Transcription and the Central Dogma
... from many genes averages out to this. – The closer these 2 regions actually are to the consensus sequences, the “stronger” the promoter, meaning the more likely RNA polymerase binding and transcription will occur. ...
... from many genes averages out to this. – The closer these 2 regions actually are to the consensus sequences, the “stronger” the promoter, meaning the more likely RNA polymerase binding and transcription will occur. ...
Lecture 12
... (T1) plants transformed with a β-glucuronidase (uidA or GUS) gene driven by the 35S cauliflower mosaic virus promoter (p35S), the incidence of highly expressing transformants shifted from 20% in wild type background to 100% in sgs2 and sgs3 backgrounds. Likewise, when sgs2 mutants were transformed w ...
... (T1) plants transformed with a β-glucuronidase (uidA or GUS) gene driven by the 35S cauliflower mosaic virus promoter (p35S), the incidence of highly expressing transformants shifted from 20% in wild type background to 100% in sgs2 and sgs3 backgrounds. Likewise, when sgs2 mutants were transformed w ...
A Penetrating Look at stochasticity in Development
... Figure 1. Gene Expression Variability and Incomplete Penetrance (A) The circuit of transcription factors that controls intestinal differentiation. The dotted arrow indicates a putative regulatory interaction between skn-1 and elt-2 based on the altered threshold response observed for one skn-1 alle ...
... Figure 1. Gene Expression Variability and Incomplete Penetrance (A) The circuit of transcription factors that controls intestinal differentiation. The dotted arrow indicates a putative regulatory interaction between skn-1 and elt-2 based on the altered threshold response observed for one skn-1 alle ...
The Epigenetics of Non
... regulation of other RNAs such as mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. Processing-type ncRNAs include small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) involved in splicing, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) that modify nucleotides in rRNAs and other RNAs, and RNase P that cleaves pre-tRNAs. Other small ncRNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) an ...
... regulation of other RNAs such as mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. Processing-type ncRNAs include small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) involved in splicing, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) that modify nucleotides in rRNAs and other RNAs, and RNase P that cleaves pre-tRNAs. Other small ncRNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) an ...
Chapter 4. The Epigenetics of Non
... regulation of other RNAs such as mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. Processing-type ncRNAs include small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) involved in splicing, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) that modify nucleotides in rRNAs and other RNAs, and RNase P that cleaves pre-tRNAs. Other small ncRNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) an ...
... regulation of other RNAs such as mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. Processing-type ncRNAs include small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) involved in splicing, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) that modify nucleotides in rRNAs and other RNAs, and RNase P that cleaves pre-tRNAs. Other small ncRNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) an ...
Genetic Code and Transcription
... Translational Initiation • Small subunit and initiator tRNA bind to start codon. – tRNAi is in P site • Large subunit binds clamping down on mRNA • GTP is hydrolyzed to allow large subunit binding ...
... Translational Initiation • Small subunit and initiator tRNA bind to start codon. – tRNAi is in P site • Large subunit binds clamping down on mRNA • GTP is hydrolyzed to allow large subunit binding ...
CENTRAL DOGMA AND GENE REGULATION
... GENE REGULATION: Determines when a protein is expressed (produced) in a cell. Some proteins are always expressed while others are expressed intermittently (inducible). The Lac Operon: This is an example of a inducible expression. For E. coli to metabolize lactose several proteins must be produced by ...
... GENE REGULATION: Determines when a protein is expressed (produced) in a cell. Some proteins are always expressed while others are expressed intermittently (inducible). The Lac Operon: This is an example of a inducible expression. For E. coli to metabolize lactose several proteins must be produced by ...
Eukaryotic Gene Control
... Eukaryotes multicellular evolved to maintain constant internal conditions while facing changing external conditions ...
... Eukaryotes multicellular evolved to maintain constant internal conditions while facing changing external conditions ...
Gene expression powerpoint
... DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA sequence only one of two DNA strands (template or antisense strand) is transcribed non-transcribed strand is termed coding strand or sense strand same as RNA (except T’s are U’s) In both bacteria and eukaryotes, the polymerase adds ribonucleotides to the growing ...
... DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA sequence only one of two DNA strands (template or antisense strand) is transcribed non-transcribed strand is termed coding strand or sense strand same as RNA (except T’s are U’s) In both bacteria and eukaryotes, the polymerase adds ribonucleotides to the growing ...
Gene Section MIR196B (microRNA 196b) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... HOXA10 genes, on chromosome 7 (7p15.2) in human beings. miR-196a-1 and miR-196a-2 genes transcribe the same functional mature miRNA sequence (3GGGUUGUUGUACUUUGAUGGAU-5), whereas miR-196b gene produces a small RNA (3GGGUUGUUGUCCUUUGAUGGAU-5), which differs from the sequence of miR-196a by one nucleot ...
... HOXA10 genes, on chromosome 7 (7p15.2) in human beings. miR-196a-1 and miR-196a-2 genes transcribe the same functional mature miRNA sequence (3GGGUUGUUGUACUUUGAUGGAU-5), whereas miR-196b gene produces a small RNA (3GGGUUGUUGUCCUUUGAUGGAU-5), which differs from the sequence of miR-196a by one nucleot ...
Regulation of gene expression
... Regulation of transcription in procaryotes • OPERON – transcription unit , a cluster of genes on the chromosome , which are regulated by a single promoter and operator, they are transcribed as one long mRNA molecule – 1 mRNA (with several genes) = 1 transcription unit – polycistronic transcript • P ...
... Regulation of transcription in procaryotes • OPERON – transcription unit , a cluster of genes on the chromosome , which are regulated by a single promoter and operator, they are transcribed as one long mRNA molecule – 1 mRNA (with several genes) = 1 transcription unit – polycistronic transcript • P ...
RNA
... tRNA- is a cloverleaf shaped single strand that matches the amino acid to the correct sequence of mRNA ...
... tRNA- is a cloverleaf shaped single strand that matches the amino acid to the correct sequence of mRNA ...
From Gene to Protein
... rRNA= makes up 60% of the ribosome; site of protein synthesis snRNA=small nuclear RNA; part of a spliceosome. Has structural and catalytic roles srpRNA=a signal recognition particle that binds to signal peptides RNAi= interference RNA; a regulatory molecule ...
... rRNA= makes up 60% of the ribosome; site of protein synthesis snRNA=small nuclear RNA; part of a spliceosome. Has structural and catalytic roles srpRNA=a signal recognition particle that binds to signal peptides RNAi= interference RNA; a regulatory molecule ...
transcription
... The number of intermediates between the closed and open complex is variable and promoter-dependent; each step may be subject to regulation in vivo (2, 3). At least for some promoters, Es binding to promoters is thought to be reversible on the time scale of transcription initiation in vivo (3); rever ...
... The number of intermediates between the closed and open complex is variable and promoter-dependent; each step may be subject to regulation in vivo (2, 3). At least for some promoters, Es binding to promoters is thought to be reversible on the time scale of transcription initiation in vivo (3); rever ...
exportin-5 mediates their nuclear export
... all pre-miRNAs. Analysis of the precursor microRNA premiR-30a showed that pre-miR-30a is a stem – loop of 63-nt containing a 2-nt 30 overhang [3] (Figure 2). Other premiRNAs were also found to contain a short 30 overhang [7], which is likely to represent a key structural feature in nuclear export. T ...
... all pre-miRNAs. Analysis of the precursor microRNA premiR-30a showed that pre-miR-30a is a stem – loop of 63-nt containing a 2-nt 30 overhang [3] (Figure 2). Other premiRNAs were also found to contain a short 30 overhang [7], which is likely to represent a key structural feature in nuclear export. T ...
DNA & RNA
... instructions are known as mRNA Proteins are assembled on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of several dozen proteins as well as a form of RNA called rRNA During protein construction, a third type of RNA molecule transfers each amino acid to the ribosome as it is specified by coded messages in ...
... instructions are known as mRNA Proteins are assembled on the ribosomes. Ribosomes are made up of several dozen proteins as well as a form of RNA called rRNA During protein construction, a third type of RNA molecule transfers each amino acid to the ribosome as it is specified by coded messages in ...
Stem Cells, Cancer, and Human Health
... • There are 64 codons that make up the information in the genetic code • Start @ start codon. End @ stop codon 1 start codon, 3 stop codons ...
... • There are 64 codons that make up the information in the genetic code • Start @ start codon. End @ stop codon 1 start codon, 3 stop codons ...
Discovery through RNA-Seq
... Consistent with Circular RNA? • In poly-A depleted samples, expect to see strong evidence of scrambled exons (circular RNA) • In poly-A selected samples, expect to see little evidence of scrambled exons (circular RNA) ...
... Consistent with Circular RNA? • In poly-A depleted samples, expect to see strong evidence of scrambled exons (circular RNA) • In poly-A selected samples, expect to see little evidence of scrambled exons (circular RNA) ...
View Poster - Technology Networks
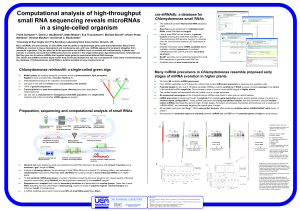
... Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predicted miRNA target site. This is similar to what is found in most miRNA targets of higher plants Two verified targets are associated with cell motility, one i ...
... Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predicted miRNA target site. This is similar to what is found in most miRNA targets of higher plants Two verified targets are associated with cell motility, one i ...
Poster
... RNA Polymerase II (Pol II), a major up-keeper of our cells, is found in the nucleus of all eukaryotic cells and is one of the most important enzymes in our body. Pol II has twelve protein subunits, which also makes it one of the largest molecules. Its function is to surround the DNA, unwind it, sepa ...
... RNA Polymerase II (Pol II), a major up-keeper of our cells, is found in the nucleus of all eukaryotic cells and is one of the most important enzymes in our body. Pol II has twelve protein subunits, which also makes it one of the largest molecules. Its function is to surround the DNA, unwind it, sepa ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the idea that all biological catalysts are proteins. Introns may play a regulatory role in the cell. Specific functions have not been identified for most introns, but some contain sequences that regulate gene expression, and many affect gene products ...
... The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the idea that all biological catalysts are proteins. Introns may play a regulatory role in the cell. Specific functions have not been identified for most introns, but some contain sequences that regulate gene expression, and many affect gene products ...
S2452302X16000073_mmc1 - JACC: Basic to Translational
... (Abcam 6994) and α-smooth muscle actin (Abcam 32575). Arterioles were identified by von Willebrand factor and α-smooth muscle actin positive staining and capillaries by von Willebrand factor positive staining only. For cardiomyocyte cross sectional area, slides were immunostained with wheat-germ agg ...
... (Abcam 6994) and α-smooth muscle actin (Abcam 32575). Arterioles were identified by von Willebrand factor and α-smooth muscle actin positive staining and capillaries by von Willebrand factor positive staining only. For cardiomyocyte cross sectional area, slides were immunostained with wheat-germ agg ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.