embj201284303-sup-0001-SupportingInformation
... Figure S5: Specificity of anti-PROPEP3 antibodies and functionality of PROPEP3-Venus. (A) Synthesized peptides (3 µl) were blotted to the membranes at the indicated concentrations and then probed with anti-PROPEP3 antibodies. (B) Nicotiana benthamiana leaves transiently expressing 19K, Venus, or PR ...
... Figure S5: Specificity of anti-PROPEP3 antibodies and functionality of PROPEP3-Venus. (A) Synthesized peptides (3 µl) were blotted to the membranes at the indicated concentrations and then probed with anti-PROPEP3 antibodies. (B) Nicotiana benthamiana leaves transiently expressing 19K, Venus, or PR ...
Bio1A Unit 2-7 Gene Expression Pt 1 Notes File
... • Bacteria can digest lactose - requires proteins / enzymes. i.e. – β-galactosidase • Bacteria will not produce lactose metabolic enzyme unless needed Lactose present • If lactose is absent enzyme are not made in order to conserve energy No β-gal • Bacteria prefer Glucose (fewer enzymatic steps ...
... • Bacteria can digest lactose - requires proteins / enzymes. i.e. – β-galactosidase • Bacteria will not produce lactose metabolic enzyme unless needed Lactose present • If lactose is absent enzyme are not made in order to conserve energy No β-gal • Bacteria prefer Glucose (fewer enzymatic steps ...
Genes and RNA
... amino acid chain of a protein. Ribosomes are composed of several types of rRNA and about 100 different proteins. As in the case of tRNA, the rRNAs are general translational components that can be used to translate the mRNA of any protein-coding gene. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a. 03-04 prof S. ...
... amino acid chain of a protein. Ribosomes are composed of several types of rRNA and about 100 different proteins. As in the case of tRNA, the rRNAs are general translational components that can be used to translate the mRNA of any protein-coding gene. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a. 03-04 prof S. ...
Recombinant human RNA polymerase II CTD repeat
... DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Largest and catalytic component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Forms the polymerase active center together ...
... DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Largest and catalytic component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Forms the polymerase active center together ...
RNAi phenotypes are influenced by the genetic background of the
... which cuts the long dsRNA into 21mers. These are loaded into the destruction complex (RISC complex), which is guided by the single stranded small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to mRNAs with complementary sequence. The Argonaute protein as part of the RISC complex eventually cuts the mRNAs within the reg ...
... which cuts the long dsRNA into 21mers. These are loaded into the destruction complex (RISC complex), which is guided by the single stranded small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to mRNAs with complementary sequence. The Argonaute protein as part of the RISC complex eventually cuts the mRNAs within the reg ...
nuclear structure (2): the nucleolus
... (2) The black “dots” on the DNA (at the bottom of each “branch”) are the RNA polymerase molecules. (3) The “branches” are the nascent 45S rRNA molecules. (4) At various locations along each “branch” (each nascent 45S rRNA molecule) are black dots. These are places where proteins have bound. (5) The ...
... (2) The black “dots” on the DNA (at the bottom of each “branch”) are the RNA polymerase molecules. (3) The “branches” are the nascent 45S rRNA molecules. (4) At various locations along each “branch” (each nascent 45S rRNA molecule) are black dots. These are places where proteins have bound. (5) The ...
Improving Intergenic miRNA Target Genes Prediction
... to play important roles in gene regulation. It’s a short (21- to 23-nt) RNAs that bind to the 3′ untranslated regions (3′ UTRs) of target genes. ...
... to play important roles in gene regulation. It’s a short (21- to 23-nt) RNAs that bind to the 3′ untranslated regions (3′ UTRs) of target genes. ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA, functioning as the hereditary
... DNA, functioning as the hereditary material, ultimately determines the traits of an individual. The idea that this one type of molecule can play such a singular role in determining our characteristics is remarkable. What is still more amazing is the manner in which DNA affects these traits. DNA func ...
... DNA, functioning as the hereditary material, ultimately determines the traits of an individual. The idea that this one type of molecule can play such a singular role in determining our characteristics is remarkable. What is still more amazing is the manner in which DNA affects these traits. DNA func ...
Protein Synthesis
... Definition - A linear polymer of amino acids linked together in a specific order or sequence. Formed in the process known as translation. B. Translation ...
... Definition - A linear polymer of amino acids linked together in a specific order or sequence. Formed in the process known as translation. B. Translation ...
The Family of MADS – Box Genes Controlling Flower Development
... Three AP1-, Five PI-, two AP3-, two AG- and two SEP-like MADS Box genes were isolated from Crocus sativus L. The sequence alignment revealed that the five CsPI proteins contain the typical domain structure of plant MADS box proteins consisted of the conserved N-terminal MADS-box, the I domain, the c ...
... Three AP1-, Five PI-, two AP3-, two AG- and two SEP-like MADS Box genes were isolated from Crocus sativus L. The sequence alignment revealed that the five CsPI proteins contain the typical domain structure of plant MADS box proteins consisted of the conserved N-terminal MADS-box, the I domain, the c ...
Sookie, a student in Genetics 200A, is a little too obsessed with
... 4. Assuming that silencing of a ura4+ gene that is placed outside of heterochromatin means that there has been a lateral spread of heterochromatin outside of its normal boundaries, suggest a hypothesis (or two) for what might be the molecular cause of fission yeast vampirism. Many possible correct a ...
... 4. Assuming that silencing of a ura4+ gene that is placed outside of heterochromatin means that there has been a lateral spread of heterochromatin outside of its normal boundaries, suggest a hypothesis (or two) for what might be the molecular cause of fission yeast vampirism. Many possible correct a ...
mRNA and protein abundance for glutathione-S
... Comprehensive identification of all functional elements encoded in the human genome is a fundamental need in biomedical research. Here, we present a comparative analysis of the human, mouse, rat and dog genomes to create a systematic catalogue of common regulatory motifs in promoters and 3' untransl ...
... Comprehensive identification of all functional elements encoded in the human genome is a fundamental need in biomedical research. Here, we present a comparative analysis of the human, mouse, rat and dog genomes to create a systematic catalogue of common regulatory motifs in promoters and 3' untransl ...
Bio1100Ch17W
... 1. The study of metabolic defects provided evidence that genes specify proteins • The idea of __________ pathways was suggested • 1930s- George Beadle and Boris Ephrussi speculated that each mutation affecting ________ in Drosophila blocks pigment synthesis at a specific step by preventing producti ...
... 1. The study of metabolic defects provided evidence that genes specify proteins • The idea of __________ pathways was suggested • 1930s- George Beadle and Boris Ephrussi speculated that each mutation affecting ________ in Drosophila blocks pigment synthesis at a specific step by preventing producti ...
21st 2014 Célia Miguel
... Small RNA pathways across all stages of embryo development Vega-Bartol et al. (2013) BMC Plant Biol 13:123 ...
... Small RNA pathways across all stages of embryo development Vega-Bartol et al. (2013) BMC Plant Biol 13:123 ...
BIO S - Chapter 13 RNA
... transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries (transfers) each amino acid to the ribosome ...
... transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries (transfers) each amino acid to the ribosome ...
Chapter 7: Gene Expression: The Flow of Genetic Information from
... together the remaining exons. Alternative splicing makes it possible to produce different mRNAs from the same primary transcript. Translation is the stage of gene expression when the cell synthesizes proteins according to instructions in the mRNA. a. tRNAs carry amino acids to the translation machin ...
... together the remaining exons. Alternative splicing makes it possible to produce different mRNAs from the same primary transcript. Translation is the stage of gene expression when the cell synthesizes proteins according to instructions in the mRNA. a. tRNAs carry amino acids to the translation machin ...
Chapter 15 Outline - Adelphi University
... Chapter 15 Outline Genes and How They Work Advanced Placement Biology Roslyn High School The Central Dogma Traces The Flow Of Gene-Encoded Information. How Do Cells Use RNA To Make Protein? ...
... Chapter 15 Outline Genes and How They Work Advanced Placement Biology Roslyn High School The Central Dogma Traces The Flow Of Gene-Encoded Information. How Do Cells Use RNA To Make Protein? ...
How do viruses differ?
... a. averages 20 - 40 minutes b. the number of phage particles released from a single cell is referred to burst size Ranging from 50 to 200 particles D. Life cycle of a lysogenic phage Lysogeny is a state of cell chromosome where a bacteriophage genome has been inserted into the bacterial chromosome b ...
... a. averages 20 - 40 minutes b. the number of phage particles released from a single cell is referred to burst size Ranging from 50 to 200 particles D. Life cycle of a lysogenic phage Lysogeny is a state of cell chromosome where a bacteriophage genome has been inserted into the bacterial chromosome b ...
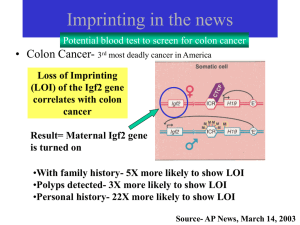
Imprinting
... Two general mechanisms proposed: 1. Passive process via direct methylation of Dnmt1 2. Active process via specific demethylation ...
... Two general mechanisms proposed: 1. Passive process via direct methylation of Dnmt1 2. Active process via specific demethylation ...
Tools for genetic analysis in Trypanosoma brucei unlinked fields
... case of the pyrimidine synthesis pathway; see below), or there may be strain-specific differences that are not reflected in the strain that is predominantly used for T. brucei genetics. Deletion of genes involved in recombination or DNA repair may not have significant consequences in vitro, but may ...
... case of the pyrimidine synthesis pathway; see below), or there may be strain-specific differences that are not reflected in the strain that is predominantly used for T. brucei genetics. Deletion of genes involved in recombination or DNA repair may not have significant consequences in vitro, but may ...
Transcription
... TATA box at ~-30 bases Initiator—on the transcription start site Downstream element-further downstream ...
... TATA box at ~-30 bases Initiator—on the transcription start site Downstream element-further downstream ...
Translation
... mRNA is transported "om the nucleus cytoplasm where it attached with the ribosomes which are the site of protein synthesis. ...
... mRNA is transported "om the nucleus cytoplasm where it attached with the ribosomes which are the site of protein synthesis. ...
AnnotatorsInterface-GUS
... Manual annotation efforts have focused on – validating the automated annotation and – adding additional information at the central dogma level ...
... Manual annotation efforts have focused on – validating the automated annotation and – adding additional information at the central dogma level ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.