BICH/GENE 431 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 9 – Mutations
... Double-strand break repair – two major pathways - recombination repair mainly used in bacteria and lower eukaryotes (yeast): details covered in next chapter; uses homologous recombination - NHEJ (nonhomologous end joining) is major pathway in higher eukaryotes – by nature it is mutagenic; identifie ...
... Double-strand break repair – two major pathways - recombination repair mainly used in bacteria and lower eukaryotes (yeast): details covered in next chapter; uses homologous recombination - NHEJ (nonhomologous end joining) is major pathway in higher eukaryotes – by nature it is mutagenic; identifie ...
CHNOPS- Simulating Protein Synthesis
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
Chapter 20
... • The polymerase chain reaction, PCR, can produce many copies of a specific target segment of DNA • A three-step cycle—heating, cooling, and replication—brings about a chain reaction that ...
... • The polymerase chain reaction, PCR, can produce many copies of a specific target segment of DNA • A three-step cycle—heating, cooling, and replication—brings about a chain reaction that ...
Quantification and DNA Sequencing of IL-13Rα1 and IL
... •A signaling ligand called Interleulin 13 (IL-13) is produced and released by activated T cells which normally attach to the intramembranous protein receptor complex IL-13α1/IL-4α. •This triggers an immune response pathway to fight against foreign invaders. ...
... •A signaling ligand called Interleulin 13 (IL-13) is produced and released by activated T cells which normally attach to the intramembranous protein receptor complex IL-13α1/IL-4α. •This triggers an immune response pathway to fight against foreign invaders. ...
VACCINES
... •Do NOT use entire virus or bacteria (pathogenic agent) •Use components of pathogenic organism instead of whole organism •Advantage: no extraneous pathogenic particles i.e. DNA •Disadvantage: Is protein the same as in situ? ...
... •Do NOT use entire virus or bacteria (pathogenic agent) •Use components of pathogenic organism instead of whole organism •Advantage: no extraneous pathogenic particles i.e. DNA •Disadvantage: Is protein the same as in situ? ...
S2 Science - Kelso High School
... Advantages of DNA Profiling and Databases: Police can use it as evidence from crime scenes Criminals can be identified more easily Victims can be identified more quickly Can be used to identify the parents or other relatives of a person Scientists can use it to find genes responsible for ...
... Advantages of DNA Profiling and Databases: Police can use it as evidence from crime scenes Criminals can be identified more easily Victims can be identified more quickly Can be used to identify the parents or other relatives of a person Scientists can use it to find genes responsible for ...
Use of Bacteria in Antibody Production - BLI-Research-Synbio
... • Use modified E. Coli to create antibodies for certain diseases ahead of time, so that an immune boost can be given via injection, or so a response can begin before it normally would. ...
... • Use modified E. Coli to create antibodies for certain diseases ahead of time, so that an immune boost can be given via injection, or so a response can begin before it normally would. ...
Richard A. Spinello, Sarah Cabral Presentation
... …three types of inventions that can be excluded from patentability, 1. inventions contrary to morality, 2. diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical methods for the treatment of humans or animals, and 3. plants and ...
... …three types of inventions that can be excluded from patentability, 1. inventions contrary to morality, 2. diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical methods for the treatment of humans or animals, and 3. plants and ...
Chapter 7 Genes and Protein Synthesis
... Transposons – small sequences of DNA that move about the genome and insert themselves into different ...
... Transposons – small sequences of DNA that move about the genome and insert themselves into different ...
Mutations (1 of 2)
... cytosine, and adenine. The cellular machinery uses these instructions to assemble a string of corresponding amino acids (one amino acid for each three bases). The amino acid that corresponds to “GCA” is called alanine; there are twenty different amino acids synthesized this way in humans. “Stop” cod ...
... cytosine, and adenine. The cellular machinery uses these instructions to assemble a string of corresponding amino acids (one amino acid for each three bases). The amino acid that corresponds to “GCA” is called alanine; there are twenty different amino acids synthesized this way in humans. “Stop” cod ...
Recombinant DNA key
... transcription. In addition, eukaryotic ribosomes find the correct AUG codon by scanning from the cap to the first AUG, while bacteria rely on a Shine-Dalgarno sequence in the mRNA. These bacterial regulatory signals are provided by the expression vector. If we use a plasmid that did not have these s ...
... transcription. In addition, eukaryotic ribosomes find the correct AUG codon by scanning from the cap to the first AUG, while bacteria rely on a Shine-Dalgarno sequence in the mRNA. These bacterial regulatory signals are provided by the expression vector. If we use a plasmid that did not have these s ...
Study reveals that adrenergic nerves control immune cells` daily
... decreased during the night, when they accumulated in lymph nodes instead. This daily, or circadian, cycle of immune cell trafficking was regulated by the neurotransmitter noradrenaline, released from adrenergic nerves innervating the lymph nodes. The nerves secreted more noradrenaline at night, acti ...
... decreased during the night, when they accumulated in lymph nodes instead. This daily, or circadian, cycle of immune cell trafficking was regulated by the neurotransmitter noradrenaline, released from adrenergic nerves innervating the lymph nodes. The nerves secreted more noradrenaline at night, acti ...
Design Genes with Ease Using In-Fusion® Cloning
... fragments as part of the 15 bp complementary overhang with the linearized backbone (see Table I). No restriction sites were incorporated between the fusion protein domains. Since no restriction digestion of inserts is needed when using In-Fusion technology, the presence of NcoI and SalI restriction ...
... fragments as part of the 15 bp complementary overhang with the linearized backbone (see Table I). No restriction sites were incorporated between the fusion protein domains. Since no restriction digestion of inserts is needed when using In-Fusion technology, the presence of NcoI and SalI restriction ...
Chapter 12: Genetic Engineering
... code for protein – in the human genome Junk DNA is made up of repeated sequences that are called repeats Although individuals may have identical genes, there may be different numbers of repeats between these genes The more repeats, the longer the junk DNA between genes Restriction enzymes are ...
... code for protein – in the human genome Junk DNA is made up of repeated sequences that are called repeats Although individuals may have identical genes, there may be different numbers of repeats between these genes The more repeats, the longer the junk DNA between genes Restriction enzymes are ...
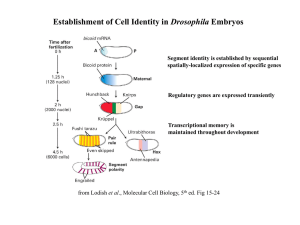
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... from Cedar and Bergman, Nature Rev.Genet. 10, 295 (2009) Repressive histone methylation marks must be removed, followed by removal of DNA methylation which activates the gene ...
... from Cedar and Bergman, Nature Rev.Genet. 10, 295 (2009) Repressive histone methylation marks must be removed, followed by removal of DNA methylation which activates the gene ...
Electrical induction hypothesis to explain enhancer-promoter
... concentration of RNA polymerase, in the vicinity of its binding site. But, even if a protein complex was recruited to enhancer, its concentration at the target would not necessarily be increased because the E/P do not typically co‐localize. Furthermore, they analyze the hypothetical mechanisms of lo ...
... concentration of RNA polymerase, in the vicinity of its binding site. But, even if a protein complex was recruited to enhancer, its concentration at the target would not necessarily be increased because the E/P do not typically co‐localize. Furthermore, they analyze the hypothetical mechanisms of lo ...
Genetics
... molecules, the DNA is usually found attached to the cell membrane at some point or points. Although bacteria do not possess a nucleus, the DNA is localized in a distinct area with in the cell called the nucleoid region. There is no membrane around the nucleoid region and lies free in the cytoplasm o ...
... molecules, the DNA is usually found attached to the cell membrane at some point or points. Although bacteria do not possess a nucleus, the DNA is localized in a distinct area with in the cell called the nucleoid region. There is no membrane around the nucleoid region and lies free in the cytoplasm o ...
What is a GENE? - West East University
... carried out of the nucleus into the cell's cytoplasm. The RNA combines with protein/nucleic acid organelles in the cytoplasm called ribosomes. Special molecules of RNA (called transfer RNA or tRNA) bring amino acides to the ribosome, which can then construct a long chain of amino acids by reading th ...
... carried out of the nucleus into the cell's cytoplasm. The RNA combines with protein/nucleic acid organelles in the cytoplasm called ribosomes. Special molecules of RNA (called transfer RNA or tRNA) bring amino acides to the ribosome, which can then construct a long chain of amino acids by reading th ...
T4 DNA Ligase (5U/µl) - GRiSP Research Solutions
... 3. (Optional): heat-inactivate at 65ºC for 10min (do not perform if PEG 6000 was included!). 4. Use 5-10µl of the ligation mixture for the transformation of 50µl competent cells. *The addition of polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000), greatly increases the ligation efficiency of blunt-ended DNA ligation. I ...
... 3. (Optional): heat-inactivate at 65ºC for 10min (do not perform if PEG 6000 was included!). 4. Use 5-10µl of the ligation mixture for the transformation of 50µl competent cells. *The addition of polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000), greatly increases the ligation efficiency of blunt-ended DNA ligation. I ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.