The Human Genome Project CH 13 Sec 3 notes
... •Uses restriction enzymes to create fragments –unique to each individual –gel electrophoresis separates fragments –Observe band patterns •______________________________________ •Coding sequences almost identical Identifying Genes ...
... •Uses restriction enzymes to create fragments –unique to each individual –gel electrophoresis separates fragments –Observe band patterns •______________________________________ •Coding sequences almost identical Identifying Genes ...
Slide 1
... • Where is DNA found? • nucleus • Where else? • mitochondria, chloroplast (the endosymbiont theory) • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chroma ...
... • Where is DNA found? • nucleus • Where else? • mitochondria, chloroplast (the endosymbiont theory) • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chroma ...
Invertebrate epigenomics: the brave new world of
... embryo. Nowadays, we know that such signals consist of regulatory mechanisms such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, long noncoding RNA and others. Myriad studies carried out throughout the past decades transformed our understanding of the role of epigenetic processes in embryonic developmen ...
... embryo. Nowadays, we know that such signals consist of regulatory mechanisms such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, long noncoding RNA and others. Myriad studies carried out throughout the past decades transformed our understanding of the role of epigenetic processes in embryonic developmen ...
Chromatin Structure and Function
... A) Non-histone DNA binding proteins may disrupt 30 nm fiber. Or prevent binding of a nucleosome. Creates DNAse I sensitive region ...
... A) Non-histone DNA binding proteins may disrupt 30 nm fiber. Or prevent binding of a nucleosome. Creates DNAse I sensitive region ...
SW describe how techniques such as DNA
... Sex-Influenced and Sex-Limited Traits Sex-influenced traits are those that are expressed differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
... Sex-Influenced and Sex-Limited Traits Sex-influenced traits are those that are expressed differently in the two sexes. Such traits are autosomal, which means that the genes responsible for their expression are not carried on the sex chromosomes. ...
Slide 1
... • At the end of spermatogenesis the DNA is not methylated small RNAs may transfer the information for methylation • Discovery of a new class of small, non-coding RNAs of unknown function ...
... • At the end of spermatogenesis the DNA is not methylated small RNAs may transfer the information for methylation • Discovery of a new class of small, non-coding RNAs of unknown function ...
AP Biology
... 21. What specific nucleotide is modified by methylation of DNA? What affect(s) may methylation of DNA have on DNA packaging and gene expression? Give one example of this phenomenon in eukaryotes. ...
... 21. What specific nucleotide is modified by methylation of DNA? What affect(s) may methylation of DNA have on DNA packaging and gene expression? Give one example of this phenomenon in eukaryotes. ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... Selective Breeding • Allowing only those with desired character istics to produce the next generation ...
... Selective Breeding • Allowing only those with desired character istics to produce the next generation ...
Case name Owner Website description Integrates DNA Methylation
... tissue sample is valuable information about a person s health. By studying the language of cells, genes and proteins, researchers can better understand disease development, including how cancer progresses. DNA methylation, which helps control gene expression, and chromatin structures, protein-DNA in ...
... tissue sample is valuable information about a person s health. By studying the language of cells, genes and proteins, researchers can better understand disease development, including how cancer progresses. DNA methylation, which helps control gene expression, and chromatin structures, protein-DNA in ...
Epigenetics - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Histone modifying complexes and nucleosome remodeling complexes recognize the modified histones through specific domains ...
... Histone modifying complexes and nucleosome remodeling complexes recognize the modified histones through specific domains ...
Worksheet for 4/16
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
So You Think
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...
DNA Methylation
... • If the allele inherited from the father is imprinted, it is thereby silenced, and only the allele from the mother is expressed. • If the allele from the mother is imprinted, then only the allele from the father is expressed. • Forms of genomic imprinting have been demonstrated in fungi, plants and ...
... • If the allele inherited from the father is imprinted, it is thereby silenced, and only the allele from the mother is expressed. • If the allele from the mother is imprinted, then only the allele from the father is expressed. • Forms of genomic imprinting have been demonstrated in fungi, plants and ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
The Code of Life: Topic 3
... mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is ...
... mother and one from your father. • Each chromosome in a pair holds all the same genes as the other. • So what determines which gene is ...
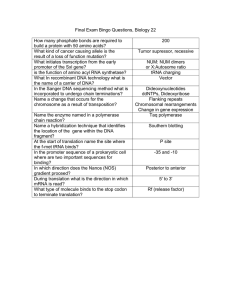
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing method what is incorporated to undergo chain terminations? Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hyb ...
... What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing method what is incorporated to undergo chain terminations? Name a change that occurs for the chromosome as a result of transposition? Name the enzyme named in a polymerase chain reaction? Name a hyb ...
DNA, Genes and Chromosomes
... • The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). ...
... • The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). ...
a10c Biotechnology
... in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzymes are used in the process? What form of bacterial gene transfer is used in the lab to facilit ...
... in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzymes are used in the process? What form of bacterial gene transfer is used in the lab to facilit ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
Chromatin Structure and Gene Regulation
... • Almost all cells of an organism have an identical genome, but only certain genes are expressed in each type of cell – Differential gene expression – cause of expression of different genes by cells with the same genome ...
... • Almost all cells of an organism have an identical genome, but only certain genes are expressed in each type of cell – Differential gene expression – cause of expression of different genes by cells with the same genome ...