Lecture 9
... surfaces. Clays attract positively charged ions to their surface which can act as catalysts. Scientists have used clays to demonstrate spontaneous synthesis of RNAlike molecules from nucleotide precursors. RNA has been found to be both catalytic (synthesizing peptide bonds in protein synthesis, carr ...
... surfaces. Clays attract positively charged ions to their surface which can act as catalysts. Scientists have used clays to demonstrate spontaneous synthesis of RNAlike molecules from nucleotide precursors. RNA has been found to be both catalytic (synthesizing peptide bonds in protein synthesis, carr ...
BIOL 241 Nucleic Acids and Gene Expression I. Genes (Overview) A
... B. Each amino acid (20) coded for by at least one codon See Figure 3.35 1. all but two amino acids can have more than one codon - usually differ in the third base 2. 3 codons are STOP codons 3. mRNA = series of codons translated into chains of amino acids C. Change in a single nucleotide (mRNA) can ...
... B. Each amino acid (20) coded for by at least one codon See Figure 3.35 1. all but two amino acids can have more than one codon - usually differ in the third base 2. 3 codons are STOP codons 3. mRNA = series of codons translated into chains of amino acids C. Change in a single nucleotide (mRNA) can ...
Amal Awwad 23 Abd Alraheem Jerdaneh st. Amman, Jordan
... Studied the formation of G-quadruplexes in more than 500 DNA and RNA aptamer sequences. Aptamers are single stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotides that bind with high affinity and specificity to unique targets such as peptides, cells, organelles and viruses. The main purpose of the project was to stud ...
... Studied the formation of G-quadruplexes in more than 500 DNA and RNA aptamer sequences. Aptamers are single stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotides that bind with high affinity and specificity to unique targets such as peptides, cells, organelles and viruses. The main purpose of the project was to stud ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription & Translation
... How DNA determines proteins • DNA molecules serve as templates for making messenger RNA molecules • Messenger RNA molecules move to ribosomes • Transfer RNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome • Polypeptides (proteins) are formed as ribosomes move along the messenger RNA strand ...
... How DNA determines proteins • DNA molecules serve as templates for making messenger RNA molecules • Messenger RNA molecules move to ribosomes • Transfer RNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome • Polypeptides (proteins) are formed as ribosomes move along the messenger RNA strand ...
Protein RNA DNA - Molecular Systems Biology
... in all tissues, while 13% show a mixed expression. The number of tissueenriched genes in the different tissues and the overlap between the Human Protein Atlas consortium (HPA) and the genome-based tissue expression consortium (GTEx) are shown in B. Overall, it is reassuring that there is a significa ...
... in all tissues, while 13% show a mixed expression. The number of tissueenriched genes in the different tissues and the overlap between the Human Protein Atlas consortium (HPA) and the genome-based tissue expression consortium (GTEx) are shown in B. Overall, it is reassuring that there is a significa ...
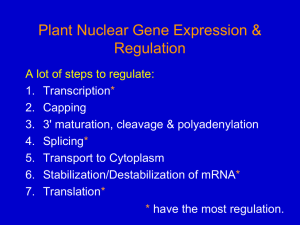
How Genes Are Regulated
... • Describe how prokaryotic gene expression occurs at the transcriptional level • Understand that eukaryotic gene expression occurs at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels For a cell to function properly, necessary proteins must be synthe ...
... • Describe how prokaryotic gene expression occurs at the transcriptional level • Understand that eukaryotic gene expression occurs at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels For a cell to function properly, necessary proteins must be synthe ...
Name
... Directions: Open the PowerPoint titled “Translation Tutorial” and press the F5 button to start. Place your keyboard aside (if possible) and only use the mouse. Translation 1. What happens at the ribosome? _________________________________________________________________ 2. Define TRANSLATION. ______ ...
... Directions: Open the PowerPoint titled “Translation Tutorial” and press the F5 button to start. Place your keyboard aside (if possible) and only use the mouse. Translation 1. What happens at the ribosome? _________________________________________________________________ 2. Define TRANSLATION. ______ ...
Document
... The genome of any organism contains all the information for making that organism. The information is encoded in various types of genes that are transcribed into 4 types of RNA: mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes du ...
... The genome of any organism contains all the information for making that organism. The information is encoded in various types of genes that are transcribed into 4 types of RNA: mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes du ...
Introductory Biology Primer - A computational tour of the human
... – Cascade has “master regulators” turning on many proteins, which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
... – Cascade has “master regulators” turning on many proteins, which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
12.3 DNA, RNA, and Protein
... – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome. ...
... – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome. ...
HISTORY OF LIFE
... ORIGIN OF HEREDITY • Genetic information made it possible to pass along information for making new molecules • Today: DNA RNAProtein • Originally: RNA protein • Support – RNA acts as enzyme (ribozymes) – Synthesized short segments of RNA in lab; replicate short segments of RNA without enzymes ...
... ORIGIN OF HEREDITY • Genetic information made it possible to pass along information for making new molecules • Today: DNA RNAProtein • Originally: RNA protein • Support – RNA acts as enzyme (ribozymes) – Synthesized short segments of RNA in lab; replicate short segments of RNA without enzymes ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... What is a gene? A gene is a specific section of DNA along the length of a chromosome. It has a beginning (the “promoter”) and an end (the “termination signal”). A gene holds the instructions for making a specific protein. ...
... What is a gene? A gene is a specific section of DNA along the length of a chromosome. It has a beginning (the “promoter”) and an end (the “termination signal”). A gene holds the instructions for making a specific protein. ...
Recombinant human RNA polymerase II CTD repeat
... EDTA, pH 8.0 This product is an active protein and may elicit a biological response in vivo, handle with caution. ...
... EDTA, pH 8.0 This product is an active protein and may elicit a biological response in vivo, handle with caution. ...
Review Sheet : DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis
... Which of the following is not true about DNA replication? a. It must occur before a cell can divide b. Two complementary strands are duplicated. c. The double strand unwinds and unzips while it is being duplicated. d. The process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA mutagens. ...
... Which of the following is not true about DNA replication? a. It must occur before a cell can divide b. Two complementary strands are duplicated. c. The double strand unwinds and unzips while it is being duplicated. d. The process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA mutagens. ...
methodology for high-quality RNA extraction from poultry whole
... from avian whole blood is challenging because of nucleated red blood cells (RBCs) that increase DNA and protein contamination. Recently, total RNA has been successfully isolated from an iguana species (Glaberman et al., 2008), and methods for RNA isolation from sauropsid species were evaluated (Chia ...
... from avian whole blood is challenging because of nucleated red blood cells (RBCs) that increase DNA and protein contamination. Recently, total RNA has been successfully isolated from an iguana species (Glaberman et al., 2008), and methods for RNA isolation from sauropsid species were evaluated (Chia ...
Ch. 10 DNA Review Questions
... a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promoters, which have specific base sequences. d. Promoters are signals in RNA ...
... a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase binds only to DNA promoters, which have specific base sequences. d. Promoters are signals in RNA ...
Discovering the material for heredity: DNA
... BRCA1 or BRCA2, they are at an increased risk of being diagnosed with breast or ovarian cancer at some point in their lives. • These genes participate in repairing radiationinduced breaks in double-stranded DNA. It is thought that mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 might disable this mechanism, leading to ...
... BRCA1 or BRCA2, they are at an increased risk of being diagnosed with breast or ovarian cancer at some point in their lives. • These genes participate in repairing radiationinduced breaks in double-stranded DNA. It is thought that mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 might disable this mechanism, leading to ...
Name: Period _______ Date FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE G
... Be able to calculate half-life: If the half-life of (carbon 14-12) is 5,000 years old, how many halflives did carbon go through to be 15,000 years old. How much parent material is left over, how much daughter material is left over? Evolution of DNA/RNA-which came first? Examples of Fossils: First li ...
... Be able to calculate half-life: If the half-life of (carbon 14-12) is 5,000 years old, how many halflives did carbon go through to be 15,000 years old. How much parent material is left over, how much daughter material is left over? Evolution of DNA/RNA-which came first? Examples of Fossils: First li ...
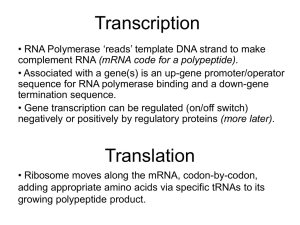
Transcription & Translation
... • Associated with a gene(s) is an up-gene promoter/operator sequence for RNA polymerase binding and a down-gene termination sequence. • Gene transcription can be regulated (on/off switch) negatively or positively by regulatory proteins (more later). ...
... • Associated with a gene(s) is an up-gene promoter/operator sequence for RNA polymerase binding and a down-gene termination sequence. • Gene transcription can be regulated (on/off switch) negatively or positively by regulatory proteins (more later). ...