Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering
... in a population by inducing mutations, which are the ultimate source of genetic variability ...
... in a population by inducing mutations, which are the ultimate source of genetic variability ...
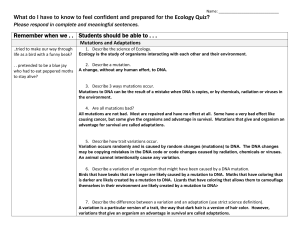
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... 10. Describe an example where the environment affects the benefits of a variation. The most famous example is the peppered moths Before the Industrial Revolution; the trees were light colored so light colored moths have a variation that helped them survive. However, when the trees became dark becaus ...
... 10. Describe an example where the environment affects the benefits of a variation. The most famous example is the peppered moths Before the Industrial Revolution; the trees were light colored so light colored moths have a variation that helped them survive. However, when the trees became dark becaus ...
Gene Section TACC2 (transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2)
... ORF-BC015736 and AAF63433, beginning at an "internal" AUG present in exon 9, are identical except for 4 amino acids missing in AAF63433 (amino acid 2429-2432). BAH12132 prematurely terminates due to a C-T mutation in the cDNA generating a nonsense codon; the partial cDNA coding this open reading fra ...
... ORF-BC015736 and AAF63433, beginning at an "internal" AUG present in exon 9, are identical except for 4 amino acids missing in AAF63433 (amino acid 2429-2432). BAH12132 prematurely terminates due to a C-T mutation in the cDNA generating a nonsense codon; the partial cDNA coding this open reading fra ...
DNA Extraction from Bacteria
... toothpicks full of meat tenderizer to the tube, cap the tube, mix gently but thoroughly, and return the tube to the 55-60°C water bath for 20 minutes. Meat tenderizer contains papain, an enzyme that breaks down any proteins that may be attached to the DNA. ...
... toothpicks full of meat tenderizer to the tube, cap the tube, mix gently but thoroughly, and return the tube to the 55-60°C water bath for 20 minutes. Meat tenderizer contains papain, an enzyme that breaks down any proteins that may be attached to the DNA. ...
LESSON 4 Genetics: STUDY GUIDE
... • Describe mutations as well as the different types of mutations. (pg. 372) • Explain the effects mutations can have on genes. (pg. 374) • Characterize gene regulation in prokaryotes. (pg. 377) • Discuss how most eukaryotic genes are regulated. (pg. 379) • Relate gene regulation to development in mu ...
... • Describe mutations as well as the different types of mutations. (pg. 372) • Explain the effects mutations can have on genes. (pg. 374) • Characterize gene regulation in prokaryotes. (pg. 377) • Discuss how most eukaryotic genes are regulated. (pg. 379) • Relate gene regulation to development in mu ...
The Genetic Code
... DNA code is read in groups of three nucleotide bases. Each group of three is called a TRIPLET Each triplet codes for ONE amino acid in the polypeptide chain. For example, the following segment of DNA codes for 6 amino acids: ...
... DNA code is read in groups of three nucleotide bases. Each group of three is called a TRIPLET Each triplet codes for ONE amino acid in the polypeptide chain. For example, the following segment of DNA codes for 6 amino acids: ...
4. Protein Synthesis and Biotechnology
... occur when base pairs are incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. Mutation ...
... occur when base pairs are incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. Mutation ...
An Investigation into the Genomic Evolution of the Histone Gene
... The extremely high level of within and between species similarity of the histone gene family has lead to the proposal that the histone gene family is subject to concerted evolution. Both mechanisms of concerted evolution – unequal crossing over and gene conversion - have been documented to occur, an ...
... The extremely high level of within and between species similarity of the histone gene family has lead to the proposal that the histone gene family is subject to concerted evolution. Both mechanisms of concerted evolution – unequal crossing over and gene conversion - have been documented to occur, an ...
File
... In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the cytoplasm. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly all of the cell’s genetic information. Eukaryotic DNA is located in the cell nucleus inside chromosomes. Each chromosome contains a single, long, coiled DNA molecule. The mitochondria ...
... In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in the cytoplasm. Most prokaryotes have a single DNA molecule containing nearly all of the cell’s genetic information. Eukaryotic DNA is located in the cell nucleus inside chromosomes. Each chromosome contains a single, long, coiled DNA molecule. The mitochondria ...
regulatory transcription factors
... CpG islands near their promoters (not common in yeast and Drosophila) – These CpG islands are 1,000 to 2,000 nucleotides long – In housekeeping genes • The CpG islands are unmethylated • Genes tend to be expressed in most cell types ...
... CpG islands near their promoters (not common in yeast and Drosophila) – These CpG islands are 1,000 to 2,000 nucleotides long – In housekeeping genes • The CpG islands are unmethylated • Genes tend to be expressed in most cell types ...
The Avery and Hershey-Chase Experiments
... “transforming principle” from Griffith’s experiment. – They prepared a mixture of dead S Streptococcus and live R Streptococcus. (That Griffith had used). – Avery and his colleagues achieved 99.98% purity by removing as they could form their mixtures. – The transforming activity was NOT reduced. ...
... “transforming principle” from Griffith’s experiment. – They prepared a mixture of dead S Streptococcus and live R Streptococcus. (That Griffith had used). – Avery and his colleagues achieved 99.98% purity by removing as they could form their mixtures. – The transforming activity was NOT reduced. ...
2nd semester exam Review packet
... 14. What is synapsis? When does it occur? What also MIGHT happen during synapsis? ...
... 14. What is synapsis? When does it occur? What also MIGHT happen during synapsis? ...
1 Biotechnology: Old and New
... debate among scientists, ethicists, the media, venture capitalists, lawyers, and others. b) It was concluded in the 1980s that no disasters had occurred through the use of recombinant DNA technology, and that the technology does not pose a threat to human health or the environment. ...
... debate among scientists, ethicists, the media, venture capitalists, lawyers, and others. b) It was concluded in the 1980s that no disasters had occurred through the use of recombinant DNA technology, and that the technology does not pose a threat to human health or the environment. ...
figure 9-9
... twentieth-century biology and promises a vastly changed scientific landscape for the new century. In international cooperative research efforts, the genomes ...
... twentieth-century biology and promises a vastly changed scientific landscape for the new century. In international cooperative research efforts, the genomes ...
Slideshow
... Non disjunction mutations (monosomy and trisomy) can result in Down Syndrome, Kleinfelter’s Syndrome and Turner’s Syndrome ...
... Non disjunction mutations (monosomy and trisomy) can result in Down Syndrome, Kleinfelter’s Syndrome and Turner’s Syndrome ...
Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid)
... • Reinforce the following process: DNA RNA Protein Trait • Observe how genes are regulated ...
... • Reinforce the following process: DNA RNA Protein Trait • Observe how genes are regulated ...
Did you ever get a message from a friend that was in code
... -Protein is made (polypeptide chains—poly=many, peptides bonds =___________________________ ...
... -Protein is made (polypeptide chains—poly=many, peptides bonds =___________________________ ...
Genetic Changes Chapter 11.3
... where: parts of the chromosome may break off and become lost in the cell during mitosis or meiosis chromosomes may rejoin incorrectly ...
... where: parts of the chromosome may break off and become lost in the cell during mitosis or meiosis chromosomes may rejoin incorrectly ...
Document
... preferentially prime cDNA synthesis from those mRNAs where the dinucleotide TG precedes the poly(A) tail. The second primer which is used is usually an arbitrary short sequence (often 10 nucleotides long but, because of mismatching, especially at the 5 - end, it can bind to many more sites than expe ...
... preferentially prime cDNA synthesis from those mRNAs where the dinucleotide TG precedes the poly(A) tail. The second primer which is used is usually an arbitrary short sequence (often 10 nucleotides long but, because of mismatching, especially at the 5 - end, it can bind to many more sites than expe ...
Cancer epigenetics

Cancer epigenetics is the study of epigenetic modifications to the genome of cancer cells that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence. Epigenetic alterations are as important as genetic mutations in a cell’s transformation to cancer, and their manipulation holds great promise for cancer prevention, detection, and therapy. In different types of cancer, a variety of epigenetic mechanisms can be perturbed, such as silencing of tumor suppressor genes and activation of oncogenes by altered CpG island methylation patterns, histone modifications, and dysregulation of DNA binding proteins. Several medications which have epigenetic impact are now used in several of these diseases.