bHLH Transcription Factors in Development and Disease, Vol 110. Current
... bHLH transcription factors. bHLH factors are vastly recognized for their diverse roles in developmental processes and their dysfunction underlies various human pathologies. Each chapter is authoritatively written by a leading expert in the field and discusses every possible aspect of this huge and d ...
... bHLH transcription factors. bHLH factors are vastly recognized for their diverse roles in developmental processes and their dysfunction underlies various human pathologies. Each chapter is authoritatively written by a leading expert in the field and discusses every possible aspect of this huge and d ...
Genomics and Behavior “Central Dogma” Outline
... nucleus to the ribosome • Protein synthesis takes place based on the genetic code • A three base codon codes for an amino acid ...
... nucleus to the ribosome • Protein synthesis takes place based on the genetic code • A three base codon codes for an amino acid ...
concept mapping challenge - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Although there are similarities in the regulation of gene expression in organisms from different domains, there are many differences in chromosome organization, mRNA transcripts, signaling, and cell structure II. Regulation of Transcription Initiation A. Induction and repression of enzyme synthesis ...
... Although there are similarities in the regulation of gene expression in organisms from different domains, there are many differences in chromosome organization, mRNA transcripts, signaling, and cell structure II. Regulation of Transcription Initiation A. Induction and repression of enzyme synthesis ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... Transcription does not happen all the time Operon – the “switch” to ...
... Transcription does not happen all the time Operon – the “switch” to ...
Dr Ishtiaq Regulation of gene expression
... • The repressor binding to the operator interferes with binding of RNA Pol to the promoter, and therefore mRNA encoding LacZ and LacY is only made at very low levels. • When cells are grown in the presence of lactose, however, a lactose metabolite called allolactose , which is a combination of gluco ...
... • The repressor binding to the operator interferes with binding of RNA Pol to the promoter, and therefore mRNA encoding LacZ and LacY is only made at very low levels. • When cells are grown in the presence of lactose, however, a lactose metabolite called allolactose , which is a combination of gluco ...
Document
... There are three stop (termination) codons. They are often called nonsense codons. Genetic Code is degenerate. Some amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. ...
... There are three stop (termination) codons. They are often called nonsense codons. Genetic Code is degenerate. Some amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. ...
No Slide Title
... http://bmb-itservices.bmb.psu.edu/bryant/lab/Project/Hydrogen/index.html#secti on1 •euk have 1 protein/mRNA ...
... http://bmb-itservices.bmb.psu.edu/bryant/lab/Project/Hydrogen/index.html#secti on1 •euk have 1 protein/mRNA ...
Document
... • 13.1 RNA Consisting of a Single Strand of Ribonucleotides Participates in a Variety of Cellular Functions • 13.2 Transcription Is the Synthesis of an RNA Molecule from a DNA Template • 13.3 The Process of Bacterial Transcription Consists of Initiation, Elongation, and Termination • 13.4 The Proces ...
... • 13.1 RNA Consisting of a Single Strand of Ribonucleotides Participates in a Variety of Cellular Functions • 13.2 Transcription Is the Synthesis of an RNA Molecule from a DNA Template • 13.3 The Process of Bacterial Transcription Consists of Initiation, Elongation, and Termination • 13.4 The Proces ...
The Organization and Control of Eukaryotic Genomes
... development. In all organisms, the expression of specific genes is most commonly regulated at the level of transcription by DNA-binding proteins. ...
... development. In all organisms, the expression of specific genes is most commonly regulated at the level of transcription by DNA-binding proteins. ...
Document
... The success of the GO Consortium’s work has been to demonstrate the great utility of shared community ontologies in the genomics community. This success has inspired the development of similar ontologies for other domains and has promoted open collaborations among groups working on similar projects ...
... The success of the GO Consortium’s work has been to demonstrate the great utility of shared community ontologies in the genomics community. This success has inspired the development of similar ontologies for other domains and has promoted open collaborations among groups working on similar projects ...
TITLE OF MODULE: From Gene to Function MODULE NUMBER
... Lecture 6 & 7. Regulation at post-transcriptional level. The trp operon and mechanism of attenuation. Other modes of regulation post-transcriptionally including small RNAs and riboswitches. (MVDW) Lecture 8. Sensing and responding to environmental signals. Two-component sensor regulator systems: int ...
... Lecture 6 & 7. Regulation at post-transcriptional level. The trp operon and mechanism of attenuation. Other modes of regulation post-transcriptionally including small RNAs and riboswitches. (MVDW) Lecture 8. Sensing and responding to environmental signals. Two-component sensor regulator systems: int ...
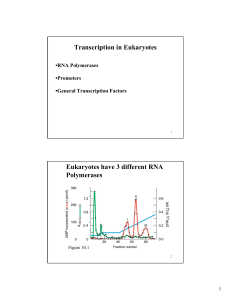
Transcription in Eukaryotes Eukaryotes have 3 different RNA
... beyond TATA box in some promoters • TAFIIs can bind initiator and downstream elements; TAFIIs help initiate transcription from promoters initiators and DPEs •Specifically, TAFII150 and TAFII250 form a ternary complex with TBP and bind to the initiator and DPE -shown by crosslinking and footprinting ...
... beyond TATA box in some promoters • TAFIIs can bind initiator and downstream elements; TAFIIs help initiate transcription from promoters initiators and DPEs •Specifically, TAFII150 and TAFII250 form a ternary complex with TBP and bind to the initiator and DPE -shown by crosslinking and footprinting ...
Chapter 17 - Madeira City Schools
... interspersed between coding segments of the gene. b. Introns = c. Exons = d. signal to splice is a short nucleotide sequence at the end of an intron. e. “small nuclear ribonucleoproteins” (aka…snRNPs) recognize site. f. snRNPs join with others and proteins to make a “spliceosome” (almost the size of ...
... interspersed between coding segments of the gene. b. Introns = c. Exons = d. signal to splice is a short nucleotide sequence at the end of an intron. e. “small nuclear ribonucleoproteins” (aka…snRNPs) recognize site. f. snRNPs join with others and proteins to make a “spliceosome” (almost the size of ...
Gene Regulation
... • Organisms have lots of genetic information, but they don’t necessarily want to use all of it (or use it fully) at one particular time. • Eukaryotes: Development, differentiation, and homeostasis – In going from zygote to fetus, e.g., many genes are used that are then turned off. – Liver cells, bra ...
... • Organisms have lots of genetic information, but they don’t necessarily want to use all of it (or use it fully) at one particular time. • Eukaryotes: Development, differentiation, and homeostasis – In going from zygote to fetus, e.g., many genes are used that are then turned off. – Liver cells, bra ...
DNA Packaging - kyoussef-mci
... circular molecule of naked DNA called a PLASMID DNA is readily available to RNA polymerase control of transcription by regulatory proteins (operon) most of DNA codes for protein or RNA no introns, small amount of non-coding DNA regulatory sequences: promoters, operators ...
... circular molecule of naked DNA called a PLASMID DNA is readily available to RNA polymerase control of transcription by regulatory proteins (operon) most of DNA codes for protein or RNA no introns, small amount of non-coding DNA regulatory sequences: promoters, operators ...
Programming Gene Expression
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
슬라이드 1
... CK1 phosphorylation of APC may induce high-affinity binding to b-cat and trigger its dissociation from LEF-1 ...
... CK1 phosphorylation of APC may induce high-affinity binding to b-cat and trigger its dissociation from LEF-1 ...
File
... 3 One strand of each short doublestranded RNA is degraded; the other strand (miRNA) then associates with a complex of proteins. ...
... 3 One strand of each short doublestranded RNA is degraded; the other strand (miRNA) then associates with a complex of proteins. ...
Transcription in Eukaryotes I and II
... Progressive Deletions and Reporter Gene Assays Assume TTR is a liver specific gene identified in the previous experiment. The upstream regulatory region of this gene was cloned in front of a reporter gene (Reporter Gene: e.g. LacZ, luciferase, GFP). The reporter gene constructs were transiently tran ...
... Progressive Deletions and Reporter Gene Assays Assume TTR is a liver specific gene identified in the previous experiment. The upstream regulatory region of this gene was cloned in front of a reporter gene (Reporter Gene: e.g. LacZ, luciferase, GFP). The reporter gene constructs were transiently tran ...
Foundations of Biology
... of a group of genes (i.e., heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e., metallothionein) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression To achieve high levels of expression, several different transcription factors binding to d ...
... of a group of genes (i.e., heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e., metallothionein) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression To achieve high levels of expression, several different transcription factors binding to d ...
Genetics 16 - Protein Synthesis Transcription Translation
... (15) Each member of the group will play a different role in the process of transcription and translation. We will then switch roles and complete the same processes for several different mutation possibilities. At the end of the lab you will compare how the mutations affected the overall product of p ...
... (15) Each member of the group will play a different role in the process of transcription and translation. We will then switch roles and complete the same processes for several different mutation possibilities. At the end of the lab you will compare how the mutations affected the overall product of p ...
Microbial Genetics
... stop transcription; however the CAP activator does by not binding to the promoter.) • Once glucose runs out the CAP activator binds, and the lac operon is expressed in the presence of lactose. • Why is there a lag in growth when glucose runs out? This is called diauxic growth. ...
... stop transcription; however the CAP activator does by not binding to the promoter.) • Once glucose runs out the CAP activator binds, and the lac operon is expressed in the presence of lactose. • Why is there a lag in growth when glucose runs out? This is called diauxic growth. ...
Gene Regulation
... • Organisms have lots of genetic information, but they don’t necessarily want to use all of it (or use it fully) at one particular time. • Eukaryotes: Development, differentiation, and homeostasis – In going from zygote to fetus, e.g., many genes are used that are then turned off. – Liver cells, bra ...
... • Organisms have lots of genetic information, but they don’t necessarily want to use all of it (or use it fully) at one particular time. • Eukaryotes: Development, differentiation, and homeostasis – In going from zygote to fetus, e.g., many genes are used that are then turned off. – Liver cells, bra ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Kent City School District
... Carries the instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to initiate translation Contains 3-base sequences called “codons” Made in transcription ...
... Carries the instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to initiate translation Contains 3-base sequences called “codons” Made in transcription ...
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor (sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of genetic information from DNA to RNA) to specific genes.A defining feature of transcription factors is that they contain one or more DNA-binding domains (DBDs), which attach to specific sequences of DNA adjacent to the genes that they regulate. Additional proteins such as coactivators, chromatin remodelers, histone acetylases, deacetylases, kinases, and methylases, while also playing crucial roles in gene regulation, lack DNA-binding domains, and, therefore, are not classified as transcription factors.