
Translation
... • Coordinated to enzyme by 2 his and 1 cys residues • Binds Thr by amino group and OH of side chain ...
... • Coordinated to enzyme by 2 his and 1 cys residues • Binds Thr by amino group and OH of side chain ...
Origins of Life - My George School
... John Sutherland (at the University of Cambridge) managed to produce 2 of RNA’s nucleotides (cytosine and uracil) using acetylene and formaldehyde ...
... John Sutherland (at the University of Cambridge) managed to produce 2 of RNA’s nucleotides (cytosine and uracil) using acetylene and formaldehyde ...
Highly specific imaging of mRNA in single cells by target RNA
... should be designed with none or minor secondary structure. Besides, multiple targeting sites on mRNA can be tested for improving the efficiency of hybridization and amplification. The second factor is the relatively low spatial resolution of amplification-based single-molecule imaging method. To pro ...
... should be designed with none or minor secondary structure. Besides, multiple targeting sites on mRNA can be tested for improving the efficiency of hybridization and amplification. The second factor is the relatively low spatial resolution of amplification-based single-molecule imaging method. To pro ...
Notes - Haiku Learning
... B. 1970’s Frederick Sanger developed the first sequencing procedure 1. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): uses fragments of DNA and produces a large number of copies and then denatured (separated in single strands) by heating to 92 °-94° C a) Can be studied and analyzed and often used in forensics wh ...
... B. 1970’s Frederick Sanger developed the first sequencing procedure 1. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): uses fragments of DNA and produces a large number of copies and then denatured (separated in single strands) by heating to 92 °-94° C a) Can be studied and analyzed and often used in forensics wh ...
Example-Abstract
... biochemical analysis and find it to be the same as described before by genetic studies. Human and Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNASEH2A/Rnh201p subunits contain the catalytic center and are similar to each other and to prokaryotic RNase HII, which is functionally active as a single polypeptide. Although ...
... biochemical analysis and find it to be the same as described before by genetic studies. Human and Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNASEH2A/Rnh201p subunits contain the catalytic center and are similar to each other and to prokaryotic RNase HII, which is functionally active as a single polypeptide. Although ...
Comparative Genomic Study of upstream Open Reading Frames
... strand is a linear arrangement of repeating similar units called nucleotides, which are each composed of one sugar, one phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Four different bases are present in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The particular order of the bases arranged alon ...
... strand is a linear arrangement of repeating similar units called nucleotides, which are each composed of one sugar, one phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Four different bases are present in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The particular order of the bases arranged alon ...
Chapter 9 - KINGERYGHS
... 3) The monomers of DNA and RNA are A) amino acids. B) monosaccharides. C) nucleotides. D) fatty acids. E) nucleic acids. C 4) Which of the following statements regarding DNA is false? A) DNA uses the sugar deoxyribose. B) DNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil. C) DNA is a nucleic acid. D) One DNA mol ...
... 3) The monomers of DNA and RNA are A) amino acids. B) monosaccharides. C) nucleotides. D) fatty acids. E) nucleic acids. C 4) Which of the following statements regarding DNA is false? A) DNA uses the sugar deoxyribose. B) DNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil. C) DNA is a nucleic acid. D) One DNA mol ...
Lecture 24 – PDF
... A. The genetic code is responsible for the incorporation of 20 common amino acids into the growing amino acid (polypeptide) chain during translation. The cracking of the code (along with other aspects of translation) led to several Nobel prizes. B. Reading the code is straightforward. C. Important p ...
... A. The genetic code is responsible for the incorporation of 20 common amino acids into the growing amino acid (polypeptide) chain during translation. The cracking of the code (along with other aspects of translation) led to several Nobel prizes. B. Reading the code is straightforward. C. Important p ...
Introduction to molecular and cell biology
... to understand the regulation, one studied the growth-phase regulatory factors and gene expression in response to specific environmental differences within the host a novel growth phase assosiated two-component-type ...
... to understand the regulation, one studied the growth-phase regulatory factors and gene expression in response to specific environmental differences within the host a novel growth phase assosiated two-component-type ...
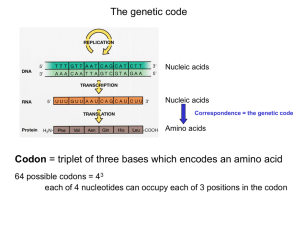
AUG
... - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
... - for STOP - UAA, UAG, UGA 61 codons encode 20 amino acids - most amino acids are specified by more than one codon - degeneracy of the genetic code ...
Astrovirus Replication: An Overview
... for five HAstV isolates — including serotypes 1, 2, 3, and 8 — has been sequenced.9,11–14 Complete capsid sequences are available for HAstV-1 through 6 and HAstV-8, as well as for feline, porcine, ovine, mink, and turkey astroviruses and for the avian nephritis virus. HAstV can be isolated and propa ...
... for five HAstV isolates — including serotypes 1, 2, 3, and 8 — has been sequenced.9,11–14 Complete capsid sequences are available for HAstV-1 through 6 and HAstV-8, as well as for feline, porcine, ovine, mink, and turkey astroviruses and for the avian nephritis virus. HAstV can be isolated and propa ...
PHYS 4xx Intro 2 1 PHYS 4xx Intro 2
... groups while the sixth is double-bonded as an aldehyde. The double-bonded oxygen can be placed at one of several different positions on the chain, each corresponding to an inequivalent, yet related, molecule. The chain can be closed into a ring using one of the oxygens in a hydroxyl group (not the o ...
... groups while the sixth is double-bonded as an aldehyde. The double-bonded oxygen can be placed at one of several different positions on the chain, each corresponding to an inequivalent, yet related, molecule. The chain can be closed into a ring using one of the oxygens in a hydroxyl group (not the o ...
The RNA origin of transfer RNA aminoacylation and beyond
... maintained the essential bases in the amino acid and tRNA-binding regions but the rest was re-randomized for the second activity selection (figure 2d ) [10]. Sequence alignment of the active species revealed that the 30 -terminal region after the tRNA-binding site has no conservation of sequence, su ...
... maintained the essential bases in the amino acid and tRNA-binding regions but the rest was re-randomized for the second activity selection (figure 2d ) [10]. Sequence alignment of the active species revealed that the 30 -terminal region after the tRNA-binding site has no conservation of sequence, su ...
Lesson Overview
... One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the nearuniversal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the same direction. Despite their enormo ...
... One of the most interesting discoveries of molecular biology is the nearuniversal nature of the genetic code. Although some organisms show slight variations in the amino acids assigned to particular codons, the code is always read three bases at a time and in the same direction. Despite their enormo ...
Alternative Splicing: How to Get More than One Protein from a Gene
... Description: Use the word key from the “Protein Synthesis and Words” activity to demonstrate how eukaryotic cells may use one DNA sequence to code for multiple proteins. Eukaryotic cells might use the same gene or DNA sequence differently depending on where the gene is located. A brain cell might ma ...
... Description: Use the word key from the “Protein Synthesis and Words” activity to demonstrate how eukaryotic cells may use one DNA sequence to code for multiple proteins. Eukaryotic cells might use the same gene or DNA sequence differently depending on where the gene is located. A brain cell might ma ...
[PDF]
... reduced its expression, suppressed the mild rough eye phenotype. The loss-of-function model revealed that dFmr1 regulates synaptic plasticity because the absence of dFmr1 results in pronounced synaptic overgrowth at the neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) of Drosophila larvae; this is reminiscent of the ...
... reduced its expression, suppressed the mild rough eye phenotype. The loss-of-function model revealed that dFmr1 regulates synaptic plasticity because the absence of dFmr1 results in pronounced synaptic overgrowth at the neuromuscular junctions (NMJs) of Drosophila larvae; this is reminiscent of the ...
Determining the nucleotide sequence and capsid
... the 30 part of the genome [20]. The N-terminal region of the APV capsid protein precursor is encoded in the downstream region of the nonstructural protein gene in the same reading frame, but the C-terminal region of the precursor is encoded in a different reading frame, suggesting that a frame-shift ...
... the 30 part of the genome [20]. The N-terminal region of the APV capsid protein precursor is encoded in the downstream region of the nonstructural protein gene in the same reading frame, but the C-terminal region of the precursor is encoded in a different reading frame, suggesting that a frame-shift ...
Preparation of MyoD mRNA for the differentiation of stem cells into
... be affected by small pieces of RNAs, it can also be affected by long noncoding RNA pieces. In human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is found to participate in very important roles in the differentiation of MSCs6. Other than siRNAs, miRNAs and lncRNAs, mRNAs c ...
... be affected by small pieces of RNAs, it can also be affected by long noncoding RNA pieces. In human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is found to participate in very important roles in the differentiation of MSCs6. Other than siRNAs, miRNAs and lncRNAs, mRNAs c ...
The Molecules of Life Biochem! - Belle Vernon Area School District
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
... R group (thus the amino acids) are classified according to several criteria (two very important) Polar or nonpolar nature of the side chain Presence of an acidic or basic group in the side chain ...
Lecture3- Molecular Biology-1(2013).
... tRNA (transfer RNA) Function: Translation process (from mRNA to protein synthesis) It transfers amino acids to the growing protein chain ...
... tRNA (transfer RNA) Function: Translation process (from mRNA to protein synthesis) It transfers amino acids to the growing protein chain ...
Lecture4 Biol302 Spring2012
... The code is nonoverlapping, with each nucleotide part of a single codon, degenerate, with most amino acids specified by two to four codons, and ordered, with similar amino acids specified by related codons. The genetic code is nearly universal; with minor exceptions, the 64 triplets have the same ...
... The code is nonoverlapping, with each nucleotide part of a single codon, degenerate, with most amino acids specified by two to four codons, and ordered, with similar amino acids specified by related codons. The genetic code is nearly universal; with minor exceptions, the 64 triplets have the same ...
Translation: A Four
... • There are two sites in the 70S ribosome: the "P" site and the "A" site. • The "P" site is the peptidyl site and contains the growing peptide chain. • By convention, this site is on the left-hand side of the 70S ribosome. • The "A" site is the acyl site. • This latter site contains the charged (a ...
... • There are two sites in the 70S ribosome: the "P" site and the "A" site. • The "P" site is the peptidyl site and contains the growing peptide chain. • By convention, this site is on the left-hand side of the 70S ribosome. • The "A" site is the acyl site. • This latter site contains the charged (a ...
Chapter 12 Translation and the Genetic Code
... The code is nonoverlapping, with each nucleotide part of a single codon, degenerate, with most amino acids specified by two to four codons, and ordered, with similar amino acids specified by related codons. The genetic code is nearly universal; with minor exceptions, the 64 triplets have the same ...
... The code is nonoverlapping, with each nucleotide part of a single codon, degenerate, with most amino acids specified by two to four codons, and ordered, with similar amino acids specified by related codons. The genetic code is nearly universal; with minor exceptions, the 64 triplets have the same ...
Molecular Beacon Product Sheet
... variations. As with most natural molecules these are prone to degradation under normal conditions, specifically once introduced in body fluids. Ubiquitous nucleases well as chemical instability lead to fast degradation with a finite half life. The premise of this product guide is to discuss various ...
... variations. As with most natural molecules these are prone to degradation under normal conditions, specifically once introduced in body fluids. Ubiquitous nucleases well as chemical instability lead to fast degradation with a finite half life. The premise of this product guide is to discuss various ...
RNA Interference Regulates Gene Action
... revealed a completely unsuspected phenomenon, one of the most remarkable discoveries of modern biology. Andrew Fire and Craig Mello (who were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2006) found, with their colleagues, neither sense nor antisense RNA alone was responsible, but both were needed. The in vitro trans ...
... revealed a completely unsuspected phenomenon, one of the most remarkable discoveries of modern biology. Andrew Fire and Craig Mello (who were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2006) found, with their colleagues, neither sense nor antisense RNA alone was responsible, but both were needed. The in vitro trans ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.













![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008788915_1-f65e05630af3e539aeba5f249bd12110-300x300.png)








