairs and over 4 th ...
... across the United States in the past several years. E. anophelis is found in the gut of certain mosquitos as well as a human pathogen (5, 10). The danger of the bacteria to humans is its resistance to multiple antibiotics. E. anophelis has a circular genome of over 4 million base pairs and over 4 th ...
Name __________________________________ Period _________________
... 7. _______________________ The cytoplasm divides and two new cells are formed. 8. _______________________ Centromere splits, chromatids separate and begin to move apart 9. _______________________ Spindle begins to form 10. _______________________ Chromosomes line up in the middle or equator of the s ...
... 7. _______________________ The cytoplasm divides and two new cells are formed. 8. _______________________ Centromere splits, chromatids separate and begin to move apart 9. _______________________ Spindle begins to form 10. _______________________ Chromosomes line up in the middle or equator of the s ...
Subject:
... Understandings: This unit is focused on patterns of inheritance and genomics. Students will learn how genes interact, how traits are expressed, how scientists study this inheritance, and current applications of this knowledge. Specifically, students will gain an understanding of: Mendelian genetic ...
... Understandings: This unit is focused on patterns of inheritance and genomics. Students will learn how genes interact, how traits are expressed, how scientists study this inheritance, and current applications of this knowledge. Specifically, students will gain an understanding of: Mendelian genetic ...
X-inactivation
... = site of transcription and processing of rRNAs, site of assembly of rRNA and proteins into two ribosomal subunits (subunits join to form cytoplasmic ribosomes) nucleoli disappear during mitosis, formed at telophase at specific sites of acrocentric chromosomes (satellite stalks of chromosomes Nos 13 ...
... = site of transcription and processing of rRNAs, site of assembly of rRNA and proteins into two ribosomal subunits (subunits join to form cytoplasmic ribosomes) nucleoli disappear during mitosis, formed at telophase at specific sites of acrocentric chromosomes (satellite stalks of chromosomes Nos 13 ...
Mitosis Meiosis
... How are traits passed to offspring? Two types of reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ...
... How are traits passed to offspring? Two types of reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ...
Genome Sequencing Machine Learning for Big Data Seminar by Guided by
... Genetic diseases often arise from simple changes to the coding region of a gene-altering the protein made by that gene. The disease arises because the protein does not work as it should do. Some genomic conditions also affect coding regions. A translocation, for example, can end up fusing genes ...
... Genetic diseases often arise from simple changes to the coding region of a gene-altering the protein made by that gene. The disease arises because the protein does not work as it should do. Some genomic conditions also affect coding regions. A translocation, for example, can end up fusing genes ...
Cell with DNA containing gene of interest
... probability that someone will win it is very large. ...
... probability that someone will win it is very large. ...
Human Biology Unit III: INHERITANCE AND HUMAN GENETIC
... Introduction: Humans begin life as just one cell and in adult form contain over 100 trillion cells. Cell Division allows this metamorphosis, and in the process of cell division chromosomes and DNA can be altered. These alterations cause variation, mutations, and genetic disease. Genetics, DNA, and g ...
... Introduction: Humans begin life as just one cell and in adult form contain over 100 trillion cells. Cell Division allows this metamorphosis, and in the process of cell division chromosomes and DNA can be altered. These alterations cause variation, mutations, and genetic disease. Genetics, DNA, and g ...
Chapter 1 - bYTEBoss
... (PCR) to make many copies of a DNA sequence – Short tandem repeats (STRs) and their forensic importance – The use of electrophoresis to analyze STRs – The Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) – DNA paternity testing – Mitochondrial DNA testing ...
... (PCR) to make many copies of a DNA sequence – Short tandem repeats (STRs) and their forensic importance – The use of electrophoresis to analyze STRs – The Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) – DNA paternity testing – Mitochondrial DNA testing ...
NATIONAL BRAIN RESEARCH CENTRE(NBRC) NH-8, Manesar-122050, HARYANA
... Mohr’s salt is prepared in warm distilled water by the reaction of (NH4)2SO4 and: ...
... Mohr’s salt is prepared in warm distilled water by the reaction of (NH4)2SO4 and: ...
Timeline
... • a rare few have been found with thirty genes in them. • cells can have anywhere from a couple to fifty or more plasmids in them. • some pop into the bacterial chromosome = episomes. ...
... • a rare few have been found with thirty genes in them. • cells can have anywhere from a couple to fifty or more plasmids in them. • some pop into the bacterial chromosome = episomes. ...
protein synthesis - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... During transcription, the DNA double helix “unzips”. As the hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, nucleotides floating in the nucleus line up next to the nucleotides of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces thymine in the RNA formation; therefore, urac ...
... During transcription, the DNA double helix “unzips”. As the hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, nucleotides floating in the nucleus line up next to the nucleotides of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces thymine in the RNA formation; therefore, urac ...
ExamView - Final Exam.tst
... 14. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? A. Some codons do not specify an amino acid. B. There are 64 different kinds of codons but only 20 amino acids. C. Some codons have the same sequence of nucleotides. D. The codon AUG codes for the amino acid met ...
... 14. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? A. Some codons do not specify an amino acid. B. There are 64 different kinds of codons but only 20 amino acids. C. Some codons have the same sequence of nucleotides. D. The codon AUG codes for the amino acid met ...
Homologous Recombination DNA break repair by homologous
... (or other duplicated loci) can result in chromosome deletion, inversion and translocation events ...
... (or other duplicated loci) can result in chromosome deletion, inversion and translocation events ...
Slides - Department of Computer Science
... • Linear sequence of amino acids folds to form a complex 3-D structure. • The structure of a protein is intimately connected to its function. ...
... • Linear sequence of amino acids folds to form a complex 3-D structure. • The structure of a protein is intimately connected to its function. ...
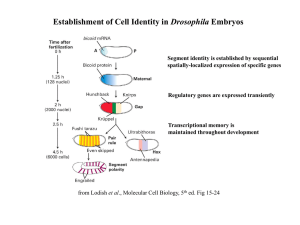
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Prions template conformational conversion of other molecules of the same protein ...
... Prions template conformational conversion of other molecules of the same protein ...
Document
... Major Patterns of Monogenic Inheritance – Patterns of autosomal dominant inheritance (AD) 常染色体显性 – Patterns of autosomal recessive inheritance (AR) 常染色体隐性 – Patterns of X-linked recessive inheritance (XD) X-连锁显性 – Patterns of X-linked dominant inheritance (XR) X-连锁隐性 – Patterns of Y-linked inherita ...
... Major Patterns of Monogenic Inheritance – Patterns of autosomal dominant inheritance (AD) 常染色体显性 – Patterns of autosomal recessive inheritance (AR) 常染色体隐性 – Patterns of X-linked recessive inheritance (XD) X-连锁显性 – Patterns of X-linked dominant inheritance (XR) X-连锁隐性 – Patterns of Y-linked inherita ...
HSA Practice Currence
... A scientist believes that a factory has been dumping acid into a local river. To test this hypothesis, which property of water should the scientist monitor? A pH B density C polarity D temperature ...
... A scientist believes that a factory has been dumping acid into a local river. To test this hypothesis, which property of water should the scientist monitor? A pH B density C polarity D temperature ...
Chapter 8: Cell Division
... 1. Understand the two-step process of protein synthesis (transcription and translation); also define what a protein is. 2. Know the difference between DNA and RNA. 3. Know the three different types of RNA. 4. Know what codons are and their role in determining the amino acid composition of proteins; ...
... 1. Understand the two-step process of protein synthesis (transcription and translation); also define what a protein is. 2. Know the difference between DNA and RNA. 3. Know the three different types of RNA. 4. Know what codons are and their role in determining the amino acid composition of proteins; ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry
... 2. In transcription (DNA is used to make ____________). A pairs with _________, T pairs with _________, G pairs with __________, C pairs with __________. ...
... 2. In transcription (DNA is used to make ____________). A pairs with _________, T pairs with _________, G pairs with __________, C pairs with __________. ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry
... Flower color in snapdragons is determined by incomplete dominance. If a homozygous red flower crosses with a homozygous ivory flower, the phenotypic outcome for F1 is 100% pink. Predict the phenotype & genotype percentages for the F2 generation. ...
... Flower color in snapdragons is determined by incomplete dominance. If a homozygous red flower crosses with a homozygous ivory flower, the phenotypic outcome for F1 is 100% pink. Predict the phenotype & genotype percentages for the F2 generation. ...
March 13
... Cytoplasmic inheritance Variegation arises because have mix of “good” and “bad” cp •Segregate randomly at division •eventually one form predominates In plants, cytoplasm comes from the egg •most pollen do not have cp or mt •can't study genetically, because no way to mix parental organelles ...
... Cytoplasmic inheritance Variegation arises because have mix of “good” and “bad” cp •Segregate randomly at division •eventually one form predominates In plants, cytoplasm comes from the egg •most pollen do not have cp or mt •can't study genetically, because no way to mix parental organelles ...
Intro to Genetics
... you expect to find in the organism’s gametes? a. 4 b. 6 c. 10 d. 12 12. During which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up side by side? a. prophase b. telophase I c. metaphase II d. anaphase II 13. The division of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is called a. mitosis. b. binary fissi ...
... you expect to find in the organism’s gametes? a. 4 b. 6 c. 10 d. 12 12. During which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up side by side? a. prophase b. telophase I c. metaphase II d. anaphase II 13. The division of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is called a. mitosis. b. binary fissi ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.