Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... b. Taq polymerase is a heat-stable form of DNA polymerase that can function after exposure to high temperatures that are necessary for PCR. c. Taq polymerase is easier to isolate than other DNA polymerases. d. Taq polymerase is the DNA polymerase commonly produced by most eukaryotic cells. e. All of ...
... b. Taq polymerase is a heat-stable form of DNA polymerase that can function after exposure to high temperatures that are necessary for PCR. c. Taq polymerase is easier to isolate than other DNA polymerases. d. Taq polymerase is the DNA polymerase commonly produced by most eukaryotic cells. e. All of ...
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis
... Codon and Protein synthesis 2. Translation-Nucleotide sequence of mRNA used to synthesize a sequence of amino acids a. Occurs on the endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) b. mRNA codons are used to specify amino acids c. Ribosomes "read" mRNA codons to synthesize a specific amino acid sequence d. Each o ...
... Codon and Protein synthesis 2. Translation-Nucleotide sequence of mRNA used to synthesize a sequence of amino acids a. Occurs on the endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) b. mRNA codons are used to specify amino acids c. Ribosomes "read" mRNA codons to synthesize a specific amino acid sequence d. Each o ...
File
... • You also need to include in your own words what mitosis and meiosis is. • Do not quickly do this. Spend time on it making it detailed. ...
... • You also need to include in your own words what mitosis and meiosis is. • Do not quickly do this. Spend time on it making it detailed. ...
chapter 10
... ____ 31. The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins are called a. mutons. c. introns. b. exons. d. exposons. ____ 32. The non-coding portions of DNA that are separated from the portions of DNA actually used during transcription are called a. mutons. c. introns. b ...
... ____ 31. The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins are called a. mutons. c. introns. b. exons. d. exposons. ____ 32. The non-coding portions of DNA that are separated from the portions of DNA actually used during transcription are called a. mutons. c. introns. b ...
Transcription & Translation
... All genes produce RNA of some kind (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA!) Structural Genes: produce proteins that become part of the structure and function of organisms Regulator Genes Produce proteins that control the action of other genes Example: Homeotic Genes in insects; HOX genes in Mammals. Actions of Reg ...
... All genes produce RNA of some kind (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA!) Structural Genes: produce proteins that become part of the structure and function of organisms Regulator Genes Produce proteins that control the action of other genes Example: Homeotic Genes in insects; HOX genes in Mammals. Actions of Reg ...
Student Worksheet Hands-on Activity Viral DNA Integration
... The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects and destroys cells of the immune system called helper T cells. Over time, HIV infection weakens a person’s ability to fight other infections and some diseases. The advanced stage of HIV infection is termed acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). An ...
... The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects and destroys cells of the immune system called helper T cells. Over time, HIV infection weakens a person’s ability to fight other infections and some diseases. The advanced stage of HIV infection is termed acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). An ...
Trends in Biotechnology
... create double-stranded DNA from RNA template, so that the DNA can integrate into the host cell’s genome. It needs to infect actively dividing cells. Adenovirus — a double-stranded DNA virus that can infect many types of host cells with high efficiency, with a low chance for causing disease. It does ...
... create double-stranded DNA from RNA template, so that the DNA can integrate into the host cell’s genome. It needs to infect actively dividing cells. Adenovirus — a double-stranded DNA virus that can infect many types of host cells with high efficiency, with a low chance for causing disease. It does ...
Cytology
... repeats are considered to be a hallmark of DNA insertion. Two classes of pseudo genes exist: (1) Traditional pseudo genes (as exemplified in the globin gene families) appear to have originated by gene duplication and been subsequently silenced by point mutations, small insertions, and deletions; the ...
... repeats are considered to be a hallmark of DNA insertion. Two classes of pseudo genes exist: (1) Traditional pseudo genes (as exemplified in the globin gene families) appear to have originated by gene duplication and been subsequently silenced by point mutations, small insertions, and deletions; the ...
Composite Transposons
... 700 to 5000 bp which can move from one location in a DNA sequence to another. They have short 16-41 bp inverted repeats on their ends. They encode a transposase which catalyses site-specific recombination. ...
... 700 to 5000 bp which can move from one location in a DNA sequence to another. They have short 16-41 bp inverted repeats on their ends. They encode a transposase which catalyses site-specific recombination. ...
TRANSCRIPTION TO TRANSLATION
... 5) Make the necessary modifications to this mRNA so that it can i) find the ribosome, and ii) avoid degradation (see course notes – posttranscriptional processing) 6) Rewrite this mRNA sequence with the modifications you made in #5 by cutting out the intron sequences (italicized sections ONLY!). Wha ...
... 5) Make the necessary modifications to this mRNA so that it can i) find the ribosome, and ii) avoid degradation (see course notes – posttranscriptional processing) 6) Rewrite this mRNA sequence with the modifications you made in #5 by cutting out the intron sequences (italicized sections ONLY!). Wha ...
Chapter 10 Topic: RNA transcription Main concepts: •Beadle and
... codon is inserted or deleted, it will change only one amino acid. But if a single base is inserted or deleted, it changes the entire reading frame so that it codes for an entirely different sequence of amino acids. • Point mutations may or may not cause a problem. Redundancy in the genetic code (the ...
... codon is inserted or deleted, it will change only one amino acid. But if a single base is inserted or deleted, it changes the entire reading frame so that it codes for an entirely different sequence of amino acids. • Point mutations may or may not cause a problem. Redundancy in the genetic code (the ...
Topic: Genetics Aim: Describe some methods that can be used to
... Directions: Read the text below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1-14. Genetic engineering involves biological and chemical methods to change the arrangement of a gene’s DNA. One method of genetic engineering is gene splicing, or recombinant DNA which involves bringing together genetic mate ...
... Directions: Read the text below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1-14. Genetic engineering involves biological and chemical methods to change the arrangement of a gene’s DNA. One method of genetic engineering is gene splicing, or recombinant DNA which involves bringing together genetic mate ...
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): produced in the nucleus, makes up part of the ribosomes. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA): shuttles amino acids to the ribosomes. It's responsible for bringing the correct amino acids into place at the appropriate time. It does this by reading th ...
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): produced in the nucleus, makes up part of the ribosomes. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA): shuttles amino acids to the ribosomes. It's responsible for bringing the correct amino acids into place at the appropriate time. It does this by reading th ...
Gene Expression/Mutations
... there is no function because it goes to so much work to keep them and remove them. - Study done where they spliced out introns of a plant leaf and crossed it: the resulting leaf was very different than original leaf. - It is thought that introns add evolutionary flexibility. ...
... there is no function because it goes to so much work to keep them and remove them. - Study done where they spliced out introns of a plant leaf and crossed it: the resulting leaf was very different than original leaf. - It is thought that introns add evolutionary flexibility. ...
File
... Bacterial DNA is made up of the same things that eukaryotic DNA is made of, but the overall structure is different. In bacteria, DNA exists in two forms: 1. Chromosome– bacteria have one chromosome, and it consists of DNA in a double helix in a closed loop. This chromosome occupies about ½ of the to ...
... Bacterial DNA is made up of the same things that eukaryotic DNA is made of, but the overall structure is different. In bacteria, DNA exists in two forms: 1. Chromosome– bacteria have one chromosome, and it consists of DNA in a double helix in a closed loop. This chromosome occupies about ½ of the to ...
Document
... • The genes are inherit from both parents but the offspring’s phenotype is determined not by its own phenotype but by the genotype of the mother. • The substances present in the cytoplasm of an egg are pivotal in early development. Example: shell coiling of the snail Limnaea peregra. ...
... • The genes are inherit from both parents but the offspring’s phenotype is determined not by its own phenotype but by the genotype of the mother. • The substances present in the cytoplasm of an egg are pivotal in early development. Example: shell coiling of the snail Limnaea peregra. ...
first of four for Chapter 9
... • Low copy number, 100 kb • F+ vs F• Pilus (pl., pili), a tube-like structure that connects two cells undergoing conjugation. • 20 genes necessary for pilus assembly and DNA transfer. ...
... • Low copy number, 100 kb • F+ vs F• Pilus (pl., pili), a tube-like structure that connects two cells undergoing conjugation. • 20 genes necessary for pilus assembly and DNA transfer. ...
DNA Replication: Seeing Double
... the Leading and Lagging strands two complete strands of DNA separate from one another. ...
... the Leading and Lagging strands two complete strands of DNA separate from one another. ...
2.7 quiz - Peoria Public Schools
... A certain gene in a bacterium codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. How many nucleotides are needed in the mRNA to code for this polypeptide? A. ...
... A certain gene in a bacterium codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. How many nucleotides are needed in the mRNA to code for this polypeptide? A. ...
BioKnowledgy Quick Quiz on DNA replication, transcription, and
... A certain gene in a bacterium codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. How many nucleotides are needed in the mRNA to code for this polypeptide? A. ...
... A certain gene in a bacterium codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. How many nucleotides are needed in the mRNA to code for this polypeptide? A. ...
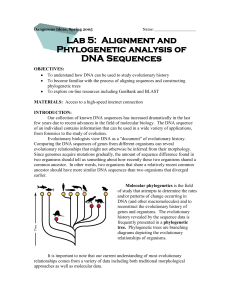
Align the DNA sequences
... of an individual contains information that can be used in a wide variety of applications, from forensics to the study of evolution. Evolutionary biologists view DNA as a “document” of evolutionary history. Comparing the DNA sequences of genes from different organisms can reveal evolutionary relation ...
... of an individual contains information that can be used in a wide variety of applications, from forensics to the study of evolution. Evolutionary biologists view DNA as a “document” of evolutionary history. Comparing the DNA sequences of genes from different organisms can reveal evolutionary relation ...
Horizontal Gene Transfer in Prokaryotes
... Prokaryotic cells are about 1 micrometer or less in size, and the cells come in a few different shapes. Unlike in the eukaryotes, the double-stranded chromosome of prokaryotes is not surrounded by a membrane; prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. They have about 1/1000 of the DNA of human cells. Prokar ...
... Prokaryotic cells are about 1 micrometer or less in size, and the cells come in a few different shapes. Unlike in the eukaryotes, the double-stranded chromosome of prokaryotes is not surrounded by a membrane; prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. They have about 1/1000 of the DNA of human cells. Prokar ...
Slayt 1
... Any strand of DNA can be transcribed No need for helicases, topoisomerases, primers RNA polymerase: 4 chains 2alpha, beta, Beta’ Promoter is recognised by the factor sigma ...
... Any strand of DNA can be transcribed No need for helicases, topoisomerases, primers RNA polymerase: 4 chains 2alpha, beta, Beta’ Promoter is recognised by the factor sigma ...