Unit #3 Map (2016) Unit_#3_Map_2016
... 1. Complementary: characteristic of nucleic acids in which the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other 2. mRNA (messenger RNA): messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome 3. Mutation: a change in the nucleotide-b ...
... 1. Complementary: characteristic of nucleic acids in which the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other 2. mRNA (messenger RNA): messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome 3. Mutation: a change in the nucleotide-b ...
Protein Synthesis
... 3. What is the purpose of transcription? How does it differ from DNA replication? The purpose of transcription is to re-write a portion of DNA, a gene, Transcription constructs an mRNA molecule through complimentary base pairing a portion of DNA. DNA replication makes an exact copy of the entire DNA ...
... 3. What is the purpose of transcription? How does it differ from DNA replication? The purpose of transcription is to re-write a portion of DNA, a gene, Transcription constructs an mRNA molecule through complimentary base pairing a portion of DNA. DNA replication makes an exact copy of the entire DNA ...
DNA Technology and Genomics I.
... The typical human gene specifies several different polypeptides by using different combinations of exons. D. Nearly all human genes contain several exons, and an estimated 75% of these multiexon genes are alternatively spliced. Along with this is additional polypeptide diversity via posttranslationa ...
... The typical human gene specifies several different polypeptides by using different combinations of exons. D. Nearly all human genes contain several exons, and an estimated 75% of these multiexon genes are alternatively spliced. Along with this is additional polypeptide diversity via posttranslationa ...
Chapter 11: DNA and the Language of Life - Rebecca Waggett
... DNA in all organisms and accounts for similarities in related individuals. • Manipulation of DNA in organisms has led to commercial production of biological molecules on a large scale and genetically modified organisms. ...
... DNA in all organisms and accounts for similarities in related individuals. • Manipulation of DNA in organisms has led to commercial production of biological molecules on a large scale and genetically modified organisms. ...
At the Forefront in PGD
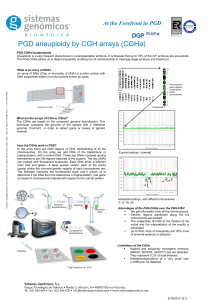
... diseases not ensure that the embryo will be euploid. On the other hand, it is well known that the aneuploidy is a common phenomenon in primplantation embryos, involving monosomies and trisomies of the 22 autosomes and sex chromosomes. In conclusion, combined molecular PGD allows the transfer of heal ...
... diseases not ensure that the embryo will be euploid. On the other hand, it is well known that the aneuploidy is a common phenomenon in primplantation embryos, involving monosomies and trisomies of the 22 autosomes and sex chromosomes. In conclusion, combined molecular PGD allows the transfer of heal ...
Long Noncoding RNAs May Alter Chromosome`s 3D
... in Switzerland. This finding supports a role chromosome in mice embryonic stem cells. for lncRNAs in regulating chromosomal XIST interacted with a new set of DNA loops activity by influencing the shape of chroma- nearby. And when they put the XIST gene on tin, the protein complex that swaddles DNA. a ...
... in Switzerland. This finding supports a role chromosome in mice embryonic stem cells. for lncRNAs in regulating chromosomal XIST interacted with a new set of DNA loops activity by influencing the shape of chroma- nearby. And when they put the XIST gene on tin, the protein complex that swaddles DNA. a ...
doc Cell Cycle 1 Notes (Pause)
... (used to growing outside), and consequently favorable for in vitro studies. The reason they are large is evolutionary—they do not want to be digested by predators, so the eggs grow (without division) to 100,000X in months (so the cytoplasm is 100,000X big, but the nucleus is still that of the origin ...
... (used to growing outside), and consequently favorable for in vitro studies. The reason they are large is evolutionary—they do not want to be digested by predators, so the eggs grow (without division) to 100,000X in months (so the cytoplasm is 100,000X big, but the nucleus is still that of the origin ...
Epigenetics seminar 9-7-2014
... were once thought of as ‘junk’, but it is now found to have important roles in regulating how, where, & when genes are expressed. •An NIH study found large number of disease-associated GWAS variants located in regulatory DNA regions that are active during foetal development suggesting that environme ...
... were once thought of as ‘junk’, but it is now found to have important roles in regulating how, where, & when genes are expressed. •An NIH study found large number of disease-associated GWAS variants located in regulatory DNA regions that are active during foetal development suggesting that environme ...
dna sequencing lab - Georgia Standards
... Step 1: Using the original DNA strands as given below, compare the two given strands. Mark each of the differences in the sequences. Use circles or highlighting to mark the differences. Step 2: Transcribe from the original DNA sequence to form a strand of mRNA. Step 3: Translate the mRNA sequence us ...
... Step 1: Using the original DNA strands as given below, compare the two given strands. Mark each of the differences in the sequences. Use circles or highlighting to mark the differences. Step 2: Transcribe from the original DNA sequence to form a strand of mRNA. Step 3: Translate the mRNA sequence us ...
Physiological Homeostasis means …………
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – Using DNA replication to amplify a specific section of DNA ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – Using DNA replication to amplify a specific section of DNA ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
... Expand Long Template PCR kit (Roche). High-Tm, C. scorpioides-specific primers were designed by first amplifying an ~ 660-bp segment of the COX1 gene, using the highly conserved chelicerate forward1 (5'-TACTCTACTAATCATAAAGACATTGG – 3’) and reverse2 (5’ – GGATGGCCAAAAAATCAAAATAAATG – 3’) primers [1], ...
... Expand Long Template PCR kit (Roche). High-Tm, C. scorpioides-specific primers were designed by first amplifying an ~ 660-bp segment of the COX1 gene, using the highly conserved chelicerate forward1 (5'-TACTCTACTAATCATAAAGACATTGG – 3’) and reverse2 (5’ – GGATGGCCAAAAAATCAAAATAAATG – 3’) primers [1], ...
PPT file - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... number would be 268 + 3 + 3 + 5 + 5 = 284 / 1448 = 19.6. Aaah! In general, to minimize the effect of double crossovers, it is necessary to measure a number of small RF distances and sum to ...
... number would be 268 + 3 + 3 + 5 + 5 = 284 / 1448 = 19.6. Aaah! In general, to minimize the effect of double crossovers, it is necessary to measure a number of small RF distances and sum to ...
Cell Division Mitosis vs. Meiosis - kromko
... Double-stranded DNA Single-stranded DNA Double-stranded RNA Single-stranded RNA ...
... Double-stranded DNA Single-stranded DNA Double-stranded RNA Single-stranded RNA ...
Biol 178 Practice Exam 2
... (A) mitochondra and chloroplasts were once free-living cells, (B) mitochondria and chloroplasts can exist independently of the eukaryotic cell. (C) lysosomes were once prokaryotes. (D) all organelles have 2 membranes. (E) all of the above. ...
... (A) mitochondra and chloroplasts were once free-living cells, (B) mitochondria and chloroplasts can exist independently of the eukaryotic cell. (C) lysosomes were once prokaryotes. (D) all organelles have 2 membranes. (E) all of the above. ...
Genetic Technology
... • Each time the host cell divides it copies the recombinant DNA along with its own. • The host cell can produce the protein encoded on the recombinant DNA. ...
... • Each time the host cell divides it copies the recombinant DNA along with its own. • The host cell can produce the protein encoded on the recombinant DNA. ...
The Dolan DNA Learning Center at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
... 4. What role does the repressor (product of the lacI gene) play in control of transcription of the lac operon? It is inhibits transcription when physically bound to the regulatory region. 5. What effect does the inducer have on the lacI gene product? It has an allosteric effect on the repressor, cha ...
... 4. What role does the repressor (product of the lacI gene) play in control of transcription of the lac operon? It is inhibits transcription when physically bound to the regulatory region. 5. What effect does the inducer have on the lacI gene product? It has an allosteric effect on the repressor, cha ...
THE GENOME AND THE ORIGIN OF MAN
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
SPIS TREŚCI
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
... reduced nucleotide variability, excess synonymous over non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphism, and other features that are expected in genes or DNA sequences that have functional roles. It has been very premature to suggest that pseudogenes are simply genetic fossils. This is not to say that there ...
DNA to Protein - byrdistheword
... There are 20 amino acids, but only 4 different nucleotide bases they can combine in so many different ways, ...
... There are 20 amino acids, but only 4 different nucleotide bases they can combine in so many different ways, ...
wattsmisc03 - Centre for Genomic Research
... region. We can look at a whole set of such regions, determine which alleles are present at each and we have a genetic ‘fingerprint’ which uniquely identifies that individual (see Box 1). Furthermore, if we also fingerprint possible parents, we can usually tell which is the offspring of which parent ...
... region. We can look at a whole set of such regions, determine which alleles are present at each and we have a genetic ‘fingerprint’ which uniquely identifies that individual (see Box 1). Furthermore, if we also fingerprint possible parents, we can usually tell which is the offspring of which parent ...
General enquiries on this form should be made to
... needed to be amplified. This was successfully done using a technique called GenomiPhi amplification; yielding high concentrations of DNA. This amplified DNA will be the main resource for future screening of the TILLING population for mutations in genes of interest. The strategy for doing this is to ...
... needed to be amplified. This was successfully done using a technique called GenomiPhi amplification; yielding high concentrations of DNA. This amplified DNA will be the main resource for future screening of the TILLING population for mutations in genes of interest. The strategy for doing this is to ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.