The basic Hebb rule
... • Although the covariance rule allows LTD and reflects a causal preand postsynaptic relationship it is still unstable due to positive ...
... • Although the covariance rule allows LTD and reflects a causal preand postsynaptic relationship it is still unstable due to positive ...
Regulation of Astrocyte Plasticity
... years), but the dissociation to me seems most powerful-synapse addition may mediate LTP, but synapse addition need not involve an LTP-like process for its induction. ...
... years), but the dissociation to me seems most powerful-synapse addition may mediate LTP, but synapse addition need not involve an LTP-like process for its induction. ...
Three Types of Behavior : involuntary responses to stimuli
... H.M.’s deficits appear in explicit memory tasks The Delayed Nonmatching to Sample Task Monkeys with __________________________ damage do poorly on the DNMS task The DNMS task requires the ability to form long-term memories Conclusion thus far The _______________________ and the _____________________ ...
... H.M.’s deficits appear in explicit memory tasks The Delayed Nonmatching to Sample Task Monkeys with __________________________ damage do poorly on the DNMS task The DNMS task requires the ability to form long-term memories Conclusion thus far The _______________________ and the _____________________ ...
Learning and Memory Lecture Notes Page
... H.M.’s deficits appear in explicit memory tasks The Delayed Nonmatching to Sample Task Monkeys with __________________________ damage do poorly on the DNMS task The DNMS task requires the ability to form long-term memories Conclusion thus far The _______________________ and the _____________________ ...
... H.M.’s deficits appear in explicit memory tasks The Delayed Nonmatching to Sample Task Monkeys with __________________________ damage do poorly on the DNMS task The DNMS task requires the ability to form long-term memories Conclusion thus far The _______________________ and the _____________________ ...
Actin , Synaptic plasticity in Parallel fibre-Purkinje Neuron
... current amplitude is decreasing after Latrunculin injection over a time period. This has been reported in many other cells even though not well documented in neurons. To study the possibility of the variations in the morphology due to altered stability of actin cytoskeleton affecting neuronal plasti ...
... current amplitude is decreasing after Latrunculin injection over a time period. This has been reported in many other cells even though not well documented in neurons. To study the possibility of the variations in the morphology due to altered stability of actin cytoskeleton affecting neuronal plasti ...
How Ca2+ triggers neurotransmitter release
... neurotransmitter release from the presynaptic neuron. Furthermore, his work identified Munc18-1 and SNARE proteins mediate the fusion of the vesicles with the presynaptic plasma membrane, the process that effects neurotransmitter release and that is controlled by synaptotagmins. He also found RIMs a ...
... neurotransmitter release from the presynaptic neuron. Furthermore, his work identified Munc18-1 and SNARE proteins mediate the fusion of the vesicles with the presynaptic plasma membrane, the process that effects neurotransmitter release and that is controlled by synaptotagmins. He also found RIMs a ...
Modeling Synaptic Plasticity
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
Week 2 Lecture Notes
... contains a salt solution resembling the fluid normally found within the cell, is lowered to the cell membrane where a tight seal is formed. When a little suction is applied to the pipette, the "patch" of membrane within the pipette ruptures, permitting access to the whole cell. The electrode, which ...
... contains a salt solution resembling the fluid normally found within the cell, is lowered to the cell membrane where a tight seal is formed. When a little suction is applied to the pipette, the "patch" of membrane within the pipette ruptures, permitting access to the whole cell. The electrode, which ...
doc Chapter 13 Notes
... proteins, receptors and all that good stuff) It has also been suggested that LTP changes the synaptic structure and causes production of new synapses. - thin dendritic spines become fatter, mushroom shaped spines - also new dendrites can grow that then form connections with nearby axons Some researc ...
... proteins, receptors and all that good stuff) It has also been suggested that LTP changes the synaptic structure and causes production of new synapses. - thin dendritic spines become fatter, mushroom shaped spines - also new dendrites can grow that then form connections with nearby axons Some researc ...
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... won’t start AP in next neuron—may need several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
... won’t start AP in next neuron—may need several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
Chapter 13
... Electrical stimulation of circuits within the hippocampal formation (forebrain structure of the temporal lobe, part of the limbic system) can lead to long-term synaptic changes that seem to be among those responsible for learning LTP – a long-term increase in the excitability of a neuron to a part ...
... Electrical stimulation of circuits within the hippocampal formation (forebrain structure of the temporal lobe, part of the limbic system) can lead to long-term synaptic changes that seem to be among those responsible for learning LTP – a long-term increase in the excitability of a neuron to a part ...
Modulation of neuronal protein synthesis by IMPACT
... synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity. One of the central mechanisms underlying regulation of translation in all eukaryotes is the phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2, which reduces general protein synthesis but increases translation of specific mRNAs, such as ATF ...
... synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity. One of the central mechanisms underlying regulation of translation in all eukaryotes is the phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2, which reduces general protein synthesis but increases translation of specific mRNAs, such as ATF ...
Pull out the stops for plasticity
... synapse as that analysed in the current study9. The activity of various metabotropic receptors, including mGlu1, can increase glutamatemediated responses through this pathway10. It will be interesting to investigate whether the mGlu1-triggered blockade of SK channels identified by Tigaret et al. act ...
... synapse as that analysed in the current study9. The activity of various metabotropic receptors, including mGlu1, can increase glutamatemediated responses through this pathway10. It will be interesting to investigate whether the mGlu1-triggered blockade of SK channels identified by Tigaret et al. act ...
Neuronal signaling and synapses
... *short-term decreases in strength includes depression, which can occur d/t highfrequency stimulation, and habituation (a slowly progressing decrease as a result of lowfrequency activation) ...
... *short-term decreases in strength includes depression, which can occur d/t highfrequency stimulation, and habituation (a slowly progressing decrease as a result of lowfrequency activation) ...
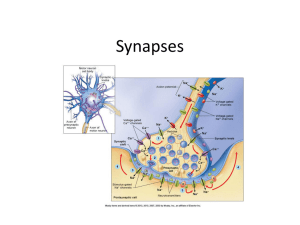
THE SYNAPSE
... A presynaptic element, an axon, and a postsynaptic element, for example a dendritic spine, are in close apposition at the synapse but not in direct contact. The pre- and postsynaptic membranes are separated by a gap, the synaptic cleft. Chemical transmitters bridge this gap by diffusing from release ...
... A presynaptic element, an axon, and a postsynaptic element, for example a dendritic spine, are in close apposition at the synapse but not in direct contact. The pre- and postsynaptic membranes are separated by a gap, the synaptic cleft. Chemical transmitters bridge this gap by diffusing from release ...
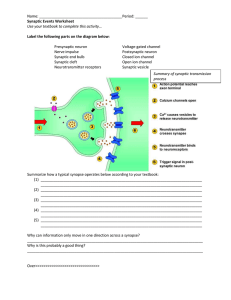
synaptic transmission worksheet
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
Syllabus
... An introductory survey of designed to provide a general understanding of the nervous system including how it functions, how it develops, and how it changes with learning and memory. Analysis from the ...
... An introductory survey of designed to provide a general understanding of the nervous system including how it functions, how it develops, and how it changes with learning and memory. Analysis from the ...
Neuroplasticity
... increases with number of stimulated afferents – Associativity: LTP only induced at weak input when associated with activity in strong input – Input specificity: Unstimulated weak pathway not facilitated after tetanus of strong pathway ...
... increases with number of stimulated afferents – Associativity: LTP only induced at weak input when associated with activity in strong input – Input specificity: Unstimulated weak pathway not facilitated after tetanus of strong pathway ...
1 - U-System
... 1. NMDA receptors and LTP in learning and memory - long term potentiation LTP; a neuron is given a brief, but rapid series of stimuli leaves neuron potentiated (highly responsive to new input of same type); LTP occurs in hippocampal neurons - LTP depends on activation of NMDA receptors - NMDA re ...
... 1. NMDA receptors and LTP in learning and memory - long term potentiation LTP; a neuron is given a brief, but rapid series of stimuli leaves neuron potentiated (highly responsive to new input of same type); LTP occurs in hippocampal neurons - LTP depends on activation of NMDA receptors - NMDA re ...
Molecular basis of learning in the hippocampus and the amygdala
... protein binding CREB (CBP) and in that complex it binds to specific region on DNACRE (Silva et al., 1998). CREB is an activator of immediate early genes (IEGs) like Arc, c-fos, Zif268 (Rosen et al., 1998). Activation of c-fos leads to expression of matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9) which is responsi ...
... protein binding CREB (CBP) and in that complex it binds to specific region on DNACRE (Silva et al., 1998). CREB is an activator of immediate early genes (IEGs) like Arc, c-fos, Zif268 (Rosen et al., 1998). Activation of c-fos leads to expression of matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9) which is responsi ...
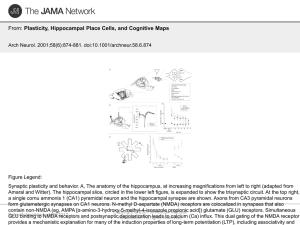
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
... Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) pyramidal neuron and the hippocampal synapse are shown. Axons from CA3 pyramidal neurons form glutamatergic synapses on CA1 neuro ...
... Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) pyramidal neuron and the hippocampal synapse are shown. Axons from CA3 pyramidal neurons form glutamatergic synapses on CA1 neuro ...
slides
... learn the general task requirement as well as the specific location of the hidden platform Spatial pretraining can separate the two kinds of learning Rats first made familiar with the general task requirements and subsequently trained after receiving NMDAR antagonists could learn the spatial locatio ...
... learn the general task requirement as well as the specific location of the hidden platform Spatial pretraining can separate the two kinds of learning Rats first made familiar with the general task requirements and subsequently trained after receiving NMDAR antagonists could learn the spatial locatio ...
June 24_Learning & Memory
... cortex, regions that are known to be involved in memory formation. It doesn’t seem to be observed elsewhere. Like memory formation, LTP is quickly performed and lasts for a very long time. Drugs or genetic manipulations that enhance learning also enhance LTP. ...
... cortex, regions that are known to be involved in memory formation. It doesn’t seem to be observed elsewhere. Like memory formation, LTP is quickly performed and lasts for a very long time. Drugs or genetic manipulations that enhance learning also enhance LTP. ...
Long-term potentiation

In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons. The opposite of LTP is long-term depression, which produces a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength.It is one of several phenomena underlying synaptic plasticity, the ability of chemical synapses to change their strength. As memories are thought to be encoded by modification of synaptic strength, LTP is widely considered one of the major cellular mechanisms that underlies learning and memory.LTP was discovered in the rabbit hippocampus by Terje Lømo in 1966 and has remained a popular subject of research since. Many modern LTP studies seek to better understand its basic biology, while others aim to draw a causal link between LTP and behavioral learning. Still others try to develop methods, pharmacologic or otherwise, of enhancing LTP to improve learning and memory. LTP is also a subject of clinical research, for example, in the areas of Alzheimer's disease and addiction medicine.