Whatever happened to the Floreana Mockingbird?
... mockingbird but not others. N. trifasciatus. though, was common on FIoreana when Porter visited the island in 1813 while patrolling the archipelago in the U.S. Frigate Essex. (Porter, 1815). It seems eertain that even if Darwin did not calleet mockingbirds on Floreana, he did see mockingbirds there ...
... mockingbird but not others. N. trifasciatus. though, was common on FIoreana when Porter visited the island in 1813 while patrolling the archipelago in the U.S. Frigate Essex. (Porter, 1815). It seems eertain that even if Darwin did not calleet mockingbirds on Floreana, he did see mockingbirds there ...
Marbled Murrelet - Endangered Species Coalition
... While the Northwest Forest Plan has been effective at restoring murrelet habitat, this is a very slow process given the condition of the landscape. Here are some details from the monitoring report: …it can take more than 100 years for Class 2 habitat to become Class 3 and more than 200 years to beco ...
... While the Northwest Forest Plan has been effective at restoring murrelet habitat, this is a very slow process given the condition of the landscape. Here are some details from the monitoring report: …it can take more than 100 years for Class 2 habitat to become Class 3 and more than 200 years to beco ...
Wildlife Habitat Improvements in Wetlands
... generally exhibit low plant species diversity and do not provide the quality of wildlife habitat that similar type wetlands having an undisturbed plant community would provide. These wetlands would typically have a vegetative diversity rating of “low” as measured by the Minnesota Routine Assessment ...
... generally exhibit low plant species diversity and do not provide the quality of wildlife habitat that similar type wetlands having an undisturbed plant community would provide. These wetlands would typically have a vegetative diversity rating of “low” as measured by the Minnesota Routine Assessment ...
Metacommunity Dynamics: Decline of Functional
... urbanization than their hosts [12,30,31] and the absence of higher trophic levels can affect the population dynamics of lower levels and even the stability of the trophic system as a whole [32]. Recent plant-insect community studies showed that interactions between species were influenced either by ...
... urbanization than their hosts [12,30,31] and the absence of higher trophic levels can affect the population dynamics of lower levels and even the stability of the trophic system as a whole [32]. Recent plant-insect community studies showed that interactions between species were influenced either by ...
HABIT-CHANGE Priority matrix impacts per region and habitat
... based on a literature review (see Output 3.1.1). They will give a broader overview on the topic and allow for a comparison of the data from investigation areas with information provided on a more general scale. The information on impacts per investigation area in chapter 4 is based on expert knowled ...
... based on a literature review (see Output 3.1.1). They will give a broader overview on the topic and allow for a comparison of the data from investigation areas with information provided on a more general scale. The information on impacts per investigation area in chapter 4 is based on expert knowled ...
Colonization in metapopulations: a review of
... Colonization studies in natural systems have encountered at least three major difficulties. Except under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g. Forney & Gilpin, 1989), it has been difficult to estimate the relative importance, or even the existence of different types of stochasticity. Another diffic ...
... Colonization studies in natural systems have encountered at least three major difficulties. Except under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g. Forney & Gilpin, 1989), it has been difficult to estimate the relative importance, or even the existence of different types of stochasticity. Another diffic ...
Dispersal traits determine plant response to habitat
... Johst et al. 2002). Plants will be most vulnerable to fragmentation if their capacities for local persistence and dispersal among patches are low. Translated to a functional perspective, this means that traits enabling a species to survive within and to move between habitat patches confer the abilit ...
... Johst et al. 2002). Plants will be most vulnerable to fragmentation if their capacities for local persistence and dispersal among patches are low. Translated to a functional perspective, this means that traits enabling a species to survive within and to move between habitat patches confer the abilit ...
On size and area: Patterns of mammalian body size extremes
... because one of the explanations for the pattern (see below) is framed in terms of the relationship between ecological traits ± at the level of organisms and populations ± and body size. Thus the use of body size as the independent variable in our analyses is justi®ed to the extent that we are not lo ...
... because one of the explanations for the pattern (see below) is framed in terms of the relationship between ecological traits ± at the level of organisms and populations ± and body size. Thus the use of body size as the independent variable in our analyses is justi®ed to the extent that we are not lo ...
Consequences of forest fragmentation for the dynamics of bird
... evaluate whether birds are likely to possess metapopulation dynamics in fragmented forests. Bird populations in forest ecosystems provide good opportunities to study the consequences of habitat fragmentation for two reasons: first, birds are easy to observe and their habitat affinities are mostly we ...
... evaluate whether birds are likely to possess metapopulation dynamics in fragmented forests. Bird populations in forest ecosystems provide good opportunities to study the consequences of habitat fragmentation for two reasons: first, birds are easy to observe and their habitat affinities are mostly we ...
The metacommunity concept
... by other kinds of spatial dynamics, such as the flow of individuals that create mass effects (Shmida & Wilson 1985) and source–sink dynamics (Holt 1985; Pulliam 1988). These dynamics involve interactions among local communities at larger scales that we refer to as metacommunities. We define a metaco ...
... by other kinds of spatial dynamics, such as the flow of individuals that create mass effects (Shmida & Wilson 1985) and source–sink dynamics (Holt 1985; Pulliam 1988). These dynamics involve interactions among local communities at larger scales that we refer to as metacommunities. We define a metaco ...
Leibold et al. 2004
... by other kinds of spatial dynamics, such as the flow of individuals that create mass effects (Shmida & Wilson 1985) and source–sink dynamics (Holt 1985; Pulliam 1988). These dynamics involve interactions among local communities at larger scales that we refer to as metacommunities. We define a metaco ...
... by other kinds of spatial dynamics, such as the flow of individuals that create mass effects (Shmida & Wilson 1985) and source–sink dynamics (Holt 1985; Pulliam 1988). These dynamics involve interactions among local communities at larger scales that we refer to as metacommunities. We define a metaco ...
Beyond species loss: The extinction of ecological
... Box 1: Predicting interaction losses in a changing world We define an axis of habitat loss (x) that ranges from a pristine, undisturbed stage (zero) to a stage (one) of complete disturbance where all species present in the zero stage have lost their habitat. This axis may represent a reversed area ax ...
... Box 1: Predicting interaction losses in a changing world We define an axis of habitat loss (x) that ranges from a pristine, undisturbed stage (zero) to a stage (one) of complete disturbance where all species present in the zero stage have lost their habitat. This axis may represent a reversed area ax ...
Beyond species loss: the extinction of ecological interactions in a
... Box 1: Predicting interaction losses in a changing world We define an axis of habitat loss (x) that ranges from a pristine, undisturbed stage (zero) to a stage (one) of complete disturbance where all species present in the zero stage have lost their habitat. This axis may represent a reversed area ax ...
... Box 1: Predicting interaction losses in a changing world We define an axis of habitat loss (x) that ranges from a pristine, undisturbed stage (zero) to a stage (one) of complete disturbance where all species present in the zero stage have lost their habitat. This axis may represent a reversed area ax ...
Chapter 50 Conservation Biology
... – Biodiversity brought about by evolutionary change has value in and of itself. Mader: Biology 8th Ed. ...
... – Biodiversity brought about by evolutionary change has value in and of itself. Mader: Biology 8th Ed. ...
Blue-grey Taildropper Fact Sheet
... mycorrhizal fungi, which grow on the roots of many trees, capturing nutrients from the soil and transferring it to the roots. This is beneficial to the plants and helps to create thriving forests (HAT, 2012). It appears that this species is of little threat to horticulture, as it prefers forest habi ...
... mycorrhizal fungi, which grow on the roots of many trees, capturing nutrients from the soil and transferring it to the roots. This is beneficial to the plants and helps to create thriving forests (HAT, 2012). It appears that this species is of little threat to horticulture, as it prefers forest habi ...
a landscape simulation model for understanding animal
... in the habitat (e.g. , for two resources that occur equally in a habitat, each has a resource-proportion of 0.5). • A patch is the area composed of all adjacent cells sharing a habitat type where the local-scale processes take place. Individuals of a species in one patch (population) interact among ...
... in the habitat (e.g. , for two resources that occur equally in a habitat, each has a resource-proportion of 0.5). • A patch is the area composed of all adjacent cells sharing a habitat type where the local-scale processes take place. Individuals of a species in one patch (population) interact among ...
THE GREATER SAGE
... Activities may have an effect if occurring directly on critical habitat, and may also have negative impacts if they occur some distance away. For example, Greater Sage-Grouse are known to be sensitive to loud noises and may abandon critical habitat as the result of noisy activity. Greater Sage-Grous ...
... Activities may have an effect if occurring directly on critical habitat, and may also have negative impacts if they occur some distance away. For example, Greater Sage-Grouse are known to be sensitive to loud noises and may abandon critical habitat as the result of noisy activity. Greater Sage-Grous ...
Pimm_pages 1..10 - Department of Geographical Sciences
... of incomplete knowledge. So how many eukaryote species are there (4)? For land plants, there are 298,900 accepted species’ names, 477,601 synonyms, and 263,925 names unresolved (5). Because the accepted names among those resolved is 38%, it seems reasonable to predict that the same proportion of unr ...
... of incomplete knowledge. So how many eukaryote species are there (4)? For land plants, there are 298,900 accepted species’ names, 477,601 synonyms, and 263,925 names unresolved (5). Because the accepted names among those resolved is 38%, it seems reasonable to predict that the same proportion of unr ...
Staddon et al 2010
... Gonzalez et al. 2009) asserts that productivity and stability of ecosystem functions are dependent on the rate of dispersal within fragmented landscapes. We tested a prediction from the spatial insurance hypothesis (Loreau et al. 2003), that habitat connectivity mediates the magnitude and timing of ...
... Gonzalez et al. 2009) asserts that productivity and stability of ecosystem functions are dependent on the rate of dispersal within fragmented landscapes. We tested a prediction from the spatial insurance hypothesis (Loreau et al. 2003), that habitat connectivity mediates the magnitude and timing of ...
Conservation biology as a profession[edit]
... those that are readily fossilized. The labels of the "Big Five" extinction events are clickable hyperlinks; see Extinction event for more details. (source and image info) Extinction rates are measured in a variety of ways. Conservation biologists measure and apply statistical measures of fossil reco ...
... those that are readily fossilized. The labels of the "Big Five" extinction events are clickable hyperlinks; see Extinction event for more details. (source and image info) Extinction rates are measured in a variety of ways. Conservation biologists measure and apply statistical measures of fossil reco ...
Laurance 2008 - Reed F. Noss Lab at the University of Central
... relationships is a litmus test for IBT (Gilbert, 1980; Abbott, 1983) because other biogeographic phenomena, such as the species–area relationship, can arise for reasons aside from those hypothesized by IBT (for example, higher habitat diversity, rather than lower extinction rates, can cause species ...
... relationships is a litmus test for IBT (Gilbert, 1980; Abbott, 1983) because other biogeographic phenomena, such as the species–area relationship, can arise for reasons aside from those hypothesized by IBT (for example, higher habitat diversity, rather than lower extinction rates, can cause species ...
Experimental Zoogeography of Islands
... colonist. This definition says nothing about whether food and a breeding site exist; a species whose propagule lands on one of our islands is a colonist even if it is doomed to quick extinction for purely physical reasons (e.g., the absence of a suitable nest site in the Rhizophora for a given speci ...
... colonist. This definition says nothing about whether food and a breeding site exist; a species whose propagule lands on one of our islands is a colonist even if it is doomed to quick extinction for purely physical reasons (e.g., the absence of a suitable nest site in the Rhizophora for a given speci ...
Fauna Technical Note No. 18 Threatened frogs 1
... waterbodies (to approx 1.5 m deep) where there is generally a complex vegetation structure including emergent and submerged plants. However, they have also been found using farm dams frequented by stock that have polluted water and no aquatic vegetation (Threatened Species Section 2014). In addition ...
... waterbodies (to approx 1.5 m deep) where there is generally a complex vegetation structure including emergent and submerged plants. However, they have also been found using farm dams frequented by stock that have polluted water and no aquatic vegetation (Threatened Species Section 2014). In addition ...
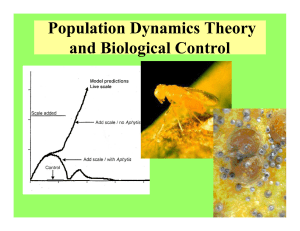
Biocontrol and Population Dynamics Theory
... Two mechanisms are possible” 1. Many desynchronized populations 2. Systems in which the host is a better colonizer than the natural enemy, conferring on it some “enemy free” habitat patches ...
... Two mechanisms are possible” 1. Many desynchronized populations 2. Systems in which the host is a better colonizer than the natural enemy, conferring on it some “enemy free” habitat patches ...
Chapter 3 - Santa Rosa Home
... populations and communities Some introduced species thrive in their new environments, eliminating native species Native island species are particularly vulnerable Evolved in isolation with limited need for defenses ...
... populations and communities Some introduced species thrive in their new environments, eliminating native species Native island species are particularly vulnerable Evolved in isolation with limited need for defenses ...

















![Conservation biology as a profession[edit]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000226038_1-05c49ceb5ea1e28cf988051086edd157-300x300.png)