Bio 93 2013 Final: 1. Which option best describes transformation in
... C) RNA polymerase binds to the promoter. D) Transcription can begin as soon as translation has begun. E) RNA polymerase requires a primer to elongate the molecule. 13. The coding region of an mRNA molecule is 900 bases long, yet only codes for a protein of 300 amino acids. Why is this? A) many nonco ...
... C) RNA polymerase binds to the promoter. D) Transcription can begin as soon as translation has begun. E) RNA polymerase requires a primer to elongate the molecule. 13. The coding region of an mRNA molecule is 900 bases long, yet only codes for a protein of 300 amino acids. Why is this? A) many nonco ...
Chapter 3 part II
... Screening the Library • Screening the library using nucleic acid hybridization is the most direct and very sensitive means for detecting the desired clones. • This requires knowledge of the sequences of the gene being sought. • In some case, part of the gene may have already been cloned, and this ...
... Screening the Library • Screening the library using nucleic acid hybridization is the most direct and very sensitive means for detecting the desired clones. • This requires knowledge of the sequences of the gene being sought. • In some case, part of the gene may have already been cloned, and this ...
Cloning Restriction Fragments of Cellular DNA
... cell must be provided because they will not be part of the cDNA. • For instance, to produce recombinant human insulin in bacteria, a bacterial promoter and a ShineDalgarno sequence must be included in the cloning plasmid near the insertion site for the cDNA. • Figure 1-6-5 shows an example of an exp ...
... cell must be provided because they will not be part of the cDNA. • For instance, to produce recombinant human insulin in bacteria, a bacterial promoter and a ShineDalgarno sequence must be included in the cloning plasmid near the insertion site for the cDNA. • Figure 1-6-5 shows an example of an exp ...
DNA vaccines
... Immunodeficiency Virus). It is the final and most serious stage of HIV disease. It is characterized by signs and symptoms of severe immune deficiency, such as opportunistic infection and cancer (Kaposi’s sarcoma), and finally death. AIDS has unique characteristics, such as multiple transmission rout ...
... Immunodeficiency Virus). It is the final and most serious stage of HIV disease. It is characterized by signs and symptoms of severe immune deficiency, such as opportunistic infection and cancer (Kaposi’s sarcoma), and finally death. AIDS has unique characteristics, such as multiple transmission rout ...
lecture5
... NER. Some of them: XPA, which encodes a protein that binds the damaged site and helps assemble the other proteins needed for NER. XPB and XPD, which are part of TFIIH. Some mutations in XPB and XPD also produce signs of premature aging. XPF, which cuts the backbone on the 5' side of the damage XPG, ...
... NER. Some of them: XPA, which encodes a protein that binds the damaged site and helps assemble the other proteins needed for NER. XPB and XPD, which are part of TFIIH. Some mutations in XPB and XPD also produce signs of premature aging. XPF, which cuts the backbone on the 5' side of the damage XPG, ...
Defense against infectious disease
... • The bloodstream contains many different types of B lymphocytes or B cells • Each type is capable of synthesizing and secreting a specific antibody which binds to a specific antigen • Problem: there isn’t enough room to have enough of each type of B cell for the amount of antibody secretion that ma ...
... • The bloodstream contains many different types of B lymphocytes or B cells • Each type is capable of synthesizing and secreting a specific antibody which binds to a specific antigen • Problem: there isn’t enough room to have enough of each type of B cell for the amount of antibody secretion that ma ...
A1984TD25400001
... was pushed further by means of autoradiography 3 of whole cells labeled in various ways by H-thymine. We could show that if cells more or less double their DNA content in the absence of protein synthesis, they do not initiate a new round of replication until protein (and mass) synthesis has caught u ...
... was pushed further by means of autoradiography 3 of whole cells labeled in various ways by H-thymine. We could show that if cells more or less double their DNA content in the absence of protein synthesis, they do not initiate a new round of replication until protein (and mass) synthesis has caught u ...
Immune system notes - St Paul`s School Intranet
... a molecule that makes up part of the cell wall of a bacterial cell, of perhaps a protein on the outside of a virus. What is important is that the lymphocyte can recognize it as a foreign molecule i.e. one that would not normally be found in the body. Each antigen has a particular molecular shape, wh ...
... a molecule that makes up part of the cell wall of a bacterial cell, of perhaps a protein on the outside of a virus. What is important is that the lymphocyte can recognize it as a foreign molecule i.e. one that would not normally be found in the body. Each antigen has a particular molecular shape, wh ...
GENETICS
... Causes a cell to produce an incorrect protein during protein synthesis Some are result of small change in hereditary material such as substitution of single base pair for another Can occur during DNA replication process Some occur when chromosomes don’t separate correctly during meiosis Will cause t ...
... Causes a cell to produce an incorrect protein during protein synthesis Some are result of small change in hereditary material such as substitution of single base pair for another Can occur during DNA replication process Some occur when chromosomes don’t separate correctly during meiosis Will cause t ...
Dr. Becker`s Review – Exam 4 Notes provided by Kadie Keen
... If mRNA begins with SRP it stays inside the cell SRP (signal recognition particle) sends to rough ER then ends up outside the cell. ...
... If mRNA begins with SRP it stays inside the cell SRP (signal recognition particle) sends to rough ER then ends up outside the cell. ...
Ch 15 Help - Practice Regents Answer Key
... Many people are allergic to substances in the environment. Of the many foods that contain allergens (allergy-inducing substances), peanuts cause some of the most severe reactions. Mildly allergic people may only get hives. Highly allergic people can go into a form of shock. Some people die each year ...
... Many people are allergic to substances in the environment. Of the many foods that contain allergens (allergy-inducing substances), peanuts cause some of the most severe reactions. Mildly allergic people may only get hives. Highly allergic people can go into a form of shock. Some people die each year ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction
... mRNA (messenger RNA transcripts) • Detection of mRNA transcript size • Study RNA degradation • Study RNA splicing • Study RNA half-life • Often used to confirm and check transgenic / knockout mice (animals) ...
... mRNA (messenger RNA transcripts) • Detection of mRNA transcript size • Study RNA degradation • Study RNA splicing • Study RNA half-life • Often used to confirm and check transgenic / knockout mice (animals) ...
Sex and Behaviour * Immune Response to Parasites
... evolve mechanisms that evade the specific immune system of the human body and can affect vaccination strategies globally. • Antigenic variation is a process by which a pathogen is able to change its surface proteins so that it can evade the host immune responses. ...
... evolve mechanisms that evade the specific immune system of the human body and can affect vaccination strategies globally. • Antigenic variation is a process by which a pathogen is able to change its surface proteins so that it can evade the host immune responses. ...
C1. Self-assembly occurs spontaneously, without the aid of other
... C. No, it is too big to fit inside of E. coli. Supercoiling is needed to make the loops more compact. C7. DNA is a double helix. The helix is a coiled structure. Supercoiling involves additional coiling to a structure that is already a coil. Positive supercoiling is called overwinding because it add ...
... C. No, it is too big to fit inside of E. coli. Supercoiling is needed to make the loops more compact. C7. DNA is a double helix. The helix is a coiled structure. Supercoiling involves additional coiling to a structure that is already a coil. Positive supercoiling is called overwinding because it add ...
Honors Biology
... base triplets/codons/anticodons: what are they?, what type of information do they represent?, to what molecules do these terms refer to? redundancy of the DNA code: what advantage does having multiple codons for a single amino acid give when a mutation occurs? amino acid sequence in determinin ...
... base triplets/codons/anticodons: what are they?, what type of information do they represent?, to what molecules do these terms refer to? redundancy of the DNA code: what advantage does having multiple codons for a single amino acid give when a mutation occurs? amino acid sequence in determinin ...
Document
... C. No, it is too big to fit inside of E. coli. Supercoiling is needed to make the loops more compact. C7. DNA is a double helix. The helix is a coiled structure. Supercoiling involves additional coiling to a structure that is already a coil. Positive supercoiling is called overwinding because it add ...
... C. No, it is too big to fit inside of E. coli. Supercoiling is needed to make the loops more compact. C7. DNA is a double helix. The helix is a coiled structure. Supercoiling involves additional coiling to a structure that is already a coil. Positive supercoiling is called overwinding because it add ...
BIOLOGY Cells Unit GUIDE SHEET
... 14. Explain why frameshift mutations (mutations involving the insertion of deletion of one or more nucleotides in a gene) usually have major effects on the amino acid sequence of a protein (page 199). ...
... 14. Explain why frameshift mutations (mutations involving the insertion of deletion of one or more nucleotides in a gene) usually have major effects on the amino acid sequence of a protein (page 199). ...
notes
... • Gene was identified by genetic mapping (using CF families) • This approach (also applied to many other genetic diseases) uses 100s of DNA polymorphisms all over genome ...
... • Gene was identified by genetic mapping (using CF families) • This approach (also applied to many other genetic diseases) uses 100s of DNA polymorphisms all over genome ...
Lecture 5 - Andrew.cmu.edu
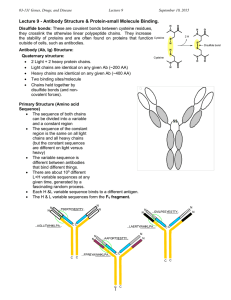
... Each H &L variable sequence binds to a different antigen. The H & L variable sequences form the FV fragment. NN- ...
... Each H &L variable sequence binds to a different antigen. The H & L variable sequences form the FV fragment. NN- ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.