DNA
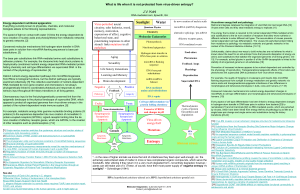
... The Nuclear genome consists of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells – this is what we typically think of as our Genome: A Genome is the unique set of chromosomes (or DNA) in one cell of an organism. • Humans have 2 sets of chromosomes (one from each parent: we are diploid.) • Our genome consists ...
... The Nuclear genome consists of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells – this is what we typically think of as our Genome: A Genome is the unique set of chromosomes (or DNA) in one cell of an organism. • Humans have 2 sets of chromosomes (one from each parent: we are diploid.) • Our genome consists ...
No Slide Title
... of discrete, double-strand breaks caused by nuclease digestion of chromatin. • These correspond to discrete regions of substantially altered chromatin structure – In some cases they lack nucleosomes ...
... of discrete, double-strand breaks caused by nuclease digestion of chromatin. • These correspond to discrete regions of substantially altered chromatin structure – In some cases they lack nucleosomes ...
Transposons_&_DNA_Mutations
... from one generation to the next Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
... from one generation to the next Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
slides
... – ~20,000 protein-‐coding genes were studies, which covers 2.94% of the genome – Non-‐protein coding regions of the genome? • >80% of the genome is funcFonal as regulatory sequences, based on the analysis ...
... – ~20,000 protein-‐coding genes were studies, which covers 2.94% of the genome – Non-‐protein coding regions of the genome? • >80% of the genome is funcFonal as regulatory sequences, based on the analysis ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... Standard tool in biochemistry labs Uses Diagnose disease Identify genes and gene structures Human genome project Understand evolution of plants and animals Genetic engineering of organisms (Example: drought resistant crops Forensic science ...
... Standard tool in biochemistry labs Uses Diagnose disease Identify genes and gene structures Human genome project Understand evolution of plants and animals Genetic engineering of organisms (Example: drought resistant crops Forensic science ...
Techniques in Mouse
... • Conditional mutants are needed when you want to study the effects of a gene in certain tissue late in development but the gene is also necessary early in development. A traditional knockout would result in a mutant that does not develop to stage needed. • Cre is a recombinase that excises DNA loca ...
... • Conditional mutants are needed when you want to study the effects of a gene in certain tissue late in development but the gene is also necessary early in development. A traditional knockout would result in a mutant that does not develop to stage needed. • Cre is a recombinase that excises DNA loca ...
DNA - morescience
... Lactose digestion in E.coli begins with its hydrolysis by the enzyme ß-galactosidase. The gene encoding ß-galactosidase, lacZ, is part of a coordinately regulated operon containing other genes required for lactose utilization. Which of the following figures correctly depicts the interactions at the ...
... Lactose digestion in E.coli begins with its hydrolysis by the enzyme ß-galactosidase. The gene encoding ß-galactosidase, lacZ, is part of a coordinately regulated operon containing other genes required for lactose utilization. Which of the following figures correctly depicts the interactions at the ...
Biology Midterm Review
... 9. Within the cytoplasm of cells there are specific enzymes able to catalyze a specific reaction. How are enzymes able to perform these actions? 10. Based on the Graph what would you conclude about temperature’s effect on enzymes? ...
... 9. Within the cytoplasm of cells there are specific enzymes able to catalyze a specific reaction. How are enzymes able to perform these actions? 10. Based on the Graph what would you conclude about temperature’s effect on enzymes? ...
Gene Cloning and Karyotyping
... • One goal may be to produce a protein product for use. • A second goal may be to prepare many copies of the gene itself. – This may enable scientists to determine the gene’s nucleotide sequence or provide an organism with a new metabolic capability by transferring a gene from another organism. ...
... • One goal may be to produce a protein product for use. • A second goal may be to prepare many copies of the gene itself. – This may enable scientists to determine the gene’s nucleotide sequence or provide an organism with a new metabolic capability by transferring a gene from another organism. ...
Sunlight Water Entropy
... flanking sequences from sunlight to energy metabolism and genetic networks via amino acids and transgenerational epigenetic inheritance of sex differences in morphological and behavioral phenotypes in bulls, cows and humans. [17-18] Conserved molecular mechanisms link nutrient energy-dependent chang ...
... flanking sequences from sunlight to energy metabolism and genetic networks via amino acids and transgenerational epigenetic inheritance of sex differences in morphological and behavioral phenotypes in bulls, cows and humans. [17-18] Conserved molecular mechanisms link nutrient energy-dependent chang ...
Human karyotype
... DNA is packaged into chromosomes • Each human cell contains 2 metres of DNA (3,000,000,000 bases in a haploid cell) • Nucleus is 5 microns (0.005 mm) diameter • DNA must be properly packaged, not just tangled up and stuffed into nucleus • Packaging involves coiling and folding the DNA in specific w ...
... DNA is packaged into chromosomes • Each human cell contains 2 metres of DNA (3,000,000,000 bases in a haploid cell) • Nucleus is 5 microns (0.005 mm) diameter • DNA must be properly packaged, not just tangled up and stuffed into nucleus • Packaging involves coiling and folding the DNA in specific w ...
Chapter 15 Genetics Engineering
... construct organisms that are transgenic, containing genes from other species. S ...
... construct organisms that are transgenic, containing genes from other species. S ...
The Genome of Theobroma Cacao
... have more than two paired sets of chromosomes and may contain three (watermelon), four (cotton) or even eight sets (sugarcane). Genome sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of consecutive DNA “letters” spanning all of the chromosomes of a cell from start to finish (the four chemical ...
... have more than two paired sets of chromosomes and may contain three (watermelon), four (cotton) or even eight sets (sugarcane). Genome sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of consecutive DNA “letters” spanning all of the chromosomes of a cell from start to finish (the four chemical ...
5`-cgaucggauccagcuggacgcuagcguaaaaaaaa-3`
... capillary transfer in alkaline buffer to denature DNA strands ...
... capillary transfer in alkaline buffer to denature DNA strands ...
B3 * student gap fill
... 8. A protein may change shape because: (1) it is _______, (2) wrong ____, (3) the _______of the gene for that protein is wrong (a M___________) 9. The part of the enzyme that works is called the A_____ S_____ – this recognises its substrate 10. Increasing temperature increases the C_____ betwe ...
... 8. A protein may change shape because: (1) it is _______, (2) wrong ____, (3) the _______of the gene for that protein is wrong (a M___________) 9. The part of the enzyme that works is called the A_____ S_____ – this recognises its substrate 10. Increasing temperature increases the C_____ betwe ...
JF lect 5 12
... Arguments in favour of genes being made of DNA • All cells of a given species contain a constant amount of DNA but the types and amounts of proteins differ in different cells • The amount of DNA doubles in every cell just before it divides and an exactly equal amount is distributed to the two dau ...
... Arguments in favour of genes being made of DNA • All cells of a given species contain a constant amount of DNA but the types and amounts of proteins differ in different cells • The amount of DNA doubles in every cell just before it divides and an exactly equal amount is distributed to the two dau ...
Microbial Genetics
... DNA transfer between two bacteria that are in contact with one another Contact between donor and recipient cells is initiated by sex pili DNA is transfer through a conjugation bridge or open pore between donor and recipient cell Mediated by a plasmid, called an F-factor (fertility factor) or a conju ...
... DNA transfer between two bacteria that are in contact with one another Contact between donor and recipient cells is initiated by sex pili DNA is transfer through a conjugation bridge or open pore between donor and recipient cell Mediated by a plasmid, called an F-factor (fertility factor) or a conju ...
DNA replication and inheritance File
... 11 Describe DNA replication (including the role of DNA polymerase), and explain how Meselson and Stahl’s classic experiment provided new data that supported the accepted theory of replication of DNA and refuted competing theories. ...
... 11 Describe DNA replication (including the role of DNA polymerase), and explain how Meselson and Stahl’s classic experiment provided new data that supported the accepted theory of replication of DNA and refuted competing theories. ...
Tic Tac Toe Questions - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 15. WHICH TYPE OF CELL CONTAINS A NUCLEUS? (eukaryotic) 16. IN THE CELL CYCLE, THE PHASE OF NUCLEAR DIVISION IS CALLED? (Mitosis) 17. What is the name of a portion of DNA that codes for a specific protein? (a gene) 18. What has to happen with DNA before a cell can divide? (DNA replication) 19. Enzym ...
... 15. WHICH TYPE OF CELL CONTAINS A NUCLEUS? (eukaryotic) 16. IN THE CELL CYCLE, THE PHASE OF NUCLEAR DIVISION IS CALLED? (Mitosis) 17. What is the name of a portion of DNA that codes for a specific protein? (a gene) 18. What has to happen with DNA before a cell can divide? (DNA replication) 19. Enzym ...
Unit VII: Genetics
... found in the nucleus - Because of ______________________ (2 of each chromosome) ______________________________ __________________________ called _____________________ ...
... found in the nucleus - Because of ______________________ (2 of each chromosome) ______________________________ __________________________ called _____________________ ...
LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... This is a set of lab techniques for combining genes from ...
... This is a set of lab techniques for combining genes from ...
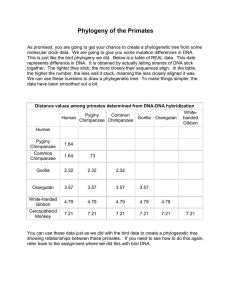
Phylogeny of the Primates
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...