
structure and effectively suppress the mutation in B· 4. Transfer
... Chapter 1), would you expect there to be any protein detectable by the antibody in the mutant? Explain. Answer: There are a number of mutational changes that can lead to the absence of enzymatic function in the product of a gene. Some of these changes would result in the complete absence of protein ...
... Chapter 1), would you expect there to be any protein detectable by the antibody in the mutant? Explain. Answer: There are a number of mutational changes that can lead to the absence of enzymatic function in the product of a gene. Some of these changes would result in the complete absence of protein ...
CHAPTER 16: ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS
... 16.44 Ribosomes are the parts of a cell that build proteins. They are made from RNA and proteins. 16.45 Transfer RNA bonds to an amino acid, carries it to the ribosome, and binds to a mRNA codon so the amino acid can be added to a growing protein. Transfer RNA ensures that each codon is matched with ...
... 16.44 Ribosomes are the parts of a cell that build proteins. They are made from RNA and proteins. 16.45 Transfer RNA bonds to an amino acid, carries it to the ribosome, and binds to a mRNA codon so the amino acid can be added to a growing protein. Transfer RNA ensures that each codon is matched with ...
Structure and Transcription of the singed Locus of Drosophila
... was used. A total of 22 clones were isolated fromfour different libraries. Two of the cDNAs werefrom olj??, and 4 of the 20 sn cDNA inserts were smaller than 1.5kb. The remaining 16 weremapped and their maps can be aligned with that of the largest clone,the 2.9-kb pupal cDNA P5. The other cDNAs appe ...
... was used. A total of 22 clones were isolated fromfour different libraries. Two of the cDNAs werefrom olj??, and 4 of the 20 sn cDNA inserts were smaller than 1.5kb. The remaining 16 weremapped and their maps can be aligned with that of the largest clone,the 2.9-kb pupal cDNA P5. The other cDNAs appe ...
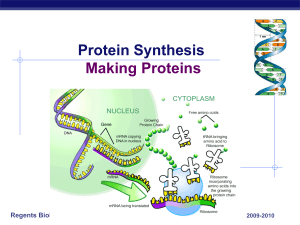
Protein Synthesis Making Proteins
... How do proteins do all the work Proteins proteins run living organisms ...
... How do proteins do all the work Proteins proteins run living organisms ...
Chapter 15
... Each enzyme catalyzes the next series of reactions necessary for tryptophan production ...
... Each enzyme catalyzes the next series of reactions necessary for tryptophan production ...
Introduction to self-assembly Self
... both natural and synthetic biological systems, in many cases assembly requires a more direct agent. If that agent is an already-assembled entity of the same type, the process is still considered a form of self-assembly but is more likely to be referred to as self-replication. The “RNA world” hypoth ...
... both natural and synthetic biological systems, in many cases assembly requires a more direct agent. If that agent is an already-assembled entity of the same type, the process is still considered a form of self-assembly but is more likely to be referred to as self-replication. The “RNA world” hypoth ...
workshop - Dr Amy Yasko
... Preferential resistance of dopaminergic neurons to the toxicity of glutathione depletion is independent of cellular glutathione peroxidase and is mediated by tetrahydrobiopterin. Nakamura K, Wright DA, Wiatr T, Kowlessur D, Milstien S, Lei XG, Kang UJ. Department of Neurology, University of Chicago, ...
... Preferential resistance of dopaminergic neurons to the toxicity of glutathione depletion is independent of cellular glutathione peroxidase and is mediated by tetrahydrobiopterin. Nakamura K, Wright DA, Wiatr T, Kowlessur D, Milstien S, Lei XG, Kang UJ. Department of Neurology, University of Chicago, ...
Calling names
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
DNA and RNA extraction
... Centrifuge at 12,000 x g for 2 minutes. This will precipitate the carbohydrate. Transfer the supernatant to a fresh tube for precipitation of the RNA. High-molecular weight RNA (including mRNA) is recovered by selective precipitation with NaCl. At 2.5M NaCl, DNA and low molecular weight RNA remain i ...
... Centrifuge at 12,000 x g for 2 minutes. This will precipitate the carbohydrate. Transfer the supernatant to a fresh tube for precipitation of the RNA. High-molecular weight RNA (including mRNA) is recovered by selective precipitation with NaCl. At 2.5M NaCl, DNA and low molecular weight RNA remain i ...
File
... double stranded (one strand is known as the coding strand and the other is complementary strand). Watson and Crick also discovered that this “double stranded ladder” of DNA was coiled like a staircase, called a “Double Helix.” ...
... double stranded (one strand is known as the coding strand and the other is complementary strand). Watson and Crick also discovered that this “double stranded ladder” of DNA was coiled like a staircase, called a “Double Helix.” ...
48107Ch1Hwk1
... 4. The organisms most likely to be found in a brine environment would be ______. 5. The organisms most likely to be found in high temperature environments would be ______. 6. The term used to indicate the degree of randomness within a system is ______. 7. Spontaneous processes are characterized by a ...
... 4. The organisms most likely to be found in a brine environment would be ______. 5. The organisms most likely to be found in high temperature environments would be ______. 6. The term used to indicate the degree of randomness within a system is ______. 7. Spontaneous processes are characterized by a ...
BI0I 121 cel]
... Select the best fitting description for mRNA. A. Smallest of the RNA molecules; many different kinds. B. Single long strand that passes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. C. Part of chromosomes; contain the basic genetic information of the cell. D. Genome of an RNA virus. E. Made in the nucleus; pro ...
... Select the best fitting description for mRNA. A. Smallest of the RNA molecules; many different kinds. B. Single long strand that passes from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. C. Part of chromosomes; contain the basic genetic information of the cell. D. Genome of an RNA virus. E. Made in the nucleus; pro ...
Nucleic acids and protein synthesis
... It sho�ld be noted that while x-ray diffraction shows that a sub stantial portion of the DNA must be in the double helix form it is an extremely poor method for deciding how much of the DNA is in this con ...
... It sho�ld be noted that while x-ray diffraction shows that a sub stantial portion of the DNA must be in the double helix form it is an extremely poor method for deciding how much of the DNA is in this con ...
DNA and RNA Replication
... 2. Click the Legend button for information about how nitrogen bases pair. 3. Build a mRNA molecule by pairing up free nitrogen bases in the nucleus with the nitrogen bases on the exposed strand of DNA. Start at the top where there is a Blinking DOT!! Determine which free nitrogen base pairs up with ...
... 2. Click the Legend button for information about how nitrogen bases pair. 3. Build a mRNA molecule by pairing up free nitrogen bases in the nucleus with the nitrogen bases on the exposed strand of DNA. Start at the top where there is a Blinking DOT!! Determine which free nitrogen base pairs up with ...
U1Word - UTM.edu
... (There is no 0; -n precedes transcribed segment: “upstream”; +n is “downstream” from start site) 3. Promoters: Discovered in mutants with altered transcription rates. Mutations mapped to the 40 bps preceding transcription start site. (These are “up” or “down” mutants.) a. E Coli transcription units ...
... (There is no 0; -n precedes transcribed segment: “upstream”; +n is “downstream” from start site) 3. Promoters: Discovered in mutants with altered transcription rates. Mutations mapped to the 40 bps preceding transcription start site. (These are “up” or “down” mutants.) a. E Coli transcription units ...
5 - Parkway C-2
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA produced by transcription is immediately translated without more processing • In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation • Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through RNA processing to yield finished mRNA • Cells are governed by a ...
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA produced by transcription is immediately translated without more processing • In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation • Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through RNA processing to yield finished mRNA • Cells are governed by a ...
rna viruses
... and directs the host cell to make viral particles. Therefore viral replication primarily depends upon DNA, RNA and protein synthesis of the host cells. Consequently, many chemicals that inhibit viral replication also inhibit some host cell function and produce toxic effects. Another problem po ...
... and directs the host cell to make viral particles. Therefore viral replication primarily depends upon DNA, RNA and protein synthesis of the host cells. Consequently, many chemicals that inhibit viral replication also inhibit some host cell function and produce toxic effects. Another problem po ...
6.4 RNA - Part 2 - Translation rna_2_s12
... linking chains of amino acids together (polymers) • Occurs in cytoplasm or attached to RER. ...
... linking chains of amino acids together (polymers) • Occurs in cytoplasm or attached to RER. ...
Chapter 17
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA produced by transcription is immediately translated without more processing • In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation • Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through RNA processing to yield finished mRNA • Cells are governed by a ...
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA produced by transcription is immediately translated without more processing • In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription from translation • Eukaryotic RNA transcripts are modified through RNA processing to yield finished mRNA • Cells are governed by a ...
Protein Synthesis Lab
... Step 1: Transcription • Transcription is the first step of protein synthesis. This step takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Segments of DNA called genes store the information on the proper order of amino acids to construct the cells proteins. Click on one of the chromosomes to see what ...
... Step 1: Transcription • Transcription is the first step of protein synthesis. This step takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Segments of DNA called genes store the information on the proper order of amino acids to construct the cells proteins. Click on one of the chromosomes to see what ...
Highly Efficient Micro RNA Enrichment
... to 40 nucleotides, and the majority of the miRNA is composed of approximately 22 nucleotides. Most of the commercially available miRNA extraction protocols co-purify the miRNA and total RNA. Therefore, the extracted samples still contain ribosomal RNA and messenger RNA with only a low percentage of ...
... to 40 nucleotides, and the majority of the miRNA is composed of approximately 22 nucleotides. Most of the commercially available miRNA extraction protocols co-purify the miRNA and total RNA. Therefore, the extracted samples still contain ribosomal RNA and messenger RNA with only a low percentage of ...
Differential Gene Expression in the Gastrula of Xenopus Laevis
... Gastrula mRNA separate from Maternal mRNA Gradually disappear after Gastrula; Implication that it has little preceding stages. Some increase in concentration. ...
... Gastrula mRNA separate from Maternal mRNA Gradually disappear after Gastrula; Implication that it has little preceding stages. Some increase in concentration. ...
A mRNA localized to the vegetal cortex of Xenopus
... clear, however, that many of the early developmental decisions of the embryo depend on maternal information localized to the vegetal region during oogenesis. For example, the dorsal-ventral axis of the embryo, specified by a 30° rotation of the cortex before first cleavage, depends on a maternal com ...
... clear, however, that many of the early developmental decisions of the embryo depend on maternal information localized to the vegetal region during oogenesis. For example, the dorsal-ventral axis of the embryo, specified by a 30° rotation of the cortex before first cleavage, depends on a maternal com ...
transcription
... • The information in DNA is transferred to messenger RNA through complementary base pairing. • Each “C” nucleotide in a segment of DNA being transcribed results in a “G” nucleotide being added to a segment of RNA, and so ...
... • The information in DNA is transferred to messenger RNA through complementary base pairing. • Each “C” nucleotide in a segment of DNA being transcribed results in a “G” nucleotide being added to a segment of RNA, and so ...
Chapter 17 (Oct 23, 27, 28)
... Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein 13. What are the 4 levels of protein structure? 14. How does structure (sequence) influence function? 15. What are polyribosomes? 16. How is rough ER made? 17. How do mutations alter the genotype & phenotype of organisms? - Mutation – any change in the genetic mater ...
... Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein 13. What are the 4 levels of protein structure? 14. How does structure (sequence) influence function? 15. What are polyribosomes? 16. How is rough ER made? 17. How do mutations alter the genotype & phenotype of organisms? - Mutation – any change in the genetic mater ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.









![BI0I 121 cel]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004132586_1-822dfb440517eec80339a913dc1e4e97-300x300.png)












