Targeting the GAA-Repeat Region with Oligonucleotides for the
... undertook genome-wide analyses to examine the global and local RNA species and chromatin structure and composition changes in FRDA patient cells. Epigenetic screens identified two chromatin modifying complexes as being important in establishing and/or maintaining repeat expansion-induced transcripti ...
... undertook genome-wide analyses to examine the global and local RNA species and chromatin structure and composition changes in FRDA patient cells. Epigenetic screens identified two chromatin modifying complexes as being important in establishing and/or maintaining repeat expansion-induced transcripti ...
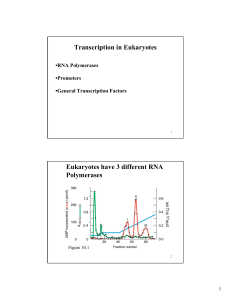
Transcription in Eukaryotes Eukaryotes have 3 different RNA
... •TAFIIs attach to TBP and extend binding of TFIID beyond TATA box in some promoters • TAFIIs can bind initiator and downstream elements; TAFIIs help initiate transcription from promoters initiators and DPEs •Specifically, TAFII150 and TAFII250 form a ternary complex with TBP and bind to the initiato ...
... •TAFIIs attach to TBP and extend binding of TFIID beyond TATA box in some promoters • TAFIIs can bind initiator and downstream elements; TAFIIs help initiate transcription from promoters initiators and DPEs •Specifically, TAFII150 and TAFII250 form a ternary complex with TBP and bind to the initiato ...
Slide 1 - SCHOOLinSITES
... • NTPs pair with antisense strand and polymerization of the mRNA occurs • Portion of transcription known as elongation ...
... • NTPs pair with antisense strand and polymerization of the mRNA occurs • Portion of transcription known as elongation ...
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction What exactly is a Virus?
... maintain homeostasis in any way **It’s hard to “kill” something that’s not really alive, so antibiotics that kill bacteria, fungi, etc, do NOT harm viruses** ...
... maintain homeostasis in any way **It’s hard to “kill” something that’s not really alive, so antibiotics that kill bacteria, fungi, etc, do NOT harm viruses** ...
Insights from the HuR-interacting transcriptome: ncRNAs, ubiquitin
... interacting RNAs. They found that the structures in HuR-positive RNAs may recognize specific fragment which has adenine and uridine bases in a locally less stable RNA duplex. Using Gene Ontology (GO) analysis, the authors showed extensive concentration of Ubiquitin Pathway genes among the HuR-positi ...
... interacting RNAs. They found that the structures in HuR-positive RNAs may recognize specific fragment which has adenine and uridine bases in a locally less stable RNA duplex. Using Gene Ontology (GO) analysis, the authors showed extensive concentration of Ubiquitin Pathway genes among the HuR-positi ...
Poster Patrocles_V3
... Using positional cloning, we have recently identified the mutation responsible for muscular phenotype of the Texel sheep. It is located in the 3’UTR of the GDF8 gene - a known developmental repressor of muscle growth - and creates an illegitimate target site for miRNA expressed in the same tissue. T ...
... Using positional cloning, we have recently identified the mutation responsible for muscular phenotype of the Texel sheep. It is located in the 3’UTR of the GDF8 gene - a known developmental repressor of muscle growth - and creates an illegitimate target site for miRNA expressed in the same tissue. T ...
Section 8.4: DNA Transcription
... • Transcription makes several types of RNA, the three that concern us are: – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein (made by transcription of DNA). – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino a ...
... • Transcription makes several types of RNA, the three that concern us are: – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein (made by transcription of DNA). – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino a ...
Transcription AND Translation
... • Before RNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons join together to form one strand: a “continuous coding sequence,” which makes up the mRNA molecule. (page 182) • This process is known as RNA splicing. The mRNA is now ready for translation. ...
... • Before RNA leaves the nucleus, the introns are removed and the exons join together to form one strand: a “continuous coding sequence,” which makes up the mRNA molecule. (page 182) • This process is known as RNA splicing. The mRNA is now ready for translation. ...
Lectures by Erin Barley Kathleen Fitzpatrick From Gene to Protein
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA (RNA processing) before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ends of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are cut out, and the other parts splice ...
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA (RNA processing) before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ends of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are cut out, and the other parts splice ...
DNA sequence of a genome determine phenotype through control of
... polypeptides to form mRNA-directed protein synthesizing machines called “ribosomes” Ø tRNA are modified and become the agents that deliver the correct AA to the growing polypeptide during translation R. Ward: Spring 2001 ...
... polypeptides to form mRNA-directed protein synthesizing machines called “ribosomes” Ø tRNA are modified and become the agents that deliver the correct AA to the growing polypeptide during translation R. Ward: Spring 2001 ...
Ensembl
... scRNA (small cytoplasmic) snRNA (small nuclear) snoRNA (small nucleolar) miRNA (microRNA) 28 of 32 ...
... scRNA (small cytoplasmic) snRNA (small nuclear) snoRNA (small nucleolar) miRNA (microRNA) 28 of 32 ...
Conceptual Translation as a part of Gene Expression
... (DNA) into protein products; RNA acts as a messenger between DNA and the protein synthesis complexes known as ribosomes, forms vital portions of ribosomes, and acts as an essential carrier molecule for amino acids to be used in protein synthesis. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few impo ...
... (DNA) into protein products; RNA acts as a messenger between DNA and the protein synthesis complexes known as ribosomes, forms vital portions of ribosomes, and acts as an essential carrier molecule for amino acids to be used in protein synthesis. RNA is very similar to DNA, but differs in a few impo ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... (a) Differential Removal of Introns This can produce variations in the mRNA produced. Different mRNA may have different introns removed. Differential removal of introns enables a gene to code for more than one different protein. An average human gene is thought to code for 3 different proteins. For ...
... (a) Differential Removal of Introns This can produce variations in the mRNA produced. Different mRNA may have different introns removed. Differential removal of introns enables a gene to code for more than one different protein. An average human gene is thought to code for 3 different proteins. For ...
7.3 Protein Synthesis
... Which gene is read on the DNA? • Promoter region – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
... Which gene is read on the DNA? • Promoter region – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
Protein Synthesis 2013
... Which gene is read on the DNA? • Promoter region – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
... Which gene is read on the DNA? • Promoter region – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 2 Questions Multiple
... become a ____3_____. If duplication occurs at the genome level, the ______3______ will often be located close to the parent gene. It may contain copies of the full length sequence of the parent gene (including the promoter, exons, and introns), and is known as a ____4_____ _____3______ . Sometimes, ...
... become a ____3_____. If duplication occurs at the genome level, the ______3______ will often be located close to the parent gene. It may contain copies of the full length sequence of the parent gene (including the promoter, exons, and introns), and is known as a ____4_____ _____3______ . Sometimes, ...
GOBASE—a database of organelle and bacterial
... The GOBASE interface contains PHP query interface pages corresponding to the classes of biological entity represented within the GOBASE database: these are Gene, Gene&ProductClass, Sequence, Protein, Exon, Intron, RNA, RNAStructure, Taxonomy, Map and GeneDistribution. Since release 8.1 (October 2003 ...
... The GOBASE interface contains PHP query interface pages corresponding to the classes of biological entity represented within the GOBASE database: these are Gene, Gene&ProductClass, Sequence, Protein, Exon, Intron, RNA, RNAStructure, Taxonomy, Map and GeneDistribution. Since release 8.1 (October 2003 ...
Protein synthesis ppt
... After subtracting start and stop codons, the remaining 60 codons code for 19 different amino acids. This means that many amino acids have more than one codon. Thus the code is redundant. However, the code is not ambiguous. Each codon is assigned only one amino acid. Except for a few very min ...
... After subtracting start and stop codons, the remaining 60 codons code for 19 different amino acids. This means that many amino acids have more than one codon. Thus the code is redundant. However, the code is not ambiguous. Each codon is assigned only one amino acid. Except for a few very min ...
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... relies on histone modifications and DNA methylation. Active chromatin regions usually contain high rate of acetylated histones and unmethylated DNA whereas inactive regions are associated with nonacetylated histones and methylated DNA. Histone modifications and DNA methylation constitute the base of ...
... relies on histone modifications and DNA methylation. Active chromatin regions usually contain high rate of acetylated histones and unmethylated DNA whereas inactive regions are associated with nonacetylated histones and methylated DNA. Histone modifications and DNA methylation constitute the base of ...
Transcription
... Transcription requires an enzyme known as RNA polymerase that is similar to DNA polymerase. During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. ...
... Transcription requires an enzyme known as RNA polymerase that is similar to DNA polymerase. During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. ...
Access Slides
... Recent structural studies have provided Information about the Pol II-based eukaryotic transcription machinery and about Mediator, the complex involved in transcription regulation during initiation. We will discuss the current model concerning the possible mechanisms of transcription initiation and r ...
... Recent structural studies have provided Information about the Pol II-based eukaryotic transcription machinery and about Mediator, the complex involved in transcription regulation during initiation. We will discuss the current model concerning the possible mechanisms of transcription initiation and r ...
Pathway Methods - people.vcu.edu
... changes in gene expression • Organize expression (or other) changes into meaningful ‘chunks’ (themes) • Identify crucial points in process where intervention could make a difference • Why? Biology is Redundant! Often sets of genes doing related functions are changed ...
... changes in gene expression • Organize expression (or other) changes into meaningful ‘chunks’ (themes) • Identify crucial points in process where intervention could make a difference • Why? Biology is Redundant! Often sets of genes doing related functions are changed ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.