Construting parallel lines
... Do each Geometric Construction twice (using a compass and straight edge). Mark all new ANGLES, LINES, and congruent parts and box a statement describing the construction. Construct eight pairs of parallel line pairs, given a line and a point off the line. Using Converse of CAP (twice: one acute /. o ...
... Do each Geometric Construction twice (using a compass and straight edge). Mark all new ANGLES, LINES, and congruent parts and box a statement describing the construction. Construct eight pairs of parallel line pairs, given a line and a point off the line. Using Converse of CAP (twice: one acute /. o ...
Math 11 Adv Distance on a sphere – another application of
... latitude are not. Thus, traveling along a line of longitude is traveling on a great circle, while traveling along a line of latitude between two points may seem like the most direct path, but it is not. Our geographic coordinate system is great for figuring distances that are parallel to lines of la ...
... latitude are not. Thus, traveling along a line of longitude is traveling on a great circle, while traveling along a line of latitude between two points may seem like the most direct path, but it is not. Our geographic coordinate system is great for figuring distances that are parallel to lines of la ...
Geometry
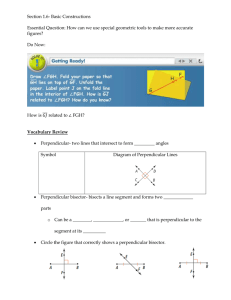
... 1. Explain what a midpoint is. Draw a diagram that contains a midpoint and mark it appropriately to show that the point you drew is actually a midpoint. 2. Explain what a segment bisector is. 3. Explain what an angle bisector is. Directions: For #4 – 7, sketch the following pictures and be sure to m ...
... 1. Explain what a midpoint is. Draw a diagram that contains a midpoint and mark it appropriately to show that the point you drew is actually a midpoint. 2. Explain what a segment bisector is. 3. Explain what an angle bisector is. Directions: For #4 – 7, sketch the following pictures and be sure to m ...
PH-Lect2-1 - LASD Haiku
... 1. We will be talking about constructions today, which is truly something hand’s on! a. This means you make geometric segments or angles using only a compass and a straight edge, but you DON’T use the straight edge as a ruler 1) Note: the above limits were noted in 300 BC by Euclid in Elements b. Th ...
... 1. We will be talking about constructions today, which is truly something hand’s on! a. This means you make geometric segments or angles using only a compass and a straight edge, but you DON’T use the straight edge as a ruler 1) Note: the above limits were noted in 300 BC by Euclid in Elements b. Th ...
constructions
... 3. Swing an arc so the pencil crosses both sides of BAC . This will create two intersection points with the sides (rays) of the angle. 4. Place the compass point on one of these new intersection points on the sides of BAC . If needed, stretch your compass to a sufficient length to place your pencil ...
... 3. Swing an arc so the pencil crosses both sides of BAC . This will create two intersection points with the sides (rays) of the angle. 4. Place the compass point on one of these new intersection points on the sides of BAC . If needed, stretch your compass to a sufficient length to place your pencil ...
point
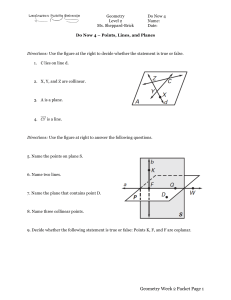
... • A plane is an infinite set of points forming a connected flat surface extending infinitely far in all directions. • A plane has infinite length, infinite width, and zero thickness. It is usually represented in drawings by a four-sided figure. • A single capital cursive letter is used to denote a p ...
... • A plane is an infinite set of points forming a connected flat surface extending infinitely far in all directions. • A plane has infinite length, infinite width, and zero thickness. It is usually represented in drawings by a four-sided figure. • A single capital cursive letter is used to denote a p ...
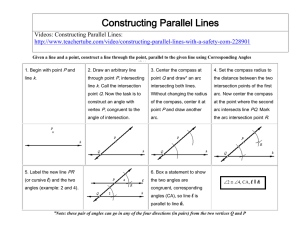
1.3 Constructing Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
... Keep your compass setting the same (you can change it if you want to but the beauty of most constructions is in their simplicity). First, place the compass point at point E and make a small arc below line m. Do the same with the compass point at point F. Label the point where these two arcs intersec ...
... Keep your compass setting the same (you can change it if you want to but the beauty of most constructions is in their simplicity). First, place the compass point at point E and make a small arc below line m. Do the same with the compass point at point F. Label the point where these two arcs intersec ...
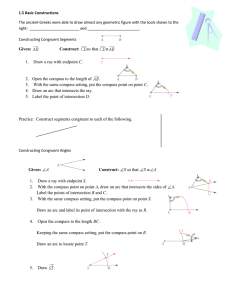
1.5 Basic Constructions The ancient Greeks were able to draw
... Draw a ray with endpoint S. With the compass point on point A, draw an arc that intersects the sides of Label the points of intersection B and C. 3. With the same compass setting, put the compass point on point S. Draw an arc and label its point of intersection with the ray as R. ...
... Draw a ray with endpoint S. With the compass point on point A, draw an arc that intersects the sides of Label the points of intersection B and C. 3. With the same compass setting, put the compass point on point S. Draw an arc and label its point of intersection with the ray as R. ...
Cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the directions of north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials: N, E, S, W. East and west are at right angles to north and south, with east being in the clockwise direction of rotation from north and west being directly opposite east. Intermediate points between the four cardinal directions form the points of the compass. The intermediate (intercardinal, or ordinal) directions are northeast (NE), southeast (SE), southwest (SW), and northwest (NW). Further, the intermediate direction of every set of intercardinal and cardinal direction is called a secondary-intercardinal direction, the eight shortest points in the compass rose to the right, i.e. NNE, ENE, ESE, and so on.