제3회 한국분자세포생물학회 이동성 유전인자분과 학술대회
... Ionizing radiation (IR) effects to genomic instability, which cause chromosomal aberrations, deletions, insertions, and point mutations, is considered to be the precursor of tumorigenesis. Even though effects on radiation exposure in cancer is very well-characterized by numbers of researchers, the u ...
... Ionizing radiation (IR) effects to genomic instability, which cause chromosomal aberrations, deletions, insertions, and point mutations, is considered to be the precursor of tumorigenesis. Even though effects on radiation exposure in cancer is very well-characterized by numbers of researchers, the u ...
12-3: RNA
... Sixty-four combinations are possible when a sequence of three bases are used; thus, 64 different mRNA _________ are in the genetic code. Some codons do not code for amino acids; they provide instructions for making the protein. More than one codon can code for the same amino acid. However, for any o ...
... Sixty-four combinations are possible when a sequence of three bases are used; thus, 64 different mRNA _________ are in the genetic code. Some codons do not code for amino acids; they provide instructions for making the protein. More than one codon can code for the same amino acid. However, for any o ...
86K(a)
... E. none of the above 24.Which one below is not a kind of direct selection method in genetic engineering: A. antibiotic screening B. marker rescue C. in situ hybridization D. nutrition rescue E. enzyme immunodetection assay 25. The sequence acts as modification point in transcription termination in e ...
... E. none of the above 24.Which one below is not a kind of direct selection method in genetic engineering: A. antibiotic screening B. marker rescue C. in situ hybridization D. nutrition rescue E. enzyme immunodetection assay 25. The sequence acts as modification point in transcription termination in e ...
EOC PRACTICE QUESTIONS #2
... The DNA is then transcribed and translated producing the __________. ...
... The DNA is then transcribed and translated producing the __________. ...
Genome Sequences of the Primary Endosymbiont “Candidatus
... to other obligate bacteria living in sap-sucking insects, “Ca. Portiera aleyrodidarum” is thought to provide essential nutrients to whiteflies (2). B. tabaci is a species complex comprised of 11 highlevel genetic groups that are well defined by DNA markers and at least 24 morphologically indistingui ...
... to other obligate bacteria living in sap-sucking insects, “Ca. Portiera aleyrodidarum” is thought to provide essential nutrients to whiteflies (2). B. tabaci is a species complex comprised of 11 highlevel genetic groups that are well defined by DNA markers and at least 24 morphologically indistingui ...
Regulation & Mutations
... • Prokaryotes turn genes on and off by controlling transcription • Promoter • DNA segment that allows a gene to be transcribed • Helps RNA polymerase find where the gene starts • Operator • DNA segment that turns genes on or off • Operon • Region of DNA including the promoter, the operator, and gene ...
... • Prokaryotes turn genes on and off by controlling transcription • Promoter • DNA segment that allows a gene to be transcribed • Helps RNA polymerase find where the gene starts • Operator • DNA segment that turns genes on or off • Operon • Region of DNA including the promoter, the operator, and gene ...
ppt
... Us Uniquely Human?>How Are Memories Stored and Retrieved?>How Did Cooperative Behavior Evolve?>How Will Big Pictures Emerge from a Sea of Biological Data?>How Far Can We Push Chemical Self-Assembly?>What Are the Limits of ...
... Us Uniquely Human?>How Are Memories Stored and Retrieved?>How Did Cooperative Behavior Evolve?>How Will Big Pictures Emerge from a Sea of Biological Data?>How Far Can We Push Chemical Self-Assembly?>What Are the Limits of ...
2) Overview of the human genome
... for the ova, the female has a chromosome from her mother (a) and her father (b) that can be used. ...
... for the ova, the female has a chromosome from her mother (a) and her father (b) that can be used. ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering
... in a population by inducing mutations, which are the ultimate source of genetic ...
... in a population by inducing mutations, which are the ultimate source of genetic ...
DNA replication.
... containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made strand. This process isn't perfect and sometimes the proteins make mistakes and put the wrong nucleotide into the strand they are building.This causes a change in the sequence of that gene.These changes in DNA sequence are called mutations. M ...
... containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made strand. This process isn't perfect and sometimes the proteins make mistakes and put the wrong nucleotide into the strand they are building.This causes a change in the sequence of that gene.These changes in DNA sequence are called mutations. M ...
Chapter 14 When Allele Frequencies Stay Constant
... 2. For X-linked recessive traits, the frequency of the recessive allele in males is q and in females it is q 2. 3. For very rare inherited disorders, p approaches 1, so the carrier frequency is essentially 2q (approximately twice the frequency of the disease-causing allele). 14.4 DNA Profiling is B ...
... 2. For X-linked recessive traits, the frequency of the recessive allele in males is q and in females it is q 2. 3. For very rare inherited disorders, p approaches 1, so the carrier frequency is essentially 2q (approximately twice the frequency of the disease-causing allele). 14.4 DNA Profiling is B ...
protein synthesis
... The steps in this part of the process are: 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA strand and unwinds a short section (about 12 base pairs long) 2. This then travels along the DNA strand building an RNA molecule from the TEMPLATE STRAND ...
... The steps in this part of the process are: 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA strand and unwinds a short section (about 12 base pairs long) 2. This then travels along the DNA strand building an RNA molecule from the TEMPLATE STRAND ...
Genomics
... passed on to successive generations. Although usually attributed to Jean Baptiste Lamarck, it was a commonly accepted method of inheritance in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The rise of the “modern synthesis” of evolution rejects this mode of inheritance, but recent findings in epigenetics ...
... passed on to successive generations. Although usually attributed to Jean Baptiste Lamarck, it was a commonly accepted method of inheritance in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The rise of the “modern synthesis” of evolution rejects this mode of inheritance, but recent findings in epigenetics ...
Document
... A specific sequence of nucleotides in a section of DNA that performs a specific function ...
... A specific sequence of nucleotides in a section of DNA that performs a specific function ...
DNA AND PROTIEN SYNTHESIS-
... Gene silencing (i.e., preventing gene use by making them inaccessible) can be cause by (but is not limited to): ...
... Gene silencing (i.e., preventing gene use by making them inaccessible) can be cause by (but is not limited to): ...
Chapter 16 - HCC Learning Web
... release the transcript, which is available for immediate use as mRNA. In eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain while RNA polymerase II continues to transcribe the DNA. Transcription is terminated when the polymerase eventually falls off the DNA. The mRNA is further processed ...
... release the transcript, which is available for immediate use as mRNA. In eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain while RNA polymerase II continues to transcribe the DNA. Transcription is terminated when the polymerase eventually falls off the DNA. The mRNA is further processed ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation
... 5. Look at the “Universal Genetic Code Chart.” Which codon (set of 3 bases) in RNA codes for the “Met” amino acid? Write the correct bases below. ___ ___ ___ 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green wind ...
... 5. Look at the “Universal Genetic Code Chart.” Which codon (set of 3 bases) in RNA codes for the “Met” amino acid? Write the correct bases below. ___ ___ ___ 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green wind ...
DNA Workshop
... The single molecule of DNA in the bacteria, E. coli contains 4.7 x 106 nucleotide pairs. DNA replication begins at a single, fixed location in this molecule, called the replication origin, it proceeds at about _______ nucleotides per second, and thus is done in approximately _____ minutes. The avera ...
... The single molecule of DNA in the bacteria, E. coli contains 4.7 x 106 nucleotide pairs. DNA replication begins at a single, fixed location in this molecule, called the replication origin, it proceeds at about _______ nucleotides per second, and thus is done in approximately _____ minutes. The avera ...
Brooker Chapter 17
... Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid)
... The Process of Heat Shock • Helps to increase the bacterial uptake of foreign DNA • Membrane becomes more permeable to DNA • Time is essential: -ice water bath (42ºC) for 50 sec. ice ...
... The Process of Heat Shock • Helps to increase the bacterial uptake of foreign DNA • Membrane becomes more permeable to DNA • Time is essential: -ice water bath (42ºC) for 50 sec. ice ...
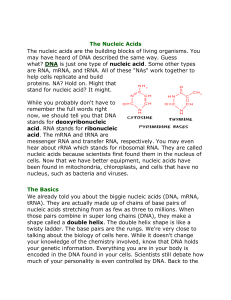
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. You may have heard of DNA described the same way. Guess what? DNA is just one type of nucleic acid. Some other types are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might ...
... The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. You may have heard of DNA described the same way. Guess what? DNA is just one type of nucleic acid. Some other types are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might ...
Genetic engineering
... Step 2: Cut it out of the chromosome (in daffodil) using restriction enzymes. Restrictions enzymes are bacterial proteins that have the ability to cut both strands of the DNA molecule at a specific nucleotide sequence Resulting fragments can have blunt ends or sticky ends ...
... Step 2: Cut it out of the chromosome (in daffodil) using restriction enzymes. Restrictions enzymes are bacterial proteins that have the ability to cut both strands of the DNA molecule at a specific nucleotide sequence Resulting fragments can have blunt ends or sticky ends ...