Ch17WordLectureOutline w pics
... spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
... spliced together; the spliceosome then comes apart, releasing mRNA, which now contains only exons. ...
Instructions for Biochemistry
... We can look at life as a connection between numbers. • 1 is for you! You are a unique life-form! • 2 is for your 2 parents and the 2 sets of genes they gave you. • 4 is for the 4 code molecules in DNA (G, C, A, T) or RNA (G, C, A, U). DNA and RNA code for proteins. • 20 is for 20 of nature’s ultimat ...
... We can look at life as a connection between numbers. • 1 is for you! You are a unique life-form! • 2 is for your 2 parents and the 2 sets of genes they gave you. • 4 is for the 4 code molecules in DNA (G, C, A, T) or RNA (G, C, A, U). DNA and RNA code for proteins. • 20 is for 20 of nature’s ultimat ...
1 Confusion from last week: Purines and Pyrimidines
... their corresponding amino acids. One end has an anti-codon which binds to the mRNA. The tRNA codon sequence is the same as the gene sequence – mRNA is inverse of DNA, tRNA is inverse of mRNA – RNA, so U instead of T ...
... their corresponding amino acids. One end has an anti-codon which binds to the mRNA. The tRNA codon sequence is the same as the gene sequence – mRNA is inverse of DNA, tRNA is inverse of mRNA – RNA, so U instead of T ...
5b . Students know how to apply base-pairing rules to explain... semiconservative replication and transcription of information from DNA into mRNA.
... semiconservative replication and transcription of information from DNA into mRNA. 4a Students know the general pathway by which ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 4b Students know how to apply the genetic code rules to predict the sequence of amino a ...
... semiconservative replication and transcription of information from DNA into mRNA. 4a Students know the general pathway by which ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 4b Students know how to apply the genetic code rules to predict the sequence of amino a ...
2009 Dental Biochemistry (Questions)
... B) readily oxidized in the brain in response to excessive intake of carbohydrates. C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the other two ketone bodies. D) present only in the liver mitochondrion where it is used for energy production during fasting. E) a precursor in the biosynthesis of N-ac ...
... B) readily oxidized in the brain in response to excessive intake of carbohydrates. C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the other two ketone bodies. D) present only in the liver mitochondrion where it is used for energy production during fasting. E) a precursor in the biosynthesis of N-ac ...
HGD Gene Expression
... Nuclear export of RNA is regulated by the Cap Binding Complex (CBC) which binds exclusively to capped RNA. The CBC is then recognized by the nuclear pore complex and exported. 2. Prevention of degradation by exonucleases. Degradation of the mRNA by 5' exonucleases is prevented by functionally lookin ...
... Nuclear export of RNA is regulated by the Cap Binding Complex (CBC) which binds exclusively to capped RNA. The CBC is then recognized by the nuclear pore complex and exported. 2. Prevention of degradation by exonucleases. Degradation of the mRNA by 5' exonucleases is prevented by functionally lookin ...
Activation sites and enhancer proteins
... Where are the genes? in DNA on chromosomes in the nucleus Where are proteins synthesized? on ribosomes (free or on the ER) in the cytoplasm How does the information get from the nucleus to the cytoplasm? mRNA is made in the nucleus and can travel into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes ...
... Where are the genes? in DNA on chromosomes in the nucleus Where are proteins synthesized? on ribosomes (free or on the ER) in the cytoplasm How does the information get from the nucleus to the cytoplasm? mRNA is made in the nucleus and can travel into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes ...
The Search for LUCA Natural History Nov. 2000 Did the Last
... circular chromosome would already have been in place: a single enzyme called reverse ...
... circular chromosome would already have been in place: a single enzyme called reverse ...
Composition and structure of DNA and RNA and differences
... DNA is thought to consist primarily of B DNA o The A form is a right-handed helix but there are 11 bases per turn and the planes of the base pairs are tilted 20o away from the perpendicular to the helical axis. The conformation found in DNA-RNA hybrids is probably close to the A form. o Z-DNA is a l ...
... DNA is thought to consist primarily of B DNA o The A form is a right-handed helix but there are 11 bases per turn and the planes of the base pairs are tilted 20o away from the perpendicular to the helical axis. The conformation found in DNA-RNA hybrids is probably close to the A form. o Z-DNA is a l ...
Codon Bingo - TeacherWeb
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
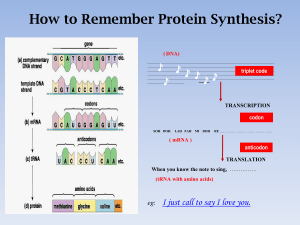
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
Chapter02 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids(核酸化学)
... Polymers linked 3' to 5' by phosphodiester bridges Ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid Know the shorthand notations Sequence is always read 5' to 3' In terms of genetic information, this corresponds to "N to C" in proteins Classes of Nucleic Acids DNA - one type, one purpose RNA - various typ ...
... Polymers linked 3' to 5' by phosphodiester bridges Ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid Know the shorthand notations Sequence is always read 5' to 3' In terms of genetic information, this corresponds to "N to C" in proteins Classes of Nucleic Acids DNA - one type, one purpose RNA - various typ ...
DNA - Doctor Jade
... • contains • carbon sugar-deoxyribose • nitrogenous base • 1-3 PO4 groups • contains 4 different nucleotides • each with different nitrogenous base • bases are found in 2 major groups • Purines – double ring structures – adenine (A) – guanine (G) • Pyrimidines – single ring structures – thymine (T) ...
... • contains • carbon sugar-deoxyribose • nitrogenous base • 1-3 PO4 groups • contains 4 different nucleotides • each with different nitrogenous base • bases are found in 2 major groups • Purines – double ring structures – adenine (A) – guanine (G) • Pyrimidines – single ring structures – thymine (T) ...
Biology for Bioinformatics - NIU Department of Biological
... In prokaryotes, transcription and translation are essentially simultaneous: translation of the messenger RNA starts before transcription is completed. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the nucleus (where the DNA is), and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. This de-coupling of transcription and ...
... In prokaryotes, transcription and translation are essentially simultaneous: translation of the messenger RNA starts before transcription is completed. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the nucleus (where the DNA is), and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. This de-coupling of transcription and ...
Biology for Bioinformatics
... In prokaryotes, transcription and translation are essentially simultaneous: translation of the messenger RNA starts before transcription is completed. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the nucleus (where the DNA is), and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. This de-coupling of transcription and ...
... In prokaryotes, transcription and translation are essentially simultaneous: translation of the messenger RNA starts before transcription is completed. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the nucleus (where the DNA is), and translation occurs in the cytoplasm. This de-coupling of transcription and ...
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein 1. Overview of Gene Expression 2. Transcription
... • 5’ cap, poly-A tail, intron, exon, splicing, spliceosome • rho protein, stem-loop, codon, anti-codon, translation • aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, polyribosome, signal ...
... • 5’ cap, poly-A tail, intron, exon, splicing, spliceosome • rho protein, stem-loop, codon, anti-codon, translation • aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, polyribosome, signal ...
DNA Lesson Plan - Penn Arts and Sciences
... 1. Glycosidic Bonds (Sugar to Nitrogenous Base) a. Anomeric bond between N-1 of pyrimidine or N-9 of purine to C1’ of sugar ...
... 1. Glycosidic Bonds (Sugar to Nitrogenous Base) a. Anomeric bond between N-1 of pyrimidine or N-9 of purine to C1’ of sugar ...
Chapter 4: Cellular Metabolism
... 16. When blood glucose levels are high, the liver uses glucose to synthesize ____ __________________________________________________________________ 17. When blood glucose levels are low, the liver releases____________________ 18. When a person takes in more carbohydrates than can be stored as glyco ...
... 16. When blood glucose levels are high, the liver uses glucose to synthesize ____ __________________________________________________________________ 17. When blood glucose levels are low, the liver releases____________________ 18. When a person takes in more carbohydrates than can be stored as glyco ...
Lab/Activity: Prot
... DNA is the molecule that stores the genetic information in your cells. That information is coded in the four bases of DNA: C (cytosine), G (guanine), A (adenine), and T (thymine). The DNA directs the functions of the cell on a daily basis and will also be used to pass on the genetic information to t ...
... DNA is the molecule that stores the genetic information in your cells. That information is coded in the four bases of DNA: C (cytosine), G (guanine), A (adenine), and T (thymine). The DNA directs the functions of the cell on a daily basis and will also be used to pass on the genetic information to t ...
Exercise 5
... We want to know the relationship of this class of maternal RNAs to the genes from which they are transcribed, and to the corresponding functional mRNAs from which cellular proteins are translated. At least some of this maternal RNA cannot be translated by polysomes as a message for proteins: transla ...
... We want to know the relationship of this class of maternal RNAs to the genes from which they are transcribed, and to the corresponding functional mRNAs from which cellular proteins are translated. At least some of this maternal RNA cannot be translated by polysomes as a message for proteins: transla ...
Document
... backbone at 180o • Actually a distorted ladder with poles closer to each other, on one side • Major/minor groove recognition ...
... backbone at 180o • Actually a distorted ladder with poles closer to each other, on one side • Major/minor groove recognition ...
Gene7-05
... 1. Genetic information carried by DNA is expressed in two stages: transcription of DNA into mRNA; and translation of the mRNA into protein. 2. The adaptor that interprets the meaning of a codon is transfer RNA, which has a compact L-shaped tertiary structure 3. The ribosome provides the apparatus th ...
... 1. Genetic information carried by DNA is expressed in two stages: transcription of DNA into mRNA; and translation of the mRNA into protein. 2. The adaptor that interprets the meaning of a codon is transfer RNA, which has a compact L-shaped tertiary structure 3. The ribosome provides the apparatus th ...
Chapter 13 Lecture Notes: DNA Function I. Transcription (General
... a) Wobble – certain different codons are recognized by the same tRNAs because the 3rd base in the codon and the 1st base of the anticodon pair via a “loose pairing”. This “loose pairing is according to a set of rules known as the wobble rules. ...
... a) Wobble – certain different codons are recognized by the same tRNAs because the 3rd base in the codon and the 1st base of the anticodon pair via a “loose pairing”. This “loose pairing is according to a set of rules known as the wobble rules. ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.