DNA-free CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering in
... The CRISPR-Cas9 system permits researchers to quickly edit genes for functional protein knockout in mammalian, fish and plant genomes, among others, and consequently has dramatically transformed biological research. The CRISPR-Cas9 system requires exogenous Cas9 nuclease to be delivered into the cel ...
... The CRISPR-Cas9 system permits researchers to quickly edit genes for functional protein knockout in mammalian, fish and plant genomes, among others, and consequently has dramatically transformed biological research. The CRISPR-Cas9 system requires exogenous Cas9 nuclease to be delivered into the cel ...
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... The anti-codon UAC will be an exact fit for that. (Remember U and A are complementary to each other and so are G and C.) b) Tyrosine (Tyr) will be coded by either UAU or UAC on the mRNA. The anti-codon will be complementary to those – either AUA or AUG. c) Tryptophan (Trp) is coded by UGG. The anti- ...
... The anti-codon UAC will be an exact fit for that. (Remember U and A are complementary to each other and so are G and C.) b) Tyrosine (Tyr) will be coded by either UAU or UAC on the mRNA. The anti-codon will be complementary to those – either AUA or AUG. c) Tryptophan (Trp) is coded by UGG. The anti- ...
Transcription and Translation RNA
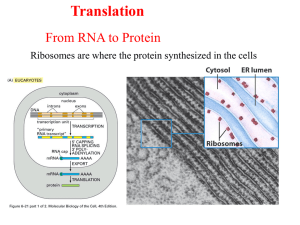
... The ribosomal subunits are named according to their Svedberg coefficients (S). This is a unit of measure that describes the sedimentation rate of a particle in a centrifuge. It is particularly useful with very large macromolecular complexes. The greater the mass the larger is the Svedberg coefficien ...
... The ribosomal subunits are named according to their Svedberg coefficients (S). This is a unit of measure that describes the sedimentation rate of a particle in a centrifuge. It is particularly useful with very large macromolecular complexes. The greater the mass the larger is the Svedberg coefficien ...
Chapter 12 Lecture Notes: Metabolism – Enzyme and Gene
... A. Regulation of transcriptional initiation by sigma factors (see notes for chapter 11) B. Regulation of transcriptional initiation by transcriptional regulator proteins (see V) 1. negative control = mRNA synthesis proceeds more rapidly in the absence of a controlling factor (repressor protein); in ...
... A. Regulation of transcriptional initiation by sigma factors (see notes for chapter 11) B. Regulation of transcriptional initiation by transcriptional regulator proteins (see V) 1. negative control = mRNA synthesis proceeds more rapidly in the absence of a controlling factor (repressor protein); in ...
CHEM 642-09 Powerpoint
... codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino acids are represented by more than one codon, and that there are some regularities in the set of codons that specifies each amino acid. Codons for the same amino acid tend to contain the same nucleotides at ...
... codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino acids are represented by more than one codon, and that there are some regularities in the set of codons that specifies each amino acid. Codons for the same amino acid tend to contain the same nucleotides at ...
Exam #3 Review Exam #3 will cover from glycolysis to complex
... for phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP! ATP synthase - allows protons pumped out during production of the PMF to pass back into the cell ---> uses energy to fuel the phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP. This is oxidative phosphorylation! • Practice: If 5 molecules of NADH are completely oxidized b ...
... for phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP! ATP synthase - allows protons pumped out during production of the PMF to pass back into the cell ---> uses energy to fuel the phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP. This is oxidative phosphorylation! • Practice: If 5 molecules of NADH are completely oxidized b ...
Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics
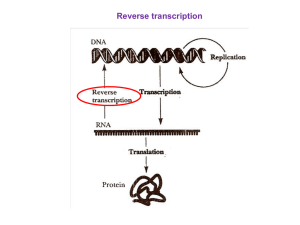
... • Gene expression occurs when gene activity leads to a protein product in the cell (Protein Synthesis). • A gene does not directly control protein synthesis; instead, it passes its genetic information on to RNA, which is more directly involved in protein synthesis. • Difference between DNA and RNA • ...
... • Gene expression occurs when gene activity leads to a protein product in the cell (Protein Synthesis). • A gene does not directly control protein synthesis; instead, it passes its genetic information on to RNA, which is more directly involved in protein synthesis. • Difference between DNA and RNA • ...
General Biology I Test V
... • The presence of two X chromsomes (XX) in the zygote results in female offspring (homogametous). • The presence of one X chromsome and one Y chromosome (XY) results in male offspring (heterogametous) • All female gametes have an X chromosome, male gametes ...
... • The presence of two X chromsomes (XX) in the zygote results in female offspring (homogametous). • The presence of one X chromsome and one Y chromosome (XY) results in male offspring (heterogametous) • All female gametes have an X chromosome, male gametes ...
Ch03Test_File+heikka
... a. DNA has thymine, whereas RNA has uracil. b. DNA usually has two polynucleotide strands, whereas RNA usually has one strand. c. DNA has deoxyribose sugar, whereas RNA has ribose sugar. d. DNA is a polymer, whereas RNA is a monomer. e. In DNA, A pairs with T, whereas in RNA, A pairs with U. Answer: ...
... a. DNA has thymine, whereas RNA has uracil. b. DNA usually has two polynucleotide strands, whereas RNA usually has one strand. c. DNA has deoxyribose sugar, whereas RNA has ribose sugar. d. DNA is a polymer, whereas RNA is a monomer. e. In DNA, A pairs with T, whereas in RNA, A pairs with U. Answer: ...
lecture 5
... In a metabolically active cell, approximately 3% to 5% of the cellular RNA is mRNA, 90% is rRNA, and about 4% is tRNA. - Hundreds of different mRNAs can be in one cell. - By contrast, there are four types of rRNA. Three of the rRNAs combine with a set of proteins to form a ribonucleoprotein complex ...
... In a metabolically active cell, approximately 3% to 5% of the cellular RNA is mRNA, 90% is rRNA, and about 4% is tRNA. - Hundreds of different mRNAs can be in one cell. - By contrast, there are four types of rRNA. Three of the rRNAs combine with a set of proteins to form a ribonucleoprotein complex ...
Crystal Structures of Two Viral IRES RNA Domains Bound to the
... normal growth under physiological conditions as well as responses to internal or external stresses. Viruses do not have their own translation apparatus and have to use the host’s ribosome to synthesize their viral proteins. During viral infections, host cells down-regulate capdependent initiation as ...
... normal growth under physiological conditions as well as responses to internal or external stresses. Viruses do not have their own translation apparatus and have to use the host’s ribosome to synthesize their viral proteins. During viral infections, host cells down-regulate capdependent initiation as ...
Combined Immunofluorescence, RNA Fluorescent In Situ
... etc.); DNA FISH enables the labeling of gene loci and chromosome territories; nuclear RNA FISH permits the detection of noncoding RNAs and primary transcripts at gene loci (to assay for the transcriptional status of a gene (3)). Such techniques have been used to investigate: 1) the specific 3D organ ...
... etc.); DNA FISH enables the labeling of gene loci and chromosome territories; nuclear RNA FISH permits the detection of noncoding RNAs and primary transcripts at gene loci (to assay for the transcriptional status of a gene (3)). Such techniques have been used to investigate: 1) the specific 3D organ ...
History and Function
... 3) NMR spectroscopy in elaborating both protein structure and protein folding pathways. ...
... 3) NMR spectroscopy in elaborating both protein structure and protein folding pathways. ...
Lecture 33
... Unpunctuated – although some codons are signals Mutations - in coding region can cause various ill-effects, such as, change in desired amino acids, early or late stop, insertion, etc. ...
... Unpunctuated – although some codons are signals Mutations - in coding region can cause various ill-effects, such as, change in desired amino acids, early or late stop, insertion, etc. ...
Sequence±structure±function studies of tRNA
... diverse class of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet)-dependent methyltransferases. The enzymes characterized to date include members of two unrelated superfamilies: `classical' Rossmann-fold-like (1,2) and SPOUT (3). The relatively small SPOUT superfamily includes only a few characterized RNAspeci®c en ...
... diverse class of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet)-dependent methyltransferases. The enzymes characterized to date include members of two unrelated superfamilies: `classical' Rossmann-fold-like (1,2) and SPOUT (3). The relatively small SPOUT superfamily includes only a few characterized RNAspeci®c en ...
Document
... • There is a single reading frame maintained throughout the process of translation • Each codon consists of three nucleotides • Code is nonoverlapping • Code is degenerate: each amino acid is specified by more than one codon ...
... • There is a single reading frame maintained throughout the process of translation • Each codon consists of three nucleotides • Code is nonoverlapping • Code is degenerate: each amino acid is specified by more than one codon ...
Chapter 15 – DNA to Proteins
... molecule, and that the sequence of bases in DNA is a kind of code in which different combinations of bases could specify the 20 amino acids. • A particular stretch of DNA (a gene) contains the information to specify the amino acid sequence of one protein. • The information encoded in the base sequen ...
... molecule, and that the sequence of bases in DNA is a kind of code in which different combinations of bases could specify the 20 amino acids. • A particular stretch of DNA (a gene) contains the information to specify the amino acid sequence of one protein. • The information encoded in the base sequen ...
Chapter 14 Lecture Notes: Nucleic Acids
... chromosomes per cell, 23 from each parent. Dogs have a total of 78 chromosomes, 39 from each parent. Fruit flies have a total of 8 chromosomes. The smallest human chromosome contains about 50 million base pairs, and the largest one contains about 250 million base pairs. Bacterial DNA In bacteria, wh ...
... chromosomes per cell, 23 from each parent. Dogs have a total of 78 chromosomes, 39 from each parent. Fruit flies have a total of 8 chromosomes. The smallest human chromosome contains about 50 million base pairs, and the largest one contains about 250 million base pairs. Bacterial DNA In bacteria, wh ...
Lesson Overview Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the nearuniversal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the same direction. Despite their enormo ...
... One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the nearuniversal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the same direction. Despite their enormo ...
Historical review: Deciphering the genetic code – a personal account
... minimum kinds of bases necessary for template activity are shown, so many amino acids that respond to randomly ordered polynucleotides composed of two or more kinds of bases are omitted. The base compositions of RNA codons were derived from these experiments [49]. Reproduced from Ref. [49]. ...
... minimum kinds of bases necessary for template activity are shown, so many amino acids that respond to randomly ordered polynucleotides composed of two or more kinds of bases are omitted. The base compositions of RNA codons were derived from these experiments [49]. Reproduced from Ref. [49]. ...
清华大学本科生考试试题专用纸
... 41. Explain why skeletal muscle does not contribute glucose to the blood. (4 points) Answer: Because it lacks the enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase. 42. Explain why untreated diabetics lose weight. (4 points) Answer: The rate of triacylglycerol biosynthesis is affected by the action of several hormones, ...
... 41. Explain why skeletal muscle does not contribute glucose to the blood. (4 points) Answer: Because it lacks the enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase. 42. Explain why untreated diabetics lose weight. (4 points) Answer: The rate of triacylglycerol biosynthesis is affected by the action of several hormones, ...
Chapter 12: DNA & RNA
... DNA – Structure Questions 1.What pair of scientists are largely credited for discovering the shape of the DNA molecule? 2.Name the scientist whose photographs helped solve the mystery of DNA’s structure 3.DNA is in the shape of a _______ _______. 4.What are the sides of the DNA molecule made of? ...
... DNA – Structure Questions 1.What pair of scientists are largely credited for discovering the shape of the DNA molecule? 2.Name the scientist whose photographs helped solve the mystery of DNA’s structure 3.DNA is in the shape of a _______ _______. 4.What are the sides of the DNA molecule made of? ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.