DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides However as shown below RNA differs from DNA in four basic ways a. RNA contains the sugar ribose, not deoxyribose found in DNA. b. RNA contains the nitrogenous base URACIL instead of Thymine found in DNA. c. RNA is usually single stranded rather ...
... Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides However as shown below RNA differs from DNA in four basic ways a. RNA contains the sugar ribose, not deoxyribose found in DNA. b. RNA contains the nitrogenous base URACIL instead of Thymine found in DNA. c. RNA is usually single stranded rather ...
Biomolecules
... amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation. It has sites for amino-acid attachment and an anticodon region for codon recognition that binds to a specific sequence on the messenger RNA chain through hydrogen bonding. It is a type of non-cod ...
... amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation. It has sites for amino-acid attachment and an anticodon region for codon recognition that binds to a specific sequence on the messenger RNA chain through hydrogen bonding. It is a type of non-cod ...
Ribonuclease P(Human)Real Time RT-PCR Kit User
... 3. Product Description All living things synthesize an enzyme — called Ribonuclease P (Rnase P) — that cleaves the head (5') end of the precursors of transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. Ribonuclease P real time RT-PCR kit contains a specific ready-to-use system for the detection of the RnaseP in human sp ...
... 3. Product Description All living things synthesize an enzyme — called Ribonuclease P (Rnase P) — that cleaves the head (5') end of the precursors of transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. Ribonuclease P real time RT-PCR kit contains a specific ready-to-use system for the detection of the RnaseP in human sp ...
Long Noncoding RNA as a Regulator for Transcription
... analyses of RNA polymerase II indicate that its major function is the precise initiation and elongation of protein-coding genes, early studies showed that RNA polymerase II possesses the ability to catalyze randomly initiated transcription from a calf thymus DNA or other crude DNA fractions as a tem ...
... analyses of RNA polymerase II indicate that its major function is the precise initiation and elongation of protein-coding genes, early studies showed that RNA polymerase II possesses the ability to catalyze randomly initiated transcription from a calf thymus DNA or other crude DNA fractions as a tem ...
Full-Text PDF
... together and where their separate abilities not only reinforced each other’s survival, but allowed life to more quickly climb the ladder of complexity. Essential for our approach is the following: Starting with small molecules (easily) derived from prebiotic chemistry, we will try to reconstruct a p ...
... together and where their separate abilities not only reinforced each other’s survival, but allowed life to more quickly climb the ladder of complexity. Essential for our approach is the following: Starting with small molecules (easily) derived from prebiotic chemistry, we will try to reconstruct a p ...
Modeling RNA Molecules
... who said, “The purpose of computing is insight, not numbers” (Hamming 1971), we should remember that the purpose of molecular modeling is functional insight, not detailed atomic models per se. Therefore, as we seek to improve our abilities to construct 3D models for molecules for which we do not yet ...
... who said, “The purpose of computing is insight, not numbers” (Hamming 1971), we should remember that the purpose of molecular modeling is functional insight, not detailed atomic models per se. Therefore, as we seek to improve our abilities to construct 3D models for molecules for which we do not yet ...
G T A C A T C T T A A C G C A T A T
... Normal hemoglobin A.A. sequence VALINE-HISTIDINE-LEUCINE-THREONINE-PROLINE-GLUTAMIC ACIDGLUTAMIC ACID -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Sickle cell hemoglobin DNA ...
... Normal hemoglobin A.A. sequence VALINE-HISTIDINE-LEUCINE-THREONINE-PROLINE-GLUTAMIC ACIDGLUTAMIC ACID -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Sickle cell hemoglobin DNA ...
Transcription, Translation, and Protein Study Guide What is the
... DNA>>RNA>>PROTEIN The Central Dogma of Biology is used to describe the “one gene-one protein” mechanism that allows for DNA to produce a code specific to an amino acid sequence needed for structural and functional proteins. This premise is losing some hold on biology since it has been discovered tha ...
... DNA>>RNA>>PROTEIN The Central Dogma of Biology is used to describe the “one gene-one protein” mechanism that allows for DNA to produce a code specific to an amino acid sequence needed for structural and functional proteins. This premise is losing some hold on biology since it has been discovered tha ...
Structure and Function of DNA
... 17.Organisms are different from each other, even though their genetic material is made up of the same molecules, because the order of nucleotides in their DNA is different. ...
... 17.Organisms are different from each other, even though their genetic material is made up of the same molecules, because the order of nucleotides in their DNA is different. ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... 19. genetic code- The set of rules that dictates the correspondence between RNA codons in an mRNA molecule and amino acids in protein. 20. RNA polymerase- An enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription, using a DNA strand as a template. 21. terminator- A spec ...
... 19. genetic code- The set of rules that dictates the correspondence between RNA codons in an mRNA molecule and amino acids in protein. 20. RNA polymerase- An enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription, using a DNA strand as a template. 21. terminator- A spec ...
Gene Regulation
... Variant mRNAs (and resulting proteins) can be generated by skipping some introns, or by using a sequence as an intron in one cell type and as an exon in another cell type. Alternative promoters or polyadenylation sites. Are also used to generated variants at the beginning and end of the mRNA (and pr ...
... Variant mRNAs (and resulting proteins) can be generated by skipping some introns, or by using a sequence as an intron in one cell type and as an exon in another cell type. Alternative promoters or polyadenylation sites. Are also used to generated variants at the beginning and end of the mRNA (and pr ...
FREE Sample Here
... Rationale: Translation is the process whereby the mRNA codon sequence directs amino acid sequence during protein synthesis. Translation takes place on ribosomes, which bind to the initiation site on mRNA. During synthesis codons are “read” by tRNA, and anticodons are bound to the amino acid molecule ...
... Rationale: Translation is the process whereby the mRNA codon sequence directs amino acid sequence during protein synthesis. Translation takes place on ribosomes, which bind to the initiation site on mRNA. During synthesis codons are “read” by tRNA, and anticodons are bound to the amino acid molecule ...
BIOL 222 - philipdarrenjones.com
... 24) In a bacterial operon, this can inhibit transcription by blocking the binding of positively acting transcription factors to the DNA: A) enhancer B) promoter C) activator D) repressor E) terminator ...
... 24) In a bacterial operon, this can inhibit transcription by blocking the binding of positively acting transcription factors to the DNA: A) enhancer B) promoter C) activator D) repressor E) terminator ...
Figure 19.5 A eukaryotic gene and its transcript
... RNA processing: Cap and tail added; introns excised and exons spliced together ...
... RNA processing: Cap and tail added; introns excised and exons spliced together ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Note Packet
... 3. The DNA inherited by an organism dictates the synthesis of certain proteins. Proteins are the link between ___________________________. The proteins that are made will determine what _____________ show up in the offspring. 4. _______________________: The process by which DNA directs the synthesi ...
... 3. The DNA inherited by an organism dictates the synthesis of certain proteins. Proteins are the link between ___________________________. The proteins that are made will determine what _____________ show up in the offspring. 4. _______________________: The process by which DNA directs the synthesi ...
Lecture16 Biol302 Spring 2011
... The code is nonoverlapping, with each nucleotide part of a single codon, degenerate, with most amino acids specified by two to four codons, and ordered, with similar amino acids specified by related codons. The genetic code is nearly universal; with minor exceptions, the 64 triplets have the same ...
... The code is nonoverlapping, with each nucleotide part of a single codon, degenerate, with most amino acids specified by two to four codons, and ordered, with similar amino acids specified by related codons. The genetic code is nearly universal; with minor exceptions, the 64 triplets have the same ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP): Variation between individuals in DNA fragment sizes cut by specific restriction enzymes; polymorphic sequences that result in RFLPs are used as markers on both physical maps and genetic linkage maps. RFLPs are usually caused by mutation at a cutting s ...
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP): Variation between individuals in DNA fragment sizes cut by specific restriction enzymes; polymorphic sequences that result in RFLPs are used as markers on both physical maps and genetic linkage maps. RFLPs are usually caused by mutation at a cutting s ...
Document
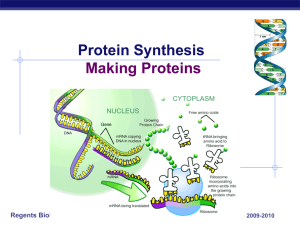
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
Chapter 8
... that are partially double-helical. The pri-miRNA is processed to a shorter ~ 70 nt pre-miRNA that is then transported to the cytoplasm. The pre-miRNA, which folds into a hairpin structure, is bound by a protein complex containing the enzyme known as Dicer. Dicer cleaves the molecule producing a 21-2 ...
... that are partially double-helical. The pri-miRNA is processed to a shorter ~ 70 nt pre-miRNA that is then transported to the cytoplasm. The pre-miRNA, which folds into a hairpin structure, is bound by a protein complex containing the enzyme known as Dicer. Dicer cleaves the molecule producing a 21-2 ...
Protein Synthesis 06-07
... – A single strand of RNA (about 80 nucleotides) – A loop at one end that contains the anticodon – Anticodon – a sequence of 3 bases on tRNA that are complementary to the bases on mRNA – At the opposite end of the loop is a site where an amino acit can attach ...
... – A single strand of RNA (about 80 nucleotides) – A loop at one end that contains the anticodon – Anticodon – a sequence of 3 bases on tRNA that are complementary to the bases on mRNA – At the opposite end of the loop is a site where an amino acit can attach ...
AP Biology Fall Semester Review
... 78) According to the Jacob-Monod (lac operon) model of the gene regulation inducer substances in bacterial cells probably a. combine with operator regions, activating the associated operons b. combine with structural genes, stimulating them to synthesize messenger RNA c. combine with repressor prot ...
... 78) According to the Jacob-Monod (lac operon) model of the gene regulation inducer substances in bacterial cells probably a. combine with operator regions, activating the associated operons b. combine with structural genes, stimulating them to synthesize messenger RNA c. combine with repressor prot ...
HA Nucleic Acids Practice Exam
... TOP: 12-11 7. ANS: B Deleting a nucleotide causes a frameshift mutation, since the codons following the deletion will code for different amino acids than the original sequence. Feedback A B C D ...
... TOP: 12-11 7. ANS: B Deleting a nucleotide causes a frameshift mutation, since the codons following the deletion will code for different amino acids than the original sequence. Feedback A B C D ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.