AP Biology - TeacherWeb
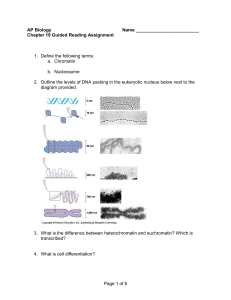
... 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. ...
... 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. ...
Biotechnology
... diabetes used insulin derived from the pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulinmaking genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
... diabetes used insulin derived from the pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulinmaking genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
scientists and philosophers find that gene has a multitude of meanings
... that serve as instructions for piecing together the body’s proteins, and, I’m sorry, but the closer we look, the less instructive they seem, less a “blueprint for life” than one of those disappointing two-page Basic Setup booklets that comes with your computer, tells you where to plug it in and then ...
... that serve as instructions for piecing together the body’s proteins, and, I’m sorry, but the closer we look, the less instructive they seem, less a “blueprint for life” than one of those disappointing two-page Basic Setup booklets that comes with your computer, tells you where to plug it in and then ...
Genetic Engineering
... Ex: Antibiotic sensitivity or the expression of a “new” trait (color, glowing etc.) ...
... Ex: Antibiotic sensitivity or the expression of a “new” trait (color, glowing etc.) ...
CHAPTER 14: Genes in Action Essential Ideas
... Gene-a segment of DNA whose nucleotide sequence codes for a protein. Mutation - Changes in the nucleotide sequence of a gene’s DNA Mutagens cause mutations, include environmental factors ike chemicals, X-rays, and UV light Genetic Mutations – single or small changes to individual genes DNA sequence ...
... Gene-a segment of DNA whose nucleotide sequence codes for a protein. Mutation - Changes in the nucleotide sequence of a gene’s DNA Mutagens cause mutations, include environmental factors ike chemicals, X-rays, and UV light Genetic Mutations – single or small changes to individual genes DNA sequence ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Under the system of genetic control of the trp operon, A. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. B. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of CAP occurs at high levels. C. when there are high level ...
... Under the system of genetic control of the trp operon, A. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. B. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of CAP occurs at high levels. C. when there are high level ...
CSE 181 Project guidelines
... Gene expression • Human genome is ~ 3 billions base pair long • Almost every cell in human body contains same set of genes • But not all genes are used or expressed by those cells • Different cell types • Different conditions ...
... Gene expression • Human genome is ~ 3 billions base pair long • Almost every cell in human body contains same set of genes • But not all genes are used or expressed by those cells • Different cell types • Different conditions ...
Genomics – The Language of DNA
... Alu elements consist of a sequence of 300 base pairs containing a site that is recognized by the restriction enzyme AluI. They appear to be reverse transcripts of 7S RNA, part of the signal recognition particle. Most SINEs do not encode any functional molecules and depend on the machinery of active ...
... Alu elements consist of a sequence of 300 base pairs containing a site that is recognized by the restriction enzyme AluI. They appear to be reverse transcripts of 7S RNA, part of the signal recognition particle. Most SINEs do not encode any functional molecules and depend on the machinery of active ...
Chromosome structure File
... In prokaryotes, a single mRNA molecule may code for one or several polypeptide chains. If it carries the code for only one polypeptide, the mRNA is monocistronic if it codes for two or more different polypeptides, the mRNA is polycistronic. In eukaryotes, most mRNAs are monocistronic ...
... In prokaryotes, a single mRNA molecule may code for one or several polypeptide chains. If it carries the code for only one polypeptide, the mRNA is monocistronic if it codes for two or more different polypeptides, the mRNA is polycistronic. In eukaryotes, most mRNAs are monocistronic ...
LECTURE 16 – Using Genomic Variation for Identity DNA Level
... Ø Bacteria can be infected by viruses known as bacteriophage Ø Inbuilt immunity in the bacteria against bacteriophage is the restriction enzyme – cleaves the DNA of the bacteriophage Ø Bacteria protects its own DNA from the restriction enzymes (by methylation) Ø Restriction enzymes cut the DNA leavi ...
... Ø Bacteria can be infected by viruses known as bacteriophage Ø Inbuilt immunity in the bacteria against bacteriophage is the restriction enzyme – cleaves the DNA of the bacteriophage Ø Bacteria protects its own DNA from the restriction enzymes (by methylation) Ø Restriction enzymes cut the DNA leavi ...
Cryptography and Linguistics of Macromolecules Cryptography and
... George Michaels April 5, 2004 ...
... George Michaels April 5, 2004 ...
Document
... entire genetic complement of a prokaryote, virus, mitochondrion or chloroplast or the haploid nuclear genetic complement of a eukaryotic species. Metabolomics -the analysis of the thousands of small molecules such as sugars and fats that are the products of metabolism. If metabolomic information can ...
... entire genetic complement of a prokaryote, virus, mitochondrion or chloroplast or the haploid nuclear genetic complement of a eukaryotic species. Metabolomics -the analysis of the thousands of small molecules such as sugars and fats that are the products of metabolism. If metabolomic information can ...
Voices - Indiana University Bloomington
... dwarfs almost any other means of interrogating a biological sample. This makes it increasingly tempting to try to ‘‘translate’’ far-flung biological questions into the language of DNA sequence. But how well can this sort of experimental shoehorning work? If the recent experience of nuclear biology is ...
... dwarfs almost any other means of interrogating a biological sample. This makes it increasingly tempting to try to ‘‘translate’’ far-flung biological questions into the language of DNA sequence. But how well can this sort of experimental shoehorning work? If the recent experience of nuclear biology is ...
DNA and RNA Review
... 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
... 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
Genetic Engineering pp 2014
... 3. Put the diploid nucleus into the empty egg. 4. Shock with electricity, the egg will start dividing. 5. Implant the embryo into the surrogate mother. 6. Clone is born. ...
... 3. Put the diploid nucleus into the empty egg. 4. Shock with electricity, the egg will start dividing. 5. Implant the embryo into the surrogate mother. 6. Clone is born. ...
Protein-coding genes in eukaryotic DNA
... and important class of genetic polymorphisms (for the presence or absence of an insertion) among and within human populations. As such, they are useful genetic markers in population genetics studies due to their identical-by-descent and essentially homoplasy-free nature. Additionally, some polymorph ...
... and important class of genetic polymorphisms (for the presence or absence of an insertion) among and within human populations. As such, they are useful genetic markers in population genetics studies due to their identical-by-descent and essentially homoplasy-free nature. Additionally, some polymorph ...
Recent advances in bioinformatics and computational biology
... choosing genes in feature selection, and compare its use with variance, which is more commonly used at present. Both are compared ...
... choosing genes in feature selection, and compare its use with variance, which is more commonly used at present. Both are compared ...
Genetic Engineering - ABC-MissAngelochsBiologyClass
... Plants and animals that contain fragments of DNA from different sources. Example: tobacco plant with firefly gene that makes the plant glow ...
... Plants and animals that contain fragments of DNA from different sources. Example: tobacco plant with firefly gene that makes the plant glow ...
DNA Lab Techniques
... of a group of genetically identical cells • May be produced by asexual reproduction (mitosis) ...
... of a group of genetically identical cells • May be produced by asexual reproduction (mitosis) ...
What is bioinformatics? - The British Association of Sport and
... The genomes for many prokaryote, eukaryote, plant, invertebrate and vertebrate model species have now been sequenced. The DNA sequences of these genomes have been posted online. However, these websites contain much more than just the “naked” DNA sequence which has limited use. With the help of speci ...
... The genomes for many prokaryote, eukaryote, plant, invertebrate and vertebrate model species have now been sequenced. The DNA sequences of these genomes have been posted online. However, these websites contain much more than just the “naked” DNA sequence which has limited use. With the help of speci ...
The Two Versions of the Human Genome - Max-Planck
... The reading of the base sequence is carried out simultaneously for millions of DNA fragments. Today, it takes just a few days to read a complete genome using a second-generation sequencing machine. “The very latest machines reach a throughput of up to three hundred billion bases,” says Hoehe. “The e ...
... The reading of the base sequence is carried out simultaneously for millions of DNA fragments. Today, it takes just a few days to read a complete genome using a second-generation sequencing machine. “The very latest machines reach a throughput of up to three hundred billion bases,” says Hoehe. “The e ...























