What Makes the “Blue” in Blueberries?
... • Abnormal chromosome number • Faulty spindle formation ...
... • Abnormal chromosome number • Faulty spindle formation ...
DNA Recombination Mechanisms
... Homologous recombination allows for the exchange of blocks of genes between homologous chromosomes and thereby is a mechanism for generating genetic diversity Recombination occurs randomly between two homologous sequences and the frequency of recombination between two sites is proportional to the di ...
... Homologous recombination allows for the exchange of blocks of genes between homologous chromosomes and thereby is a mechanism for generating genetic diversity Recombination occurs randomly between two homologous sequences and the frequency of recombination between two sites is proportional to the di ...
Genomics - FSU Biology - Florida State University
... locating transcription and translation affecter sites. Two-Dimensional Weight Matrices, cont. The TATA site (aka “Hogness” box) — a conserved A-T rich sequence found about 25 base pairs upstream of the start point of eukaryotic transcription, may be involved in positioning RNA polymerase II for corr ...
... locating transcription and translation affecter sites. Two-Dimensional Weight Matrices, cont. The TATA site (aka “Hogness” box) — a conserved A-T rich sequence found about 25 base pairs upstream of the start point of eukaryotic transcription, may be involved in positioning RNA polymerase II for corr ...
Molecular parasitology in the 21st Century
... mutagenesis in Leishmania has led to the identification of important genes involved in the synthesis of surface LPG (lipophosphoglycan). In T. brucei, RNAi (RNA interference) has been adapted to knock down genes involved in surface‑protein expression. An RNAi library containing random segments of ge ...
... mutagenesis in Leishmania has led to the identification of important genes involved in the synthesis of surface LPG (lipophosphoglycan). In T. brucei, RNAi (RNA interference) has been adapted to knock down genes involved in surface‑protein expression. An RNAi library containing random segments of ge ...
Molecular genetic basis of porcine histo
... Poly A⫹ RNA was prepared from group A porcine submaxillary glands and used for RT-PCR of a putative porcine A transferase complementary DNA using 2 primers: FY-530 (5⬘-CTCCAGGCACCTGGCTTG) and FY-531 (5⬘-CCCTCCTCCTGTTCGTCG). The sequences in these primers corresponded to the sequences in the 5⬘ UTR a ...
... Poly A⫹ RNA was prepared from group A porcine submaxillary glands and used for RT-PCR of a putative porcine A transferase complementary DNA using 2 primers: FY-530 (5⬘-CTCCAGGCACCTGGCTTG) and FY-531 (5⬘-CCCTCCTCCTGTTCGTCG). The sequences in these primers corresponded to the sequences in the 5⬘ UTR a ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... The student will plan and conduct investigations in which a) data are organized into tables showing repeated trials and means; d) sources of experimental error are identified; e) dependent variables, independent variables, and constants are identified; g) continuous line graphs are constructed, inte ...
... The student will plan and conduct investigations in which a) data are organized into tables showing repeated trials and means; d) sources of experimental error are identified; e) dependent variables, independent variables, and constants are identified; g) continuous line graphs are constructed, inte ...
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
... Disadvantages of Asexual No new DNA combinations for evolution to work on ...
... Disadvantages of Asexual No new DNA combinations for evolution to work on ...
Unoshan_project
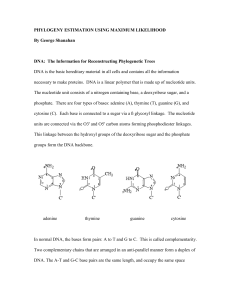
... directions, and the bases of the individual nucleotides are on the inside of the helix, stacked on top of each other. The larger base shape shown in the picture above depicts the purines (adenine and guanine). The other base shape in the illustration represents the pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) ...
... directions, and the bases of the individual nucleotides are on the inside of the helix, stacked on top of each other. The larger base shape shown in the picture above depicts the purines (adenine and guanine). The other base shape in the illustration represents the pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) ...
Work Day 1
... 2. Antibiotics are changing and subsequently becoming weaker – Antibiotics are inert chemical substances. Bacteria, however, are living organisms that can change through evolution. 3. Bacteria have mutated in order to become resistant – Bacteria do not “choose” to mutate, adapt, or develop resistanc ...
... 2. Antibiotics are changing and subsequently becoming weaker – Antibiotics are inert chemical substances. Bacteria, however, are living organisms that can change through evolution. 3. Bacteria have mutated in order to become resistant – Bacteria do not “choose” to mutate, adapt, or develop resistanc ...
Ch. 12 .1 12.2 Human Genetics Notes
... Nondisjunction in meiosis I results in all the gametes having abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Nondisjunction in meiosis II results in two normal gametes and two abnormal gametes. (Note that for simplicity only two pairs of homologous chromosomes are shown rather than all 23 pairs.) ...
... Nondisjunction in meiosis I results in all the gametes having abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Nondisjunction in meiosis II results in two normal gametes and two abnormal gametes. (Note that for simplicity only two pairs of homologous chromosomes are shown rather than all 23 pairs.) ...
Transcription and Translation
... How many different mRNA codons are there on the chart? 43 = 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 different codons (using A, G, C and U in triplets) • How many different amino acids are there? Only 20 • Which amino acids only have ONE triplet code assigned to them? Methionine and Trytophan • With the exception of Methioni ...
... How many different mRNA codons are there on the chart? 43 = 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 different codons (using A, G, C and U in triplets) • How many different amino acids are there? Only 20 • Which amino acids only have ONE triplet code assigned to them? Methionine and Trytophan • With the exception of Methioni ...
Things to know for the Final - Mercer Island School District
... Understand the structure of a DNA molecule, including knowing the 3 parts of the nucleotide subunits of DNA, and how the nucleotides are arranged in a DNA molecule. Be able to compare and contrast DNA and RNA (include 3 differences). Be able to explain the complementary base pairs in a DNA molecule, ...
... Understand the structure of a DNA molecule, including knowing the 3 parts of the nucleotide subunits of DNA, and how the nucleotides are arranged in a DNA molecule. Be able to compare and contrast DNA and RNA (include 3 differences). Be able to explain the complementary base pairs in a DNA molecule, ...
Ch. 13: Presentation Slides
... • The AP endonuclease system repairs nucleotide sites at which the base has been lost • Special enzymes repair damage caused to DNA by ...
... • The AP endonuclease system repairs nucleotide sites at which the base has been lost • Special enzymes repair damage caused to DNA by ...
08_Human_chromosomes(plain)
... mtDNA is small, only 16.6 kb, and circular, although it is double stranded like most DNA molecules. It has only 37 genes, 13 of these make mitochondrial proteins and the rest encode tRNAs and rRNAs. Each mtDNA has a single origin of replication. During DNA replication two replication forks leave the ...
... mtDNA is small, only 16.6 kb, and circular, although it is double stranded like most DNA molecules. It has only 37 genes, 13 of these make mitochondrial proteins and the rest encode tRNAs and rRNAs. Each mtDNA has a single origin of replication. During DNA replication two replication forks leave the ...
Diagnosing Mitochondrial Disorder
... Both parents are carriers of the genetic disorder, which appears on any of the 22 chromosome pairs other than the sex chromosomes. In other words, each parent has one affected chromosome and one unaffected in his/her individual pair. Because each parent contributes only one chromosome to the child, ...
... Both parents are carriers of the genetic disorder, which appears on any of the 22 chromosome pairs other than the sex chromosomes. In other words, each parent has one affected chromosome and one unaffected in his/her individual pair. Because each parent contributes only one chromosome to the child, ...
Huntingtin grabs a hammer: DNA repair in HD
... the nucleus. One caveat is that this novel technique can sometimes be a bit toxic, but it’s a completely new way to visualize huntingtin in living cells. The researchers reasoned that if huntingtin itself is part of the DNA repair team, the glowing protein would travel to sites where DNA had been da ...
... the nucleus. One caveat is that this novel technique can sometimes be a bit toxic, but it’s a completely new way to visualize huntingtin in living cells. The researchers reasoned that if huntingtin itself is part of the DNA repair team, the glowing protein would travel to sites where DNA had been da ...
Meiosis notes
... chromosome in a homologous pair come from the mother while the other comes from the father). ◦ Just because homologous chromosomes have the same order of genes, that is not to say that the genes are identical. ▪ e.g., if a specific spot on the homologous pairs has a gene for blood type, one homologu ...
... chromosome in a homologous pair come from the mother while the other comes from the father). ◦ Just because homologous chromosomes have the same order of genes, that is not to say that the genes are identical. ▪ e.g., if a specific spot on the homologous pairs has a gene for blood type, one homologu ...
Sigma Xi, Montreal Nov 2004 - Biology Department | UNC Chapel Hill
... variation. However, we do not know how frequently such variations in gene location occur among individuals within populations. Additionally, we do not know the degree to which such differences in chromosomal location affect gene expression at the transposed loci. We are studying this issue using Com ...
... variation. However, we do not know how frequently such variations in gene location occur among individuals within populations. Additionally, we do not know the degree to which such differences in chromosomal location affect gene expression at the transposed loci. We are studying this issue using Com ...
Human Genome and Human Genome Project
... instructions required to create a particular organism. • The genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA. Except for mature red blood cells, all human cells contains a complete genome arranged in 24 distinct chromosomes. ...
... instructions required to create a particular organism. • The genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA. Except for mature red blood cells, all human cells contains a complete genome arranged in 24 distinct chromosomes. ...
9/17/08 Transcript I
... promoter forming a closed promoter complex, then forms the open promoter complex and will unwind the DNA a little bit forming the open promoter complex. You will have this small abortive initiation until you get your 7-12 nucleotides. Then the sigma factor will then dissociate and the polymerase wil ...
... promoter forming a closed promoter complex, then forms the open promoter complex and will unwind the DNA a little bit forming the open promoter complex. You will have this small abortive initiation until you get your 7-12 nucleotides. Then the sigma factor will then dissociate and the polymerase wil ...
as a PDF
... • Prophage genes are copied along with cellular DNA when the host cell reproduces. As the cell divides, both prophage and cellular DNA are passed on to daughter cells. • A prophage may be carried in the host cell's chromosomes for many generations. Occasionally, a prophage may leave the bacterial ch ...
... • Prophage genes are copied along with cellular DNA when the host cell reproduces. As the cell divides, both prophage and cellular DNA are passed on to daughter cells. • A prophage may be carried in the host cell's chromosomes for many generations. Occasionally, a prophage may leave the bacterial ch ...
a code for traits: dna structure and function
... Just as an architect uses a blueprint to construct a building, an organism’s DNA is a blueprint for its traits. The blueprints for the White House are different from the blueprints for the Washington Monument, making these two buildings different on a structural level. It makes sense, therefore, tha ...
... Just as an architect uses a blueprint to construct a building, an organism’s DNA is a blueprint for its traits. The blueprints for the White House are different from the blueprints for the Washington Monument, making these two buildings different on a structural level. It makes sense, therefore, tha ...
How genetic mistakes cause short telomere diseases
... being continuously replaced. Other types of cells are either replaced when they are damaged or are produced to meet a particular demand. For example, certain types of white blood cells are produced in large numbers when they are needed to fight an infection, and then mostly die off when their job is ...
... being continuously replaced. Other types of cells are either replaced when they are damaged or are produced to meet a particular demand. For example, certain types of white blood cells are produced in large numbers when they are needed to fight an infection, and then mostly die off when their job is ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.