Slide 1
... mRNA makes a copy of the DNA strand! Adenine Base Pairs with Thymine Uracil Base Pairs with Adenine Guanine Base Pairs with Cytosine Cytosine Base Pairs with Guanine ...
... mRNA makes a copy of the DNA strand! Adenine Base Pairs with Thymine Uracil Base Pairs with Adenine Guanine Base Pairs with Cytosine Cytosine Base Pairs with Guanine ...
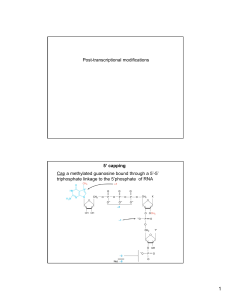
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRP), which can synthesize antisense transcripts. Antisense transcripts can also be synthesized when a gene is pr ...
... methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRP), which can synthesize antisense transcripts. Antisense transcripts can also be synthesized when a gene is pr ...
Table S1
... Subunit of DNA polymerase delta holoenzyme complex C3H8.09c RNA-binding protein, involved in packaging pre-mRNAs into ribonucleoprotein structures C25D12.06 RNA helicase ATP-dependent C660.10 Protein containing an elongation factor Tu GTP binding domain Othersc C18H10.11c C1635.01 mrs2 C1071.02 ...
... Subunit of DNA polymerase delta holoenzyme complex C3H8.09c RNA-binding protein, involved in packaging pre-mRNAs into ribonucleoprotein structures C25D12.06 RNA helicase ATP-dependent C660.10 Protein containing an elongation factor Tu GTP binding domain Othersc C18H10.11c C1635.01 mrs2 C1071.02 ...
STANDARD 10: THE CENTRAL DOGMA
... EXPLAIN THE CENTRAL DOGMA: Biologists across the world agree on what they call the “pattern of life” or the ______________ ________________. This outlines the process of how all our traits are formed. It follows the format ____________>_____________>_______________> _______________. ______ is a doub ...
... EXPLAIN THE CENTRAL DOGMA: Biologists across the world agree on what they call the “pattern of life” or the ______________ ________________. This outlines the process of how all our traits are formed. It follows the format ____________>_____________>_______________> _______________. ______ is a doub ...
Protein Synthesis Pre Test
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell's protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. McDougal Biology Florida 2012 ____ 4. A primary difference between tra ...
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell's protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. McDougal Biology Florida 2012 ____ 4. A primary difference between tra ...
Protein Synthesis Pre Test
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell's protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. McDougal Biology Florida 2012 ____ 4. A primary difference between tra ...
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell's protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. McDougal Biology Florida 2012 ____ 4. A primary difference between tra ...
Fundamentals of Nucleic Acid Biochemistry: RNA
... of generating RNA from DNA. The process is catalyzed by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme. Only “coding” segments of DNA (genes) are transcribed. Types of genes include structural genes (encode protein), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
... of generating RNA from DNA. The process is catalyzed by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme. Only “coding” segments of DNA (genes) are transcribed. Types of genes include structural genes (encode protein), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
Transcription & Translation
... At one end of the tRNA molecule are three bases that make up an anti-codon (complimentary to a codon) ...
... At one end of the tRNA molecule are three bases that make up an anti-codon (complimentary to a codon) ...
Document
... What is needed for translation to occur? What is the sequence of events? What are the roles of mRNA, ribosomes, start codon, tRNA, anticodons, stop codon? ...
... What is needed for translation to occur? What is the sequence of events? What are the roles of mRNA, ribosomes, start codon, tRNA, anticodons, stop codon? ...
From Gene to Protein
... What is needed for translation to occur? What is the sequence of events? What are the roles of mRNA, ribosomes, start codon, tRNA, anticodons, stop codon? ...
... What is needed for translation to occur? What is the sequence of events? What are the roles of mRNA, ribosomes, start codon, tRNA, anticodons, stop codon? ...
Transcription
... WHICH CAME FIRST, THE chicken or the egg? The biological silences have a variation: which came first, DNA or protein? You see, among the many tasks performed by proteins is assembling DNA molecules. But DNA contains the information needed to make proteins. So which came first? ...
... WHICH CAME FIRST, THE chicken or the egg? The biological silences have a variation: which came first, DNA or protein? You see, among the many tasks performed by proteins is assembling DNA molecules. But DNA contains the information needed to make proteins. So which came first? ...
DNA - KSUMSC
... What is the Melting temperature (MT) ?? It is the temperature at which the double-stranded DNA is separated into two single strands. Note that :MT of DNA depends on nitrogenous base content , so the bonds between G-C is stronger than the bonds which is between A-T ...
... What is the Melting temperature (MT) ?? It is the temperature at which the double-stranded DNA is separated into two single strands. Note that :MT of DNA depends on nitrogenous base content , so the bonds between G-C is stronger than the bonds which is between A-T ...
Nucleic Acid Isolation System
... production technology. It is only 80μm thick, making it incomparably thinner than conventional glass fibers. QuickGene-810's ultra thin membrane alleviates the risk of contamination from residue in the membrane. ...
... production technology. It is only 80μm thick, making it incomparably thinner than conventional glass fibers. QuickGene-810's ultra thin membrane alleviates the risk of contamination from residue in the membrane. ...
RNA/DNA catalysts
... Know four types of natural catalytic RNAs (group I introns, group II introns, RNase P, small self-cleaving), what reactions they perform, know basics of their secondary and tertiary structure, requirements for cofactors/metals/proteins/ATP Know details of glmS ribozyme self-cleavage Understand use o ...
... Know four types of natural catalytic RNAs (group I introns, group II introns, RNase P, small self-cleaving), what reactions they perform, know basics of their secondary and tertiary structure, requirements for cofactors/metals/proteins/ATP Know details of glmS ribozyme self-cleavage Understand use o ...
Key for Exam 1 Part 1 - Evolutionary Biology
... and DNA has four (D) RNA is a single strand polynucleotide and DNA is a double strand (E) RNA molecules are smaller than chromosomal DNA molecules 35. In the double helix of DNA, what belongs on the complimentary DNA strand opposite adenine? (A) thyamine (B) adenine (C) cytosine (D) guanine (E) urac ...
... and DNA has four (D) RNA is a single strand polynucleotide and DNA is a double strand (E) RNA molecules are smaller than chromosomal DNA molecules 35. In the double helix of DNA, what belongs on the complimentary DNA strand opposite adenine? (A) thyamine (B) adenine (C) cytosine (D) guanine (E) urac ...
Introductory Biology Primer
... Transcription factors: a type of protein that binds to DNA and helps initiate gene transcription. Transcription factor binding sites: Short sequences of DNA (6-20 bp) recognized and bound by TFs. RNA polymerase binds a complex of TFs in the promoter. ...
... Transcription factors: a type of protein that binds to DNA and helps initiate gene transcription. Transcription factor binding sites: Short sequences of DNA (6-20 bp) recognized and bound by TFs. RNA polymerase binds a complex of TFs in the promoter. ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... are what their proteins make them. 4. DNA is mainly a blueprint that tells the cell which kinds of proteins to make and how to make them. ...
... are what their proteins make them. 4. DNA is mainly a blueprint that tells the cell which kinds of proteins to make and how to make them. ...
BIOLOGY (Theory)
... pigment and fats. These small organic molecules are the building blocks for proteins & other components. Hence, this experiment supported that life has come from pre-existing non-living ...
... pigment and fats. These small organic molecules are the building blocks for proteins & other components. Hence, this experiment supported that life has come from pre-existing non-living ...
transcript - Mike Dyall
... a) Overall scheme of information processing in cell DNA ➔ RNA ➔ Protein (‘central dogma’) Transcription and Translation b) Components of the transcription system in bacteria RNA polymerase DNA template, nucleotides, addition of new bases c) Stages of the transcription process RNAP binding to promote ...
... a) Overall scheme of information processing in cell DNA ➔ RNA ➔ Protein (‘central dogma’) Transcription and Translation b) Components of the transcription system in bacteria RNA polymerase DNA template, nucleotides, addition of new bases c) Stages of the transcription process RNAP binding to promote ...
CHEM642-07 Powerpoint
... (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mRNA is ...
... (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mRNA is ...
Instructional Objectives—DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Objective 11: Describe the role of DNA, mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes in protein synthesis. Describe the importance of each of the following molecules during protein synthesis? DNAmRNAtRNARibosomesObjective 12:Given a DNA sequence transcribe it into mRNA and determine the amino acid sequence that will be ...
... Objective 11: Describe the role of DNA, mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes in protein synthesis. Describe the importance of each of the following molecules during protein synthesis? DNAmRNAtRNARibosomesObjective 12:Given a DNA sequence transcribe it into mRNA and determine the amino acid sequence that will be ...
Honors Biology Unit 6 Ch. 10 “DNA, RNA & Protein synthesis”
... a. I can analyze the relationship between genes, chromosomes, DNA, and a genome. b. I can explain the functions of DNA. Vocabulary: gene, chromosome, DNA, allele, genome 2. Nucleic Acid Structure a. I can describe the structure of a DNA nucleotide. b. I can describe how DNA nucleotides are connected ...
... a. I can analyze the relationship between genes, chromosomes, DNA, and a genome. b. I can explain the functions of DNA. Vocabulary: gene, chromosome, DNA, allele, genome 2. Nucleic Acid Structure a. I can describe the structure of a DNA nucleotide. b. I can describe how DNA nucleotides are connected ...
Honors Biology Unit 6 Ch. 10 “DNA, RNA & Protein synthesis”
... a. I can analyze the relationship between genes, chromosomes, DNA, and a genome. b. I can explain the functions of DNA. Vocabulary: gene, chromosome, DNA, allele, genome 2. Nucleic Acid Structure a. I can describe the structure of a DNA nucleotide. b. I can describe how DNA nucleotides are connected ...
... a. I can analyze the relationship between genes, chromosomes, DNA, and a genome. b. I can explain the functions of DNA. Vocabulary: gene, chromosome, DNA, allele, genome 2. Nucleic Acid Structure a. I can describe the structure of a DNA nucleotide. b. I can describe how DNA nucleotides are connected ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.