Roman_republic_notes
... Start of a new Roman Government Romans rebel against cruel king in 509 B.C.E. Etruscan kings were accused of crimes and expelled. Law allowing anyone plotting to be king to be killed on the spot. ...
... Start of a new Roman Government Romans rebel against cruel king in 509 B.C.E. Etruscan kings were accused of crimes and expelled. Law allowing anyone plotting to be king to be killed on the spot. ...
Roman Republic
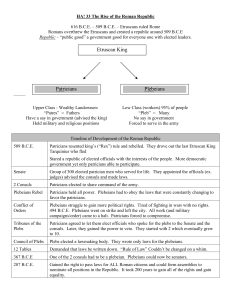
... 509 B.C.E. Rome = small city Slowly expands. 338 B.C.E. defeat the other Latins 284 B.C.E. defeat Etruscans 267 B.C.E. defeat the Greeks The Republic is growing ...
... 509 B.C.E. Rome = small city Slowly expands. 338 B.C.E. defeat the other Latins 284 B.C.E. defeat Etruscans 267 B.C.E. defeat the Greeks The Republic is growing ...
Roman Republic
... 509 B.C.E. Rome = small city Slowly expands. 338 B.C.E. defeat the other Latins 284 B.C.E. defeat Etruscans 267 B.C.E. defeat the Greeks The Republic is growing ...
... 509 B.C.E. Rome = small city Slowly expands. 338 B.C.E. defeat the other Latins 284 B.C.E. defeat Etruscans 267 B.C.E. defeat the Greeks The Republic is growing ...
Government of Rome - History on the Net
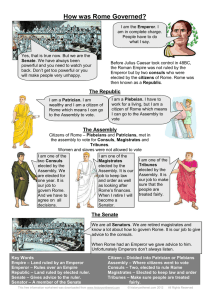
... We are all Senators. We are retired magistrates and know a lot about how to govern Rome. It is our job to give advice to the consuls. When Rome had an Emperor we gave advice to him. Unfortunately Emperors don’t always listen. ...
... We are all Senators. We are retired magistrates and know a lot about how to govern Rome. It is our job to give advice to the consuls. When Rome had an Emperor we gave advice to him. Unfortunately Emperors don’t always listen. ...
42 Roman Republic
... 509 B.C.E. Rome = small city Slowly expands. 338 B.C.E. defeat the other Latins 284 B.C.E. defeat Etruscans 267 B.C.E. defeat the Greeks The Republic is growing ...
... 509 B.C.E. Rome = small city Slowly expands. 338 B.C.E. defeat the other Latins 284 B.C.E. defeat Etruscans 267 B.C.E. defeat the Greeks The Republic is growing ...
Rome`s Rise to Power - Oakton Community College
... Magistrates ◦ Two magistrates served as consuls. These replace the king. ...
... Magistrates ◦ Two magistrates served as consuls. These replace the king. ...
Roman Hist
... 2. Major sentences--right of appeal to the Centuriate Assembly C. 445B.C.E.: Centuriate Assembly formed (army in assembly) date ??--probably earlier Rep = hoplite/phalanx army in Assembly, but its actions were subject to consent of the Senate. D. 2nd secession: 449 B.C. Centuriate Assembly--all male ...
... 2. Major sentences--right of appeal to the Centuriate Assembly C. 445B.C.E.: Centuriate Assembly formed (army in assembly) date ??--probably earlier Rep = hoplite/phalanx army in Assembly, but its actions were subject to consent of the Senate. D. 2nd secession: 449 B.C. Centuriate Assembly--all male ...
Roman Hist
... Rep = hoplite/phalanx army in Assembly, but its actions were subject to consent of the Senate. D. 2nd secession: 449 B.C. Centuriate Assembly--all male citizens, by centuries (100s)--classified men by wealth/property, a military muster evolved into a regular assembly **imp. change: based on property ...
... Rep = hoplite/phalanx army in Assembly, but its actions were subject to consent of the Senate. D. 2nd secession: 449 B.C. Centuriate Assembly--all male citizens, by centuries (100s)--classified men by wealth/property, a military muster evolved into a regular assembly **imp. change: based on property ...
The Foundations of Rome
... ^^ This way, judges could not make decisions based on opinions or secret laws. ...
... ^^ This way, judges could not make decisions based on opinions or secret laws. ...
The Greek City States
... • The plebeians began to demand for more rights and threatened to start their own city. This frightened the patricians, who were afraid of losing the labor of the plebeians. •Their walkout led to the creation of tribunes or officials who were elected to protect the interests of the plebeians. There ...
... • The plebeians began to demand for more rights and threatened to start their own city. This frightened the patricians, who were afraid of losing the labor of the plebeians. •Their walkout led to the creation of tribunes or officials who were elected to protect the interests of the plebeians. There ...
Patricians Plebeians Etruscan King
... 2 *consuls—chief magistrates who presided over the Senate and assemblies, administered legislation, served as generals in military campaigns, and represented Rome in foreign affairs. Consuls could appoint and/or serve as *dictator for up to 6 months in times of emergency. When their term of office w ...
... 2 *consuls—chief magistrates who presided over the Senate and assemblies, administered legislation, served as generals in military campaigns, and represented Rome in foreign affairs. Consuls could appoint and/or serve as *dictator for up to 6 months in times of emergency. When their term of office w ...
Roman Republic - Baylor School
... ladder, hopefully all the way to Consul, following what was known as the Cursus Honorum or “path of offices.” ...
... ladder, hopefully all the way to Consul, following what was known as the Cursus Honorum or “path of offices.” ...
Rome`s Republic and Its Evolution
... Reform… – Fearing military attack from their neighbors, the Patricians agreed to let the Plebeians elect officials called TRIBUNES. • The TRIBUNES, at first 2, spoke to the Senate and the consuls. – Plebeians could also elect the COUNCIL OF PLEBS. • The council made laws only for the plebeians. – W ...
... Reform… – Fearing military attack from their neighbors, the Patricians agreed to let the Plebeians elect officials called TRIBUNES. • The TRIBUNES, at first 2, spoke to the Senate and the consuls. – Plebeians could also elect the COUNCIL OF PLEBS. • The council made laws only for the plebeians. – W ...
Rome Vocab Answers - Republic Quiz
... Define and explain each term by finding it in your text. NO INTERNET – write the number of the page it’s found on. Page Number: Term: 1. _______ Etruscans A cultural group of people who had settled most of Italy before Latin (Roman) society fully developed. The Etruscans ruled Latium (the larger reg ...
... Define and explain each term by finding it in your text. NO INTERNET – write the number of the page it’s found on. Page Number: Term: 1. _______ Etruscans A cultural group of people who had settled most of Italy before Latin (Roman) society fully developed. The Etruscans ruled Latium (the larger reg ...
The Roman Republic
... • Early kings of Rome – Not much is known as their written works did not survive – Who were they? • Most developed Latin/Italic people • Located in northern, central Italy • Most likely descendants of modern-day Turkey and native Italian population • By 6th century BCE they were the most powerfu ...
... • Early kings of Rome – Not much is known as their written works did not survive – Who were they? • Most developed Latin/Italic people • Located in northern, central Italy • Most likely descendants of modern-day Turkey and native Italian population • By 6th century BCE they were the most powerfu ...
1. The Etruscans ruled Rome between 616 and 509 B.C.E. 2. The
... of the two Roman consuls was required to be a plebeian. In 287 B.C.E., plebeian assemblies could pass laws for all Roman citizens and could nominate consuls, tribunes, and members of the Senate. 3. Other countries adopted the following characteristics from the Roman Republic: a written constitution ...
... of the two Roman consuls was required to be a plebeian. In 287 B.C.E., plebeian assemblies could pass laws for all Roman citizens and could nominate consuls, tribunes, and members of the Senate. 3. Other countries adopted the following characteristics from the Roman Republic: a written constitution ...
Early Roman History
... vi. What other two functions were based on this property classification? ...
... vi. What other two functions were based on this property classification? ...
Conquest of Italy
... I - Equites (knights) = 18 Centuries = 18 votes 100,000 asses + = 82 Centuries = 82 votes II - 75,000-100,000 asses = 20 Centuries = 20 votes III - 50,000-75,000 asses = 20 Centuries = 20 votes IV - 25,000-50,000 asses = 20 Centuries = 20 votes V - 11,000-25,000 asses = 32 Centuries = 32 votes Under ...
... I - Equites (knights) = 18 Centuries = 18 votes 100,000 asses + = 82 Centuries = 82 votes II - 75,000-100,000 asses = 20 Centuries = 20 votes III - 50,000-75,000 asses = 20 Centuries = 20 votes IV - 25,000-50,000 asses = 20 Centuries = 20 votes V - 11,000-25,000 asses = 32 Centuries = 32 votes Under ...
The Patricians and the Plebeians
... elected senators to serve their interests. Senate is derived from a term meaning elder, because the Roman Senate consisted of the oldest and wisest of the patricians. The senate selected two people to rule together in place of the Etruscan king. The new patrician rulers were known as consuls. The pl ...
... elected senators to serve their interests. Senate is derived from a term meaning elder, because the Roman Senate consisted of the oldest and wisest of the patricians. The senate selected two people to rule together in place of the Etruscan king. The new patrician rulers were known as consuls. The pl ...
The Patricians and the Plebeians
... elected senators to serve their interests. Senate is derived from a term meaning elder, because the Roman Senate consisted of the oldest and wisest of the patricians. The senate selected two people to rule together in place of the Etruscan king. The new patrician rulers were known as consuls. The pl ...
... elected senators to serve their interests. Senate is derived from a term meaning elder, because the Roman Senate consisted of the oldest and wisest of the patricians. The senate selected two people to rule together in place of the Etruscan king. The new patrician rulers were known as consuls. The pl ...
Roman tribe

A tribus, or tribe, was a division of the Roman people, constituting the voting units of a legislative assembly of the Roman Republic. The word is probably derived from tribuere, to divide or distribute; a connection with tres, three, is doubtful.According to tradition, the first three tribes were established by Romulus; originally these were the voting units of the comitia curiata, but from an early date they were superseded by their own subdivisions, the thirty curiae, or wards. The original Romulean tribes gradually vanished from history.Perhaps influenced by the original division of the people into tribes, as well as the number of thirty wards, Servius Tullius established thirty new tribes, constituting the comitia tributa. This number was reduced to twenty at the beginning of the Roman Republic; but as the Roman population and its territory grew, fifteen additional tribes were enrolled, the last in 241 BC.All Roman citizens were enrolled in one of these tribes, through which they were entitled to vote on the election of certain magistrates, religious officials, judicial decisions in certain suits affecting the plebs, and pass resolutions on various proposals made by the tribunes of the plebs and the higher magistrates. Although the comitia tributa lost most of its legislative functions under the Empire, enrollment in a tribe remained an important part of Roman citizenship until at least the third century AD.