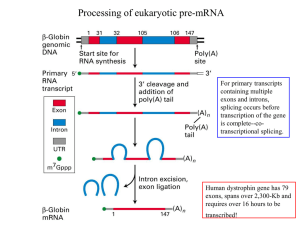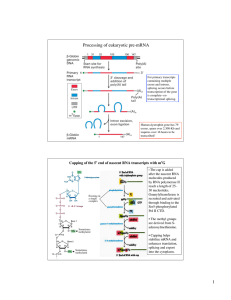
1 Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
Document
... Transcription • genes are also associated with additional sequences of DNA 1. core promoter sequence – for the binding of the RNA polymerase -RNA polymerase recognizes specific sequences of nt’s -binding is helped out by transcription factors 2. enhancer regions – help enhance transcription can be ...
... Transcription • genes are also associated with additional sequences of DNA 1. core promoter sequence – for the binding of the RNA polymerase -RNA polymerase recognizes specific sequences of nt’s -binding is helped out by transcription factors 2. enhancer regions – help enhance transcription can be ...
Attachment, Penetration and Uncoating
... The receptor for HIV is CD4 antigen. However, additional structures are also necessary, since transfection of mouse cells with CD4 does not render them permissive for HIV infection. These second receptor components have recently been identified as members of the beta-chemokine receptor family. These ...
... The receptor for HIV is CD4 antigen. However, additional structures are also necessary, since transfection of mouse cells with CD4 does not render them permissive for HIV infection. These second receptor components have recently been identified as members of the beta-chemokine receptor family. These ...
Powerpoint file - revised
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
15 points each
... -DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded -The sugars are different -RNA has uracil instead of thymine -DNA can not leave the nucleus ...
... -DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded -The sugars are different -RNA has uracil instead of thymine -DNA can not leave the nucleus ...
RNAi (PDF) (1.14 MB)
... a similar effect in nematodes (3), insects (4), and protozoa (5). PTGS can be suppressed by several virus-encoded proteins (6) and is closely related to RNA-mediated virus resistance and cross-protection in plants (7, 8). Therefore, PTGS may represent a natural antiviral defense mechanism and transg ...
... a similar effect in nematodes (3), insects (4), and protozoa (5). PTGS can be suppressed by several virus-encoded proteins (6) and is closely related to RNA-mediated virus resistance and cross-protection in plants (7, 8). Therefore, PTGS may represent a natural antiviral defense mechanism and transg ...
PCR settings, pitfalls and artefacts
... • Never opening more than one tube at a time • Using a separate thermocycler ...
... • Never opening more than one tube at a time • Using a separate thermocycler ...
Gene Section NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... 920 amino acids; 97 kDa; contains repeated motifs (GLFG and FG) in N-term and a RNA binding motif in C-term. ...
... 920 amino acids; 97 kDa; contains repeated motifs (GLFG and FG) in N-term and a RNA binding motif in C-term. ...
A1985ABY6500002
... these studies. My interests were on mechanisms used by cells to control their growth and metabolism, such as feedback control of enzyme activity and the control of enzyme formation by induction and derepression. I arranged to spend a sabbatical year to investigate enzyme induction, and the Pajama ex ...
... these studies. My interests were on mechanisms used by cells to control their growth and metabolism, such as feedback control of enzyme activity and the control of enzyme formation by induction and derepression. I arranged to spend a sabbatical year to investigate enzyme induction, and the Pajama ex ...
Taxonomy of Life • Three domains: Eukaryotes, Bacteria (Eubacteria
... number of nucleotides on one strand from each DNA double helix. – The mitochondrial genome is contained in the mitochondria and contains a subset of the information used in the mitochondria (most of the information used by the mitochondria is contained in the nuclear genome). The mitochondrial genom ...
... number of nucleotides on one strand from each DNA double helix. – The mitochondrial genome is contained in the mitochondria and contains a subset of the information used in the mitochondria (most of the information used by the mitochondria is contained in the nuclear genome). The mitochondrial genom ...
protein synthesis - Science with Mrs Beggs
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA): decodes the information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
... • Transfer RNA (tRNA): decodes the information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
SUNY-ESF Web
... Beta galactosidase-enzyme encoded by the lacZ gene responsible for the enzymatic cleavage of lactose disaccharide to glucose and galactose. When lactose is present in high concentrations, will form 1,6-allolactose, the inducer that binds to the lac repressor protein.. IPTGisopropylthiogalactoside-an ...
... Beta galactosidase-enzyme encoded by the lacZ gene responsible for the enzymatic cleavage of lactose disaccharide to glucose and galactose. When lactose is present in high concentrations, will form 1,6-allolactose, the inducer that binds to the lac repressor protein.. IPTGisopropylthiogalactoside-an ...
Macromolecule Review
... 2. Which of the molecules listed above can often be composed of C, H, and O alone? 3. Which of the compounds can be identified by looking at the C:H:O ratios alone? 4. What other elements are commonly associated with each of these four types of macromolecules? ...
... 2. Which of the molecules listed above can often be composed of C, H, and O alone? 3. Which of the compounds can be identified by looking at the C:H:O ratios alone? 4. What other elements are commonly associated with each of these four types of macromolecules? ...
Schedule
... is where a single base changes in the DNA sequence. It can have little or no effect on the amino acid produced, because amino acids have more than one possible codon sequence for them. This means that if there was a point mutation, then the same amino acid could still be coded for. This would then r ...
... is where a single base changes in the DNA sequence. It can have little or no effect on the amino acid produced, because amino acids have more than one possible codon sequence for them. This means that if there was a point mutation, then the same amino acid could still be coded for. This would then r ...
DNA to RNA practice
... needed to get to the ribosome. DNA is converted into a single stranded RNA molecule, called mRNA. This process is called transcription. Draw your codon lines to separate the triplets. Using the base pairing rules for DNA to RNA, find the anticodons for the DNA strand first. Then convert that strand ...
... needed to get to the ribosome. DNA is converted into a single stranded RNA molecule, called mRNA. This process is called transcription. Draw your codon lines to separate the triplets. Using the base pairing rules for DNA to RNA, find the anticodons for the DNA strand first. Then convert that strand ...
Slide 1
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA formed is immediately ready for protein synthesis • In eukaryotes, the mRNA formed in nucleus is very large & not fully processed. • It contains additional non-coding (interrupting) sequences called Introns. • The coding regions (exons) have to be cut and spliced together to f ...
... • In prokaryotes, mRNA formed is immediately ready for protein synthesis • In eukaryotes, the mRNA formed in nucleus is very large & not fully processed. • It contains additional non-coding (interrupting) sequences called Introns. • The coding regions (exons) have to be cut and spliced together to f ...
doc - Florida State University
... contain both DNA and RNA as their genetic information, (C) do not produce diseases in humans, (D) contain RNA as their genetic information OR (E) lack protein in their capsids. 37. Consider the DNA sequence: 3’- ATGAGGTCTTTTACGT-5’. The mRNA transcript from this DNA sequence would be _______________ ...
... contain both DNA and RNA as their genetic information, (C) do not produce diseases in humans, (D) contain RNA as their genetic information OR (E) lack protein in their capsids. 37. Consider the DNA sequence: 3’- ATGAGGTCTTTTACGT-5’. The mRNA transcript from this DNA sequence would be _______________ ...
doc - Florida State University
... that code for traits used in special environments. (A) nucleoid, (B) chromosome, (C) plasmid, (D) provirus or (E) prophage. 20. Newly synthesized mRNA in prokaryotes can be used immediately for translation because____________. (A) it does not need to be transported out of the nucleus, (B) it lacks I ...
... that code for traits used in special environments. (A) nucleoid, (B) chromosome, (C) plasmid, (D) provirus or (E) prophage. 20. Newly synthesized mRNA in prokaryotes can be used immediately for translation because____________. (A) it does not need to be transported out of the nucleus, (B) it lacks I ...
Chapter 19 - mrswehri.com
... Epigenetic inheritance occurs when traits are passed on and do not involve the nucleotide sequences (proteins, enzymes, organelles). It also seems to be very important in the regulation of gene expression. The enzymes that modify chromatin are integral parts of the cell’s machinery that regulate ...
... Epigenetic inheritance occurs when traits are passed on and do not involve the nucleotide sequences (proteins, enzymes, organelles). It also seems to be very important in the regulation of gene expression. The enzymes that modify chromatin are integral parts of the cell’s machinery that regulate ...
Chapter 10
... that DNA is the genetic material – Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacterial cells – Phages were labeled with radioactive sulfur to detect proteins or radioactive phosphorus to detect DNA – Bacteria were infected with either type of labeled phage to determine which substance was injected into ...
... that DNA is the genetic material – Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacterial cells – Phages were labeled with radioactive sulfur to detect proteins or radioactive phosphorus to detect DNA – Bacteria were infected with either type of labeled phage to determine which substance was injected into ...
Molecular Biology 240386
... The Largest Subunit in RNA Polymerase II Has Essential Carboxyl-Terminal Repeat Carboxyl end of largest subunit of RNA polymerase II,ONLY, (RPB1) contains a stretch of 7 amino acids,repeated multiple times= heptapeptide = terminal domain (CTD). -CTD critical for viability -In vitro experiments with ...
... The Largest Subunit in RNA Polymerase II Has Essential Carboxyl-Terminal Repeat Carboxyl end of largest subunit of RNA polymerase II,ONLY, (RPB1) contains a stretch of 7 amino acids,repeated multiple times= heptapeptide = terminal domain (CTD). -CTD critical for viability -In vitro experiments with ...
Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA
... Supplementary Information), which indicates that these structurally similar proteins may all share similar biochemical functions. Exogenous dsRNAs can affect gene function in early mouse embryos18, and our results suggest that this regulation may be accomplished by evolutionarily conserved RNAi mach ...
... Supplementary Information), which indicates that these structurally similar proteins may all share similar biochemical functions. Exogenous dsRNAs can affect gene function in early mouse embryos18, and our results suggest that this regulation may be accomplished by evolutionarily conserved RNAi mach ...
Instructor`s Manual to accompany Principles of Life
... (APPLY THE CONCEPT Genetics show that genes code for proteins) The gene–enzyme relationship has since been revised to the one gene–one polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene. Other genes code for RNA but are not translated to polypept ...
... (APPLY THE CONCEPT Genetics show that genes code for proteins) The gene–enzyme relationship has since been revised to the one gene–one polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene. Other genes code for RNA but are not translated to polypept ...