Using DNA Subway in the Classroom Red Line Lesson
... subway to examine new data, which can result in novel findings. ...
... subway to examine new data, which can result in novel findings. ...
Biotechnology and its applications - MrsGorukhomework
... took about 10 years.) Thought that DNA → RNA → proteins → control the body, based on that and looking at all the different phenotypes, figured we must have a lot of genes, 100, 000’s. Only about 25, 000. (doesn’t seem to be enough to account for all the different varieties) And found that most of th ...
... took about 10 years.) Thought that DNA → RNA → proteins → control the body, based on that and looking at all the different phenotypes, figured we must have a lot of genes, 100, 000’s. Only about 25, 000. (doesn’t seem to be enough to account for all the different varieties) And found that most of th ...
Restriction Enzymes, Vectors, and Genetic Libraries
... . Produce fragments of DNA using enzymes that cut DNA at specific base sequences. . Link these fragments to selfreplicating forms of DNA = vectors. ...
... . Produce fragments of DNA using enzymes that cut DNA at specific base sequences. . Link these fragments to selfreplicating forms of DNA = vectors. ...
Bioinformatics programming exercise II
... together by nucleotide bonds, where A (Adenine) only binds with T (Thymine) and G (Guanine) always with C (Cytosine). Scientists say that each strand of the double helix is a chemical “mirror image” of its vis-àvis. When cells divide, the two strands of the double helix will be separated and each of ...
... together by nucleotide bonds, where A (Adenine) only binds with T (Thymine) and G (Guanine) always with C (Cytosine). Scientists say that each strand of the double helix is a chemical “mirror image” of its vis-àvis. When cells divide, the two strands of the double helix will be separated and each of ...
Lab Quiz 4 Key
... 6. In the bacterial transformation lab, what were the dependent variables? (0.5 pt) [growth of colonies and whether the bacteria glow or not] ...
... 6. In the bacterial transformation lab, what were the dependent variables? (0.5 pt) [growth of colonies and whether the bacteria glow or not] ...
Immunology
... bringing together different gene segments – VJ encodes the variable region of light chains – VDJ encodes varible region of heavy chains ...
... bringing together different gene segments – VJ encodes the variable region of light chains – VDJ encodes varible region of heavy chains ...
Misconceptions relating to DNA and RNA
... Amino acids enter through the nuclear pores similar to nucleotides Amino acids are aligned with mRNA strand through trial and error similar to the jigsaw activity That DNA, in this helical structure, will stay straight and upright, that it won’t coil up around itself and other DNA molecules in order ...
... Amino acids enter through the nuclear pores similar to nucleotides Amino acids are aligned with mRNA strand through trial and error similar to the jigsaw activity That DNA, in this helical structure, will stay straight and upright, that it won’t coil up around itself and other DNA molecules in order ...
DNA Replication
... Eukaryotic cell has 2 genomes Nuclear genome Mitochondrial genome If not specified, “genome” usually refers to the nuclear genome. ...
... Eukaryotic cell has 2 genomes Nuclear genome Mitochondrial genome If not specified, “genome” usually refers to the nuclear genome. ...
made of three parts sugar, phosphate, and base Scientist that
... Scientist who worked with pneumonia & mice & discovered transformation ...
... Scientist who worked with pneumonia & mice & discovered transformation ...
Document
... Reading DNA The bases of a helix become a DNA sequence. Example: When you write a letter, you put together words using different letters of the alphabet. With twenty-six letters you can say anything you want. It is important that the letters go in the right order. This sentence stops making sense wh ...
... Reading DNA The bases of a helix become a DNA sequence. Example: When you write a letter, you put together words using different letters of the alphabet. With twenty-six letters you can say anything you want. It is important that the letters go in the right order. This sentence stops making sense wh ...
NAME CH11 In class assignment Due 2/18/14 Across 1. Initials of
... 3. Separates DNA into fragments by using an electrical current through a gel- ELECTROPHORESIS 4. Circular DNA commonly inserted into bacteria to allow for multiplication- PLASMID 6. Number of loci that the FBI needs from a suspect's DNA- THIRTEEN 10. Organism that contains DNA from a different speci ...
... 3. Separates DNA into fragments by using an electrical current through a gel- ELECTROPHORESIS 4. Circular DNA commonly inserted into bacteria to allow for multiplication- PLASMID 6. Number of loci that the FBI needs from a suspect's DNA- THIRTEEN 10. Organism that contains DNA from a different speci ...
Social Science
... Genes come from proteins. Each specific gene comes from a specific polypeptide within a protein. Now proteins are extremely important in living organisms. Some proteins are structural. Others, for example, are enzymes. A typical gene is about a thousand base pairs or so. Now that may seem rather a l ...
... Genes come from proteins. Each specific gene comes from a specific polypeptide within a protein. Now proteins are extremely important in living organisms. Some proteins are structural. Others, for example, are enzymes. A typical gene is about a thousand base pairs or so. Now that may seem rather a l ...
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis sharepoint
... Protein Synthesis • the transfer of genetic material to the ribosome but DNA stays in the nucleus! • Gene expression = use of DNA information to form proteins – 2 stages → – first is transcription = mRNA copy is made. – Second is translation = 3 different RNA’s (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) work to assemble am ...
... Protein Synthesis • the transfer of genetic material to the ribosome but DNA stays in the nucleus! • Gene expression = use of DNA information to form proteins – 2 stages → – first is transcription = mRNA copy is made. – Second is translation = 3 different RNA’s (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) work to assemble am ...
11. Use the following mRNA codon key as needed to... GCC Alanine AAU
... Mutations in the adenomatous polyposis of the colon (APC) gene predisposes a person to colorectal cancer. Below is the DNA nucleotide sequence of the APC gene on the non-template strand from a normal individual and an individual who was diagnosed with colorectal cancer. What type of mutation occurre ...
... Mutations in the adenomatous polyposis of the colon (APC) gene predisposes a person to colorectal cancer. Below is the DNA nucleotide sequence of the APC gene on the non-template strand from a normal individual and an individual who was diagnosed with colorectal cancer. What type of mutation occurre ...
Unzipping DNA - School Science
... In humans 22 pairs of chromosomes always match if the 23rd pair matches then the individual is female, if not they are male. The sequence of base pairs on the DNA which contains the information to make a protein is called a gene. A gene is the blueprint for a protein. One gene assembles only one pro ...
... In humans 22 pairs of chromosomes always match if the 23rd pair matches then the individual is female, if not they are male. The sequence of base pairs on the DNA which contains the information to make a protein is called a gene. A gene is the blueprint for a protein. One gene assembles only one pro ...
gene control regions?
... What is the structure of a chromosome and how does that relate to function? ...
... What is the structure of a chromosome and how does that relate to function? ...
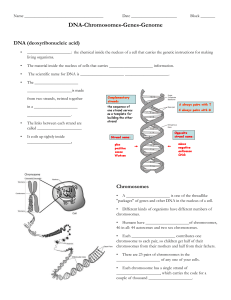
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...