DNA Transcription All#read
... the template DNA strand and begins to catalyze production of complementary RNA. Polymerases are large enzymes composed of approximately a dozen subunits, and when active on DNA, they are also typically complexed with other factors. In many cases, these factors signal which gene is to be transcribed. ...
... the template DNA strand and begins to catalyze production of complementary RNA. Polymerases are large enzymes composed of approximately a dozen subunits, and when active on DNA, they are also typically complexed with other factors. In many cases, these factors signal which gene is to be transcribed. ...
Taster Lab Student Doc PDF
... linked together in a specific order on long DNA molecules called chromosomes. The human genome is 99.9% identical from person to person. What is considered the normal number of chromosomes for human body cells? What is considered the normal number of chromosomes for human gametes? Although we are al ...
... linked together in a specific order on long DNA molecules called chromosomes. The human genome is 99.9% identical from person to person. What is considered the normal number of chromosomes for human body cells? What is considered the normal number of chromosomes for human gametes? Although we are al ...
HSV-1 - Iranian Biomedical Journal
... Keywords: Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), PCR, DNA binding protein (UL29), Thymidine Kinase (TK, UL23), Polymorphism ...
... Keywords: Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), PCR, DNA binding protein (UL29), Thymidine Kinase (TK, UL23), Polymorphism ...
Epigenetics and the exposomes: Obesity and beyond
... as the rare variant-common disease hypothesis and the common variant-common disease hypothesis.1 Through association studies, unique gene-environment interactions, which may occur with or without specific periods of permissiveness or vulnerabilities, have also been identified. Major conditions where ...
... as the rare variant-common disease hypothesis and the common variant-common disease hypothesis.1 Through association studies, unique gene-environment interactions, which may occur with or without specific periods of permissiveness or vulnerabilities, have also been identified. Major conditions where ...
Gene Tech answers622 KB
... In the ethical arguments, students should be precise, e.g. a clear example rather than simply ethical problems of animal welfare. Students need to compare both sides of an ethical discussion and show reasoned arguments in support of the points made. They may hold strong personal views, which can be ...
... In the ethical arguments, students should be precise, e.g. a clear example rather than simply ethical problems of animal welfare. Students need to compare both sides of an ethical discussion and show reasoned arguments in support of the points made. They may hold strong personal views, which can be ...
Genetics Review
... independent assortment, and dominance) support the chromosome theory of inheritance (see B-4.6). • Due to advances in technology since Mendel, inheritance patterns and genetic variations that could not be explained by Mendelian genetics are now understood using the chromosome theory of inheritance. ...
... independent assortment, and dominance) support the chromosome theory of inheritance (see B-4.6). • Due to advances in technology since Mendel, inheritance patterns and genetic variations that could not be explained by Mendelian genetics are now understood using the chromosome theory of inheritance. ...
slow-learners - WordPress.com
... 5. What are the characteristics of a wind pollinated flowers? 6. Trace the development of a mature ovule from a megaspore mother cell/ 7. What is double fertilization? Explain. 8. Differentiate between monoecious and dioecious plants. Give an example of each. ...
... 5. What are the characteristics of a wind pollinated flowers? 6. Trace the development of a mature ovule from a megaspore mother cell/ 7. What is double fertilization? Explain. 8. Differentiate between monoecious and dioecious plants. Give an example of each. ...
Genomics - California Lutheran University
... Duke University said last week that it will sequence 4,000 individuals as part of a collaborative, $25 million effort to identify as many genes as possible implicated in epilepsy. ...
... Duke University said last week that it will sequence 4,000 individuals as part of a collaborative, $25 million effort to identify as many genes as possible implicated in epilepsy. ...
Chapter 25 DNA metabolism
... Clamp loader is called RFC (Replication Factor C) Termination involved synthesis of special structures called telomeres at end of chromosomes Will look at details next chapter (But nothing is said about termination within a chromosome) ...
... Clamp loader is called RFC (Replication Factor C) Termination involved synthesis of special structures called telomeres at end of chromosomes Will look at details next chapter (But nothing is said about termination within a chromosome) ...
A Glossary of Molecular Biology Terms More can be found at http
... any purine, i.e. A or G). ZQ1 may also be able to weakly bind to ACAGTT (which differs by one base from the consensus). Contig: Several uses, all nouns. The term comes from a shortening of the word ‘contiguous’. A ‘contig’ may refer to a map showing placement of a set of clones that completely, con ...
... any purine, i.e. A or G). ZQ1 may also be able to weakly bind to ACAGTT (which differs by one base from the consensus). Contig: Several uses, all nouns. The term comes from a shortening of the word ‘contiguous’. A ‘contig’ may refer to a map showing placement of a set of clones that completely, con ...
Total Dissolved Solids
... In this lab, you will perform a procedure known as genetic transformation. Genetic transformation literally means “change caused by genes”, and occurs when the cell incorporates and expresses a new piece of genetic material – DNA derived from another organism. Transformation involves the insertion o ...
... In this lab, you will perform a procedure known as genetic transformation. Genetic transformation literally means “change caused by genes”, and occurs when the cell incorporates and expresses a new piece of genetic material – DNA derived from another organism. Transformation involves the insertion o ...
Teacher Materials
... message is delivered to the ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Since there are only about 20 different amino acids, some of the 64 possible codes will code for the same amino acid. Some amino acids have up to six different codes. The 20 amino acids combine in different sequences in order to synthesize the thousa ...
... message is delivered to the ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Since there are only about 20 different amino acids, some of the 64 possible codes will code for the same amino acid. Some amino acids have up to six different codes. The 20 amino acids combine in different sequences in order to synthesize the thousa ...
Genetic Control of Cell Function and Inheritance
... Proteins are made from a standard set of amino acids, which are joined end to end to form the long polypeptide chains of protein molecules. Each polypeptide chain may have as many as 100 to more than 300 amino acids in it. The process of protein synthesis is called translation because the genetic co ...
... Proteins are made from a standard set of amino acids, which are joined end to end to form the long polypeptide chains of protein molecules. Each polypeptide chain may have as many as 100 to more than 300 amino acids in it. The process of protein synthesis is called translation because the genetic co ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
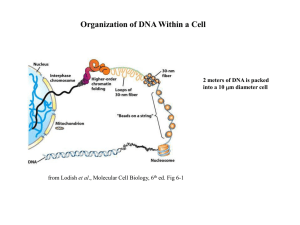
... – Core histones form a ball with DNA wrapped around the outside – H1 also lies on the outside of the nucleosome ...
... – Core histones form a ball with DNA wrapped around the outside – H1 also lies on the outside of the nucleosome ...
Genomic sequence analysis of a plant
... secreting small iron-binding molecules called siderophores. Bacteria have developed several mechanisms to compete for iron, an important element required for their growth. Siderophores are known to have an antagonistic effect by depriving iron from other microorganisms [14]. The presence of an effec ...
... secreting small iron-binding molecules called siderophores. Bacteria have developed several mechanisms to compete for iron, an important element required for their growth. Siderophores are known to have an antagonistic effect by depriving iron from other microorganisms [14]. The presence of an effec ...
Mitochondria tutorial
... default 'all restriction enzymes'. There are a lot of different enzymes, and some of them are pretty difficult (and expensive) to buy, so we will change the setting to Core set of enzymes. This way the program will only search enzymes that are common, usually inexpensive, and frequently found on the ...
... default 'all restriction enzymes'. There are a lot of different enzymes, and some of them are pretty difficult (and expensive) to buy, so we will change the setting to Core set of enzymes. This way the program will only search enzymes that are common, usually inexpensive, and frequently found on the ...
Mendelian Inheritance - DNALC::Protocols
... Next, Mendel attempted to explain why the recessive trait disappeared in the first generation, and reappeared in the second. He hypothesized that every trait in an organism is controlled by two factors, one from each parent. All factors occur in pairs (for every trait there is a pair of genes that c ...
... Next, Mendel attempted to explain why the recessive trait disappeared in the first generation, and reappeared in the second. He hypothesized that every trait in an organism is controlled by two factors, one from each parent. All factors occur in pairs (for every trait there is a pair of genes that c ...
Unit 4 Schedule
... called the cell cycle. It usually lasts about 18 – 24 hours in animals. The various phases of the cell cycle are shown below: The phase between successive mitoses is called interphase and is termed S (synthesis). The S period is between two G (gap) phases during which cell growth occurs. The G phase ...
... called the cell cycle. It usually lasts about 18 – 24 hours in animals. The various phases of the cell cycle are shown below: The phase between successive mitoses is called interphase and is termed S (synthesis). The S period is between two G (gap) phases during which cell growth occurs. The G phase ...
Skeletal Dwarfism - Info on this condition
... The DNA tests relevant to our Labrador breed seem to grow in number every few months and one of the interesting things we will also need to keep in mind, particularly as researchers investigate even more subtle but inherited traits, is the effect of what is termed epigenetics (more later). One of th ...
... The DNA tests relevant to our Labrador breed seem to grow in number every few months and one of the interesting things we will also need to keep in mind, particularly as researchers investigate even more subtle but inherited traits, is the effect of what is termed epigenetics (more later). One of th ...
Document
... Aspergillus fumigatus Genomic DNA Prep 1. Inoculate broth (usually GMM) with AF spores by gently scraping colony until tip is green and dunking it in the media. Twice should be enough. Grow overnight. Usually 10 ml of broth in a 50 ml centrifuge is adequate but 50 ml in a 250 ml flask may be necessa ...
... Aspergillus fumigatus Genomic DNA Prep 1. Inoculate broth (usually GMM) with AF spores by gently scraping colony until tip is green and dunking it in the media. Twice should be enough. Grow overnight. Usually 10 ml of broth in a 50 ml centrifuge is adequate but 50 ml in a 250 ml flask may be necessa ...
2007 - life.illinois.edu
... The lambda phage grown on the E. coli K (P1) host is modified for both K and P1 sites so they are resistant to both K and P1 restriction systems. OR the few plaques found when the K-grown phage infects the P1 lysogen are rare chromosomes that became P1 modified before the P1 restriction enzyme degra ...
... The lambda phage grown on the E. coli K (P1) host is modified for both K and P1 sites so they are resistant to both K and P1 restriction systems. OR the few plaques found when the K-grown phage infects the P1 lysogen are rare chromosomes that became P1 modified before the P1 restriction enzyme degra ...
Structure of B-DNA with Cations Tethered in the Major Groove†
... were converted to partially occupied Tl+ atoms. Successive refinements and map calculations were performed. Estimates of occupancies were obtained by monitoring negative and positive difference electron density. Additional anomalous maps were made using the position of the phosphorus atoms and the s ...
... were converted to partially occupied Tl+ atoms. Successive refinements and map calculations were performed. Estimates of occupancies were obtained by monitoring negative and positive difference electron density. Additional anomalous maps were made using the position of the phosphorus atoms and the s ...
Organisation of the human genome and our tools for
... other polypeptides, the functional endpoint of this process: the protein. As stated earlier, as a result of the variation produced during evolution the size of the genome (and our genes) has expanded compared with more simple organisms. Only 2% of the DNA sequence information in the human genome is ...
... other polypeptides, the functional endpoint of this process: the protein. As stated earlier, as a result of the variation produced during evolution the size of the genome (and our genes) has expanded compared with more simple organisms. Only 2% of the DNA sequence information in the human genome is ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.