File
... Use pages 125-132 of the BC Science 9 text to help you answer questions 1-16. There will be one mark awarded for each blank except where noted. ...
... Use pages 125-132 of the BC Science 9 text to help you answer questions 1-16. There will be one mark awarded for each blank except where noted. ...
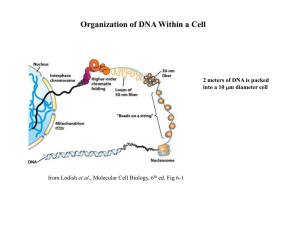
Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription
... DNA/core histones when contrasted with: – Uncatalyzed DNA exposure in nucleosomes – Simple nucleosome sliding along a DNA stretch ...
... DNA/core histones when contrasted with: – Uncatalyzed DNA exposure in nucleosomes – Simple nucleosome sliding along a DNA stretch ...
The presentation
... Genetic determinants of variation in expression levels may contribute to complex traits - phenotype is not just determined by coding regions Biochemical features associated with cis-regulatory modules are being determined genome-wide for a range of cell types. These can be used to predict CRMs, but ...
... Genetic determinants of variation in expression levels may contribute to complex traits - phenotype is not just determined by coding regions Biochemical features associated with cis-regulatory modules are being determined genome-wide for a range of cell types. These can be used to predict CRMs, but ...
Exercise week 10, with answers File
... b. the lack of blood platelets in female mice lacking one copy of Gata1 c. targeted deletion of a hematopoietic cell-specific enhancer in the Gata1 regulatory region d. promoter bashing studies showing that a fragment of the Gata1 regulatory region can direct lacZ expression in megakaryocytes b) is ...
... b. the lack of blood platelets in female mice lacking one copy of Gata1 c. targeted deletion of a hematopoietic cell-specific enhancer in the Gata1 regulatory region d. promoter bashing studies showing that a fragment of the Gata1 regulatory region can direct lacZ expression in megakaryocytes b) is ...
Chapter 4- Genes and development
... 6. X chromosome ___________A. Introduction ____________ first described in females in 1949 _____ syndrome (45,X) are Barr body negative; ________syndrome (47, XXY) are Barr body positive ___hypothesis- one of the two X chromosomes in female is inactivated; all but one is inactivated if multipl ...
... 6. X chromosome ___________A. Introduction ____________ first described in females in 1949 _____ syndrome (45,X) are Barr body negative; ________syndrome (47, XXY) are Barr body positive ___hypothesis- one of the two X chromosomes in female is inactivated; all but one is inactivated if multipl ...
Genetic Engineering pp 2014
... 3. Put the diploid nucleus into the empty egg. 4. Shock with electricity, the egg will start dividing. 5. Implant the embryo into the surrogate mother. 6. Clone is born. ...
... 3. Put the diploid nucleus into the empty egg. 4. Shock with electricity, the egg will start dividing. 5. Implant the embryo into the surrogate mother. 6. Clone is born. ...
Lesson Plan
... genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using DNA and RNA models. 6D (S) Recognize that gene expression is a regulated process. 6E (R) Identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of these changes. 10/2 ...
... genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using DNA and RNA models. 6D (S) Recognize that gene expression is a regulated process. 6E (R) Identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of these changes. 10/2 ...
Electrical induction hypothesis to explain enhancer-promoter
... concentration of RNA polymerase, in the vicinity of its binding site. But, even if a protein complex was recruited to enhancer, its concentration at the target would not necessarily be increased because the E/P do not typically co‐localize. Furthermore, they analyze the hypothetical mechanisms of lo ...
... concentration of RNA polymerase, in the vicinity of its binding site. But, even if a protein complex was recruited to enhancer, its concentration at the target would not necessarily be increased because the E/P do not typically co‐localize. Furthermore, they analyze the hypothetical mechanisms of lo ...
Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol
... The 4.6 kb Bam HI fragment is present when the b-globin gene is inactive and histones are deacetylated ...
... The 4.6 kb Bam HI fragment is present when the b-globin gene is inactive and histones are deacetylated ...
江 苏 大 学 试 题 (A)卷
... from the mother. B) The molecules used to carry out photosynthesis are encoded in nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA. C) cpDNA is found in the chloroplasts. D) Molecular evidence suggests that DNA sequences may have been transferred between mtDNA and nuclear DNA. E) Variegated four o'clock leaves hav ...
... from the mother. B) The molecules used to carry out photosynthesis are encoded in nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA. C) cpDNA is found in the chloroplasts. D) Molecular evidence suggests that DNA sequences may have been transferred between mtDNA and nuclear DNA. E) Variegated four o'clock leaves hav ...
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple
... Which, if any, of the following statements is incorrect? a) In X-chromosome inactivation the inactivated X chromosome is epigenetically silenced by a transcript, the XIST RNA, that is produced from the active X chromosome. b) The XIST RNA works by coating most of the X chromosome that is to be inact ...
... Which, if any, of the following statements is incorrect? a) In X-chromosome inactivation the inactivated X chromosome is epigenetically silenced by a transcript, the XIST RNA, that is produced from the active X chromosome. b) The XIST RNA works by coating most of the X chromosome that is to be inact ...
Identically Different: Why You Can Change Your Genes
... who sadly died during the operation meant to separate them. Despite being joined at the head, and thus spending their entire lives together, each had different interests, abilities, and aspirations. Spector asks ‘if our genes and environment are the same, how can there be any room for differences be ...
... who sadly died during the operation meant to separate them. Despite being joined at the head, and thus spending their entire lives together, each had different interests, abilities, and aspirations. Spector asks ‘if our genes and environment are the same, how can there be any room for differences be ...
DNA technology notes
... Describe DNA fingerprinting • Samples of DNA is exposed to restriction enzyme which cuts it into pieces • DNA is loaded into a gel and run through an electrophoresis machine • Since DNA is cut at certain sequences, each piece is a different length and weight • Pieces that are heavier stay at the to ...
... Describe DNA fingerprinting • Samples of DNA is exposed to restriction enzyme which cuts it into pieces • DNA is loaded into a gel and run through an electrophoresis machine • Since DNA is cut at certain sequences, each piece is a different length and weight • Pieces that are heavier stay at the to ...
Genetic Engineering
... – sample of DNA is cut using restriction enzymes – fragments are separated using electrophoresis to create a pattern of bands (negatively-charged DNA moves towards positive-end of apparatus) – Shortest segments travel the furthest (easier to move through gel) ...
... – sample of DNA is cut using restriction enzymes – fragments are separated using electrophoresis to create a pattern of bands (negatively-charged DNA moves towards positive-end of apparatus) – Shortest segments travel the furthest (easier to move through gel) ...
無投影片標題
... Gene is a sequence of DNA which contain genetic information. A messenger transports the information out the nucleus. The messenger is read by ribosome and transform to protein as building block of our body. The messenger is messenger RNA. ...
... Gene is a sequence of DNA which contain genetic information. A messenger transports the information out the nucleus. The messenger is read by ribosome and transform to protein as building block of our body. The messenger is messenger RNA. ...
Publications - Institut Curie
... Matahi Moarii, Valentina Boeva, Jean-Philippe Vert, Fabien Reyal (2015 Oct 30) ...
... Matahi Moarii, Valentina Boeva, Jean-Philippe Vert, Fabien Reyal (2015 Oct 30) ...
Mutations - nimitz163
... • In some rare cases a gene mutation may have positive effects. Mutations in body cells • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not ...
... • In some rare cases a gene mutation may have positive effects. Mutations in body cells • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not ...
- Wiley Online Library
... wrapped in ∼146 bp of DNA to form the nucleosome, and are structured from two copies each of four different subunits: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4, whose residues are subjected to an array of covalent modifications. In fact, the variety of covalent histone modifications is so extensive that researchers have ...
... wrapped in ∼146 bp of DNA to form the nucleosome, and are structured from two copies each of four different subunits: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4, whose residues are subjected to an array of covalent modifications. In fact, the variety of covalent histone modifications is so extensive that researchers have ...
Gene Regulation - Eukaryotic Cells
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
Gene regulation - Department of Plant Sciences
... • Other gene-specific elements (lightresponsive, nutrient-responsive, etc.) • Enhancer elements ...
... • Other gene-specific elements (lightresponsive, nutrient-responsive, etc.) • Enhancer elements ...
UNIT 4 PART 2 APPLIED GENETICS
... UNIT 4 PART 2: APPLIED GENETICS • Sexual reproduction brings about variation. • The offspring are genetically different from either parent. • Genetic variation allows a species to adapt to a changing environment. This can lead to evolution of the species. • Most variation is the result of segregatio ...
... UNIT 4 PART 2: APPLIED GENETICS • Sexual reproduction brings about variation. • The offspring are genetically different from either parent. • Genetic variation allows a species to adapt to a changing environment. This can lead to evolution of the species. • Most variation is the result of segregatio ...
LATg Training Course - AZ Branch AALAS Homepage
... • …focuses specifically on DNA, RNA, and protein • …is a tool used to study genetics ...
... • …focuses specifically on DNA, RNA, and protein • …is a tool used to study genetics ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... o DNA polymerase vs. DNA helicase o Direction o DNA ligase o Location in cell o When in cell cycle does it occur? ...
... o DNA polymerase vs. DNA helicase o Direction o DNA ligase o Location in cell o When in cell cycle does it occur? ...
Intro to Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab
... Where have you heard of genes before? What do genes have to do with DNA? Gene = Segments of DNA that control the production of protein ...
... Where have you heard of genes before? What do genes have to do with DNA? Gene = Segments of DNA that control the production of protein ...
Epigenetics

Epigenetics is the study, in the field of genetics, of cellular and physiological phenotypic trait variations that are caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence. Hence, epigenetic research seeks to describe dynamic alterations in the transcriptional potential of a cell. These alterations may or may not be heritable, although the use of the term ""epigenetic"" to describe processes that are not heritable is controversial. Unlike genetics based on changes to the DNA sequence (the genotype), the changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype of epigenetics have other causes, thus use of the prefix epi- (Greek: επί- over, outside of, around).The term also refers to the changes themselves: functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression can be controlled through the action of repressor proteins that attach to silencer regions of the DNA. These epigenetic changes may last through cell divisions for the duration of the cell's life, and may also last for multiple generations even though they do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence of the organism; instead, non-genetic factors cause the organism's genes to behave (or ""express themselves"") differently.One example of an epigenetic change in eukaryotic biology is the process of cellular differentiation. During morphogenesis, totipotent stem cells become the various pluripotent cell lines of the embryo, which in turn become fully differentiated cells. In other words, as a single fertilized egg cell – the zygote – continues to divide, the resulting daughter cells change into all the different cell types in an organism, including neurons, muscle cells, epithelium, endothelium of blood vessels, etc., by activating some genes while inhibiting the expression of others.