Swimmerets - Effingham County Schools
... • Many are adapted to kill prey with poison glands, stingers, or fangs • Some are parasites ...
... • Many are adapted to kill prey with poison glands, stingers, or fangs • Some are parasites ...
Section 33.1 Summary – pages 859-867
... eating the insect, the male is able to mate with her without being attacked. ...
... eating the insect, the male is able to mate with her without being attacked. ...
Ascaris Lumbricoides
... -Generally it acts by paralysing parasites, which allows the host body to easily remove or expel the invading organism. This action is mediated by its agonist effects upon the inhibitory GABA receptor. Its selectivity for helminths is because vertebrates only use GABA in the CNS and the helminths' G ...
... -Generally it acts by paralysing parasites, which allows the host body to easily remove or expel the invading organism. This action is mediated by its agonist effects upon the inhibitory GABA receptor. Its selectivity for helminths is because vertebrates only use GABA in the CNS and the helminths' G ...
Arthropods - Bowie Aquatic Science
... only have 3prs of legs and have 3 body segments (head, thorax and abdomen) • Marsh Mosquito- use proboscis to draw blood from host; (only female bite) • Sand Fly- “no-see-um” very tiny! ...
... only have 3prs of legs and have 3 body segments (head, thorax and abdomen) • Marsh Mosquito- use proboscis to draw blood from host; (only female bite) • Sand Fly- “no-see-um” very tiny! ...
Arthropods PPT - Effingham County Schools
... • Many are adapted to kill prey with poison glands, stingers, or fangs • Some are parasites ...
... • Many are adapted to kill prey with poison glands, stingers, or fangs • Some are parasites ...
FISH
... reproduction; reproductive tracts for both sexes open into the cloaca. Sex organs change size based on the season; increase in size during mating season. Internal fert. (press cloacas together) ...
... reproduction; reproductive tracts for both sexes open into the cloaca. Sex organs change size based on the season; increase in size during mating season. Internal fert. (press cloacas together) ...
Population Dynamics
... to establish identity and relationship, have resulted in an explosion of information about gut bacteria. Based on this type of study, some 7000 different types of bacteria are estimated to inhabit the human gut. The microbes in the human gut are dominated by two facultatively anaerobic or completely ...
... to establish identity and relationship, have resulted in an explosion of information about gut bacteria. Based on this type of study, some 7000 different types of bacteria are estimated to inhabit the human gut. The microbes in the human gut are dominated by two facultatively anaerobic or completely ...
bsaa hatching and brooding chicks
... a. Size. Extremely large or small eggs do not hatch well. b. Shape. Unnaturally shaped eggs do not hatch well. c. Shell quality. Strong shells hatch better than weak shells. d. Interior quality. Upon candling, better interior quality eggs tend to hatch better. 6. Handling of fertilized eggs. Good ma ...
... a. Size. Extremely large or small eggs do not hatch well. b. Shape. Unnaturally shaped eggs do not hatch well. c. Shell quality. Strong shells hatch better than weak shells. d. Interior quality. Upon candling, better interior quality eggs tend to hatch better. 6. Handling of fertilized eggs. Good ma ...
Instruction guide
... 2 pairs of wings, and 2 antennae. Their body is covered with a hard exoskeleton. They breathe through a series of holes called spiracles, which are located along the sides of the body. Their body is long (up to 8cm for females, 6cm for males) and thin (with a diameter of about 5mm). ...
... 2 pairs of wings, and 2 antennae. Their body is covered with a hard exoskeleton. They breathe through a series of holes called spiracles, which are located along the sides of the body. Their body is long (up to 8cm for females, 6cm for males) and thin (with a diameter of about 5mm). ...
Eubacteria
... A chemical process that occurs when bacteria change sugar into various products It is a way that bacterial cells get energy without using oxygen Examples: Grapes----- Wine---------- Vinegar Milk -----Yogurt or cheese Cabbage ----- Sauerkraut ...
... A chemical process that occurs when bacteria change sugar into various products It is a way that bacterial cells get energy without using oxygen Examples: Grapes----- Wine---------- Vinegar Milk -----Yogurt or cheese Cabbage ----- Sauerkraut ...
Diversity of Arthropods
... Most go through a metamorphosis – series of changes, controlled by hormones. Usual 4 stages of development 1.egg 2.larva - free-living, wormlike stage 3.pupa – period of reorganization; larva organs and tissues breakdown and are replaced w/adult tissues 4.adult Complete metamorphosis is an adv ...
... Most go through a metamorphosis – series of changes, controlled by hormones. Usual 4 stages of development 1.egg 2.larva - free-living, wormlike stage 3.pupa – period of reorganization; larva organs and tissues breakdown and are replaced w/adult tissues 4.adult Complete metamorphosis is an adv ...
Animal Presentation
... Female: has ovary, passes them to the uterus, where they are fertilized. Male: Sperm cells made in the testis and stored in the vas deferens. the male usually deposits sperm inside the female’s reproductive tract. ...
... Female: has ovary, passes them to the uterus, where they are fertilized. Male: Sperm cells made in the testis and stored in the vas deferens. the male usually deposits sperm inside the female’s reproductive tract. ...
Slide 1 - Images
... Order Coleoptera - The most unusual property of beetles is not some aspect of their structure or natural history, but their sheer number. There are more known species of Coleoptera than any other group of organisms, with over 350,000 described species. ...
... Order Coleoptera - The most unusual property of beetles is not some aspect of their structure or natural history, but their sheer number. There are more known species of Coleoptera than any other group of organisms, with over 350,000 described species. ...
Egg
... host digestive juices acts on the egg shell and liberate the larva into the small intestine. These larvae penetrate the intestinal mucosa and enter lymphatics and mesenteric vessels. They are carried by circulation to the liver, right heart and finally to the lungs where they penetrate the capillari ...
... host digestive juices acts on the egg shell and liberate the larva into the small intestine. These larvae penetrate the intestinal mucosa and enter lymphatics and mesenteric vessels. They are carried by circulation to the liver, right heart and finally to the lungs where they penetrate the capillari ...
28-3_insects - The Biology Corner
... 1. What evolutionary adaptation allowed insects to colonize new habitats? _____________________ 2. Using Fig 28-14 (pie chart), determine what percentage of animal species are not insects: _____________ 3. What are the three parts of the insect body? _________________________________________________ ...
... 1. What evolutionary adaptation allowed insects to colonize new habitats? _____________________ 2. Using Fig 28-14 (pie chart), determine what percentage of animal species are not insects: _____________ 3. What are the three parts of the insect body? _________________________________________________ ...
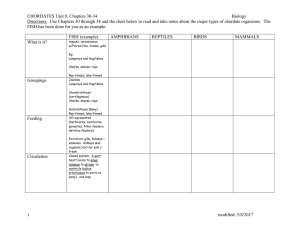
The student will be able to know about animal kingdom
... The student will be able to know about animal kingdom vertebrates The student will be able to understand the classification of animal The student will be able to give examples of each of the 7 main classes of Chordata ...
... The student will be able to know about animal kingdom vertebrates The student will be able to understand the classification of animal The student will be able to give examples of each of the 7 main classes of Chordata ...
"Behavior" and
... 6. The organism is a compromise. The result of natural selection is adequacy and not perfection. Although animals are indeed adapted to their environments, they are far from perfectly so. All sorts of constraints prevent organisms from being the best that might be theoretically possible. It has ofte ...
... 6. The organism is a compromise. The result of natural selection is adequacy and not perfection. Although animals are indeed adapted to their environments, they are far from perfectly so. All sorts of constraints prevent organisms from being the best that might be theoretically possible. It has ofte ...
Zoology Review
... Scales hold lateral line that allows for tubular canal bearing sensory organs-they are sensitive to pressure and temp changes in water currents. Mucus on scales also makes capture more difficult Light, thin and flexible, which increase mobility and speed. Help to increase feeding efficiency or preda ...
... Scales hold lateral line that allows for tubular canal bearing sensory organs-they are sensitive to pressure and temp changes in water currents. Mucus on scales also makes capture more difficult Light, thin and flexible, which increase mobility and speed. Help to increase feeding efficiency or preda ...
Anatomy of the Honey Bee - three
... too. The brain has a large area for receiving inputs from the two compound eyes, called optic lobes. The next largest input are from the antenna (antenna lobes). One important region in the middle of the brain is called the "mushroom body" because the cross section resembles two mushrooms. This area ...
... too. The brain has a large area for receiving inputs from the two compound eyes, called optic lobes. The next largest input are from the antenna (antenna lobes). One important region in the middle of the brain is called the "mushroom body" because the cross section resembles two mushrooms. This area ...
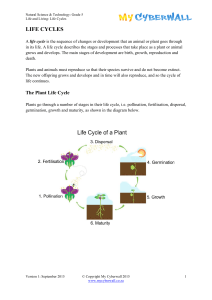
life cycles - My Cyberwall
... Salmon live in the sea but move to freshwater to reproduce.The female makes a nest and lays the eggs in it. The male salmon then fertilises the eggs. When the salmon hatch, they are known as alevins. They stay in the nest and have a food sac attached to their bodies. Once the food sac is used up, th ...
... Salmon live in the sea but move to freshwater to reproduce.The female makes a nest and lays the eggs in it. The male salmon then fertilises the eggs. When the salmon hatch, they are known as alevins. They stay in the nest and have a food sac attached to their bodies. Once the food sac is used up, th ...
Type of relationship?
... hatches in the intestine and the larvae migrate to muscle tissue. When the larvae mature, they bore into capillaries and float to the lungs, where they form a cyst. Large numbers of these can affect the breathing of the bighorn sheep. ...
... hatches in the intestine and the larvae migrate to muscle tissue. When the larvae mature, they bore into capillaries and float to the lungs, where they form a cyst. Large numbers of these can affect the breathing of the bighorn sheep. ...
Cheating (biology)

Cheating is a metaphor commonly used in behavioral ecology to describe organisms that receive a benefit at the cost of other organisms. Cheating is common in many mutualistic and altruistic relationships. A cheater is an individual who does not cooperate (or cooperates less than their fair share) but can potentially gain the benefit from others cooperating. Cheaters are also those who selfishly use common resources to maximize their individual fitness at the expense of a group. Natural selection favors cheating, but there are mechanisms to regulate cheating.