Slide 1
... IMPORTANT: Remember when dealing with probability, predictions of possible outcomes are usually realized only with large sample sizes. Any deviation from the predicted ratio in small sample sizes is attributed to chance. ...
... IMPORTANT: Remember when dealing with probability, predictions of possible outcomes are usually realized only with large sample sizes. Any deviation from the predicted ratio in small sample sizes is attributed to chance. ...
6. DNA transcription/translation
... E. coli and more than 130 repair enzymes identified in humans. A hereditary defect in one of these enzymes is associated with a form of colon cancer. ...
... E. coli and more than 130 repair enzymes identified in humans. A hereditary defect in one of these enzymes is associated with a form of colon cancer. ...
Chapter 10 Notes
... a. Codon recognition: The anticodon of an incoming tRNA molecule, carrying its amino acid, pairs with the mRNA codon in the A site of the ribosome. b. Peptide bond formation: The new amino acid is joined to the chain. c. Translocation: tRNA is released from the P site and the ribosome moves tRNA fro ...
... a. Codon recognition: The anticodon of an incoming tRNA molecule, carrying its amino acid, pairs with the mRNA codon in the A site of the ribosome. b. Peptide bond formation: The new amino acid is joined to the chain. c. Translocation: tRNA is released from the P site and the ribosome moves tRNA fro ...
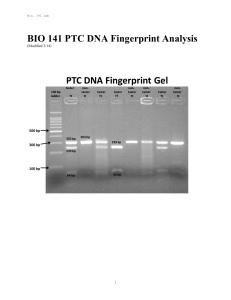
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
... DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the blueprint for that individual. Of the approximately 3.3 b ...
as a PDF
... heterodimeric sc mutants The results of the gel-®ltration experiments of the free enzymes and the DNA-binding assays performed under non-catalytic conditions both suggest that the sc enzyme is in the predicted conformation (Figure 1(b)) and the subunits of the sc enzyme interact in the same way as i ...
... heterodimeric sc mutants The results of the gel-®ltration experiments of the free enzymes and the DNA-binding assays performed under non-catalytic conditions both suggest that the sc enzyme is in the predicted conformation (Figure 1(b)) and the subunits of the sc enzyme interact in the same way as i ...
Chap 12 Jeopardy #2 - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... When lactose is present and glucose is not, what molecule binds to the repressor protein to turn on the lac operon? A: lactose binds to the repressor and keeps it away from the operator S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
... When lactose is present and glucose is not, what molecule binds to the repressor protein to turn on the lac operon? A: lactose binds to the repressor and keeps it away from the operator S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
•MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
... Transposable (mobile) DNA: non-coding region, repeat, evolutionary DNA must be contend: human cell has 2 meters DNA!!!!!SO must be highly compacted In eukaryotes, DNA + protein → chromatin → chromosome histone ...
... Transposable (mobile) DNA: non-coding region, repeat, evolutionary DNA must be contend: human cell has 2 meters DNA!!!!!SO must be highly compacted In eukaryotes, DNA + protein → chromatin → chromosome histone ...
2.4 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... –At end of gene, RNA polymerase encounters the termination sequence to create loops at the end of RNA so RNA polymerase and newly formed strand of RNA are released from DNA molecule –RNA strand is called a messenger RNA (mRNA) –Multiple copies of mRNA are transcribed from each gene during ...
... –At end of gene, RNA polymerase encounters the termination sequence to create loops at the end of RNA so RNA polymerase and newly formed strand of RNA are released from DNA molecule –RNA strand is called a messenger RNA (mRNA) –Multiple copies of mRNA are transcribed from each gene during ...
Lecture 7 - School of Science and Technology
... • As size of genomes varies dramatically from 10,000 bp for simple viruses up to several billion bp in higher animals and plants, the number of sequences covering the whole genome also varies very significantly 10 – 106. • DNA fragments presented in DB have not only very different lengths but also d ...
... • As size of genomes varies dramatically from 10,000 bp for simple viruses up to several billion bp in higher animals and plants, the number of sequences covering the whole genome also varies very significantly 10 – 106. • DNA fragments presented in DB have not only very different lengths but also d ...
PS 4 answers
... PCR, restriction enzyme digests, and agarose gels is to test samples of human cells such as blood cells to identify people for forensic analysis or paternity testing. This problem is designed to show you how this type of analysis, called DNA fingerprinting, can be used to determine paternity. There ...
... PCR, restriction enzyme digests, and agarose gels is to test samples of human cells such as blood cells to identify people for forensic analysis or paternity testing. This problem is designed to show you how this type of analysis, called DNA fingerprinting, can be used to determine paternity. There ...
Quantitating Maxwell® Extracted DNA Samples Using the
... is important to know the exact amount of input DNA, so adding an accurate DNA quantitation step prior to downstream analysis is desirable. ...
... is important to know the exact amount of input DNA, so adding an accurate DNA quantitation step prior to downstream analysis is desirable. ...
Notes to Students:
... RNA processing questions (each question worth a total of 2 points; questions #4-5, each part worth one point) 1. Which answer best describes RNA processing? a. the process by which RNA is assembled from a DNA template b. the attraction of a binding protein and other transcription factors to tell the ...
... RNA processing questions (each question worth a total of 2 points; questions #4-5, each part worth one point) 1. Which answer best describes RNA processing? a. the process by which RNA is assembled from a DNA template b. the attraction of a binding protein and other transcription factors to tell the ...
CHAPTER 10 TEST REVIEW - Hudson City School District
... #6 What does it mean for DNA… • To be anti-parallel? • The two strands run side by side in opposite directions (one has 5’ at top and the other has 3’ at top) ...
... #6 What does it mean for DNA… • To be anti-parallel? • The two strands run side by side in opposite directions (one has 5’ at top and the other has 3’ at top) ...
High-Efficiency DNA Separation by Capillary Electrophoresis in a
... MDNA is the DNA fragment length in base pairs, b is the contour length of one DNA base pair, and β and γ are constants related to the polymer and buffer. Since we were unable to find the L value of HPMC-5, we were not able to use the fully functional form of eq 1. But since L, MDNA, b, β, and γ are ...
... MDNA is the DNA fragment length in base pairs, b is the contour length of one DNA base pair, and β and γ are constants related to the polymer and buffer. Since we were unable to find the L value of HPMC-5, we were not able to use the fully functional form of eq 1. But since L, MDNA, b, β, and γ are ...
Simulation of Gene Splicing (Genetic Engineering
... hormone. In the l950's, it was found that hormone from the pituitaries of dead people could be used as a treatment. However, not enough people donated their glands to supply hormone for all those who needed it. Even more sadly, some of the pituitaries used for this purpose contained a deadly virus. ...
... hormone. In the l950's, it was found that hormone from the pituitaries of dead people could be used as a treatment. However, not enough people donated their glands to supply hormone for all those who needed it. Even more sadly, some of the pituitaries used for this purpose contained a deadly virus. ...
Heredity - lrobards
... single amino acid in the hemoglobin protein of red blood cells, leaving hemoglobin less able to carry oxygen and also causing the hemoglobin to deform to a sickle shape when the oxygen content of the blood is low. Phenylketonuria: an autosomal recessive disease caused by a single gene defect that ...
... single amino acid in the hemoglobin protein of red blood cells, leaving hemoglobin less able to carry oxygen and also causing the hemoglobin to deform to a sickle shape when the oxygen content of the blood is low. Phenylketonuria: an autosomal recessive disease caused by a single gene defect that ...
BIOD19H3 Epigenetics in Health and Disease Professor: Winter 2015
... 16. Fischer A, Sananbenesi F, Wang X, Dobbin M, Tsai LH. Recovery of learning and memory is associated with chromatin remodelling. Nature 2007;447:178–182. [PubMed: 17468743] Rodent study showing that environmental enrichment increases histone acetylation in the hippocampus. Histone deacetylase inhi ...
... 16. Fischer A, Sananbenesi F, Wang X, Dobbin M, Tsai LH. Recovery of learning and memory is associated with chromatin remodelling. Nature 2007;447:178–182. [PubMed: 17468743] Rodent study showing that environmental enrichment increases histone acetylation in the hippocampus. Histone deacetylase inhi ...
microarray activity - Blue Valley Schools
... technology is based on the basic chemistry of DNA. Adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. This base complementarity is what allows DNA from cells to bind specifically to known DNA sequences (probes) on a chip. Since a cell expresses hundreds or even thousands of genes at any giv ...
... technology is based on the basic chemistry of DNA. Adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. This base complementarity is what allows DNA from cells to bind specifically to known DNA sequences (probes) on a chip. Since a cell expresses hundreds or even thousands of genes at any giv ...
Bioreg2017_Replication1_V3
... H-bonding (binding energetics) Outside the active site, unpaired nucleotides are H-bonded to H2O. Inside the active site these H-bonds can be replaced by WC base pairing but only incompletely replaced by mismatch pairing ...
... H-bonding (binding energetics) Outside the active site, unpaired nucleotides are H-bonded to H2O. Inside the active site these H-bonds can be replaced by WC base pairing but only incompletely replaced by mismatch pairing ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.