Epigenetics - BLI-Research-Synbio-2014-session-1
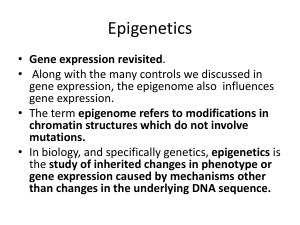
... • The term epigenome refers to modifications in chromatin structures which do not involve mutations. • In biology, and specifically genetics, epigenetics is the study of inherited changes in phenotype or gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. ...
... • The term epigenome refers to modifications in chromatin structures which do not involve mutations. • In biology, and specifically genetics, epigenetics is the study of inherited changes in phenotype or gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. ...
BIO105 Learning objectives for test 3 Topic: The Cell cycle and
... After attending lecture, reviewing their notes, and reading the chapter, a student should be able to: - Explain how RNA differs from DNA. - In their own words, briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. - Distinguish between transcription and translation. - Describe where transcript ...
... After attending lecture, reviewing their notes, and reading the chapter, a student should be able to: - Explain how RNA differs from DNA. - In their own words, briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. - Distinguish between transcription and translation. - Describe where transcript ...
DNA Questions #1
... ____chromosomes______(linear pieces) is an important type of forensic evidence even though it is ____class_______(individual/class) evidence. The strength of this evidence makes it as important as the individualized evidence you worked with in the last unit: _fingerprinting_____. Unfortunately, nDNA ...
... ____chromosomes______(linear pieces) is an important type of forensic evidence even though it is ____class_______(individual/class) evidence. The strength of this evidence makes it as important as the individualized evidence you worked with in the last unit: _fingerprinting_____. Unfortunately, nDNA ...
Patent Law Prof. Merges
... bonded to such other materials. Thus, when cleaved, an isolated DNA molecule is not a purified form of a natural material, but a distinct chemical entity. In fact, some forms of isolated DNA require no purification at all, because DNAs can be chemically synthesized directly as isolated molecules. ...
... bonded to such other materials. Thus, when cleaved, an isolated DNA molecule is not a purified form of a natural material, but a distinct chemical entity. In fact, some forms of isolated DNA require no purification at all, because DNAs can be chemically synthesized directly as isolated molecules. ...
2.1 Selective breeding
... • Crops can be developed that produce their own fertiliser. • Eggs can be taken out of a woman’s body, fertilised and then replaced. This is called fertility treatment. In the future, it might be possible to change the genes in the egg while the egg is out of the body. For example, harmful genes cou ...
... • Crops can be developed that produce their own fertiliser. • Eggs can be taken out of a woman’s body, fertilised and then replaced. This is called fertility treatment. In the future, it might be possible to change the genes in the egg while the egg is out of the body. For example, harmful genes cou ...
Supplementary material for "The Plasmodium HU homolog, which
... 1.4. Transfection of parasite and localization of expressed fluorescent proteins The bsd gene of the plasmids pEM7/Bsd (Invitrogen) was recombined to the P. falciparum expression plasmids pSSPF2/PfHsp60-GFP [1] and pSSPF2/PfACP-DsRed [3] replacing the hDHFR gene to generate pSSPF3/PfHsp60-GFP and pS ...
... 1.4. Transfection of parasite and localization of expressed fluorescent proteins The bsd gene of the plasmids pEM7/Bsd (Invitrogen) was recombined to the P. falciparum expression plasmids pSSPF2/PfHsp60-GFP [1] and pSSPF2/PfACP-DsRed [3] replacing the hDHFR gene to generate pSSPF3/PfHsp60-GFP and pS ...
Restriction Enzyme - Action of EcoRI
... 1. Why was it important to find an enzyme that would cut the plasmid at only one site? What could happen if the plasmid were cut at more than one site? (Cutting at only one site is important for controlling the variables that will be reproduced. y the restriction enzyme cut more than one site, then ...
... 1. Why was it important to find an enzyme that would cut the plasmid at only one site? What could happen if the plasmid were cut at more than one site? (Cutting at only one site is important for controlling the variables that will be reproduced. y the restriction enzyme cut more than one site, then ...
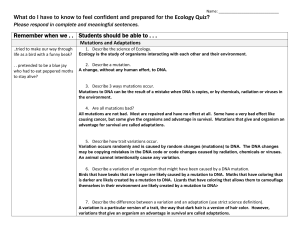
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... 3. Describe 3 ways mutations occur. Mutations to DNA can be the result of a mistake when DNA is copies, or by chemicals, radiation or viruses in the environment. 4. Are all mutations bad? All mutations are not bad. Most are repaired and have no effect at all. Some have a very bad effect like causing ...
... 3. Describe 3 ways mutations occur. Mutations to DNA can be the result of a mistake when DNA is copies, or by chemicals, radiation or viruses in the environment. 4. Are all mutations bad? All mutations are not bad. Most are repaired and have no effect at all. Some have a very bad effect like causing ...
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 1. Complete the complementary strand of the DNA. 2. Use the bottom strand of DNA to create your mRNA copy. 3. Use the mRNA code to create your tRNA code. 4. Use the mRNA code and the Genetic Wheel to determine your amino acids. 5. Answer any questions by circling the correct answer. ...
... 1. Complete the complementary strand of the DNA. 2. Use the bottom strand of DNA to create your mRNA copy. 3. Use the mRNA code to create your tRNA code. 4. Use the mRNA code and the Genetic Wheel to determine your amino acids. 5. Answer any questions by circling the correct answer. ...
Test Review Sheet - Lyndhurst Schools
... 28) The amount of DNA material required for STR analysis is ________ the amount of DNA required for RFLP analysis. A) greater than B) the same as C) less than 29. Can PCR be performed on STRs or RFLPs? ______________ Why? __________________________ ...
... 28) The amount of DNA material required for STR analysis is ________ the amount of DNA required for RFLP analysis. A) greater than B) the same as C) less than 29. Can PCR be performed on STRs or RFLPs? ______________ Why? __________________________ ...
Water Flea Boasts Whopper Gene Count
... Like other aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum live off plant sap, a sugary mix found about 11. At least two are important to Buchnera for making the low in protein. To make up for this nutritional shortfall, the insects depend microbe’s cell wall, and these are active in the nuclei of aphid cells specialon ...
... Like other aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum live off plant sap, a sugary mix found about 11. At least two are important to Buchnera for making the low in protein. To make up for this nutritional shortfall, the insects depend microbe’s cell wall, and these are active in the nuclei of aphid cells specialon ...
Pharmacogenomics
... structural and functional components,networks and pathways heritable variation genetic contributions to disease and drug response genome-based diagnostic approaches new therapeutic approaches to disease ...
... structural and functional components,networks and pathways heritable variation genetic contributions to disease and drug response genome-based diagnostic approaches new therapeutic approaches to disease ...
DNA: The Genetic Material
... helix to unwind. At the replication forks, the points where the double helix separates, a molecule of DNA polymerase attaches and begins to add nucleotides to the exposed bases according to the base-pairing rules. This continues until all of the DNA is copied. DNA polymerases are able to “proofread” ...
... helix to unwind. At the replication forks, the points where the double helix separates, a molecule of DNA polymerase attaches and begins to add nucleotides to the exposed bases according to the base-pairing rules. This continues until all of the DNA is copied. DNA polymerases are able to “proofread” ...
Slide 1 - Montville.net
... recombinant plasmid, a plasmid with a new gene inserted. The plasmid will contain DNA from two different organisms. You will use colored paper, scissors and tape to do this. If you are successful, you will have a two colored paper ring and extra pieces of paper. ...
... recombinant plasmid, a plasmid with a new gene inserted. The plasmid will contain DNA from two different organisms. You will use colored paper, scissors and tape to do this. If you are successful, you will have a two colored paper ring and extra pieces of paper. ...
8 GeneTransferBiotech
... (now has a new phenotype or ability, like being able to use a sugar it could not before) ...
... (now has a new phenotype or ability, like being able to use a sugar it could not before) ...
DNA and RNA Chapter 12 - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... __________ in humans, but beneficial in some ___________. Triploid (___) or tetraploid (___) plants are often ________________ than diploid plants. ...
... __________ in humans, but beneficial in some ___________. Triploid (___) or tetraploid (___) plants are often ________________ than diploid plants. ...
Analysis of in-vivo LacR-mediated Gene Repression Based on the
... separated by a dihedral angle of about 20 degrees [1]. This implies that the crystallographic structure should introduce some writhe into a LacR-mediated loop, which could significantly affect the J factor. In particular, non-negligible writhe, depending on its sign, will couple differently with the ...
... separated by a dihedral angle of about 20 degrees [1]. This implies that the crystallographic structure should introduce some writhe into a LacR-mediated loop, which could significantly affect the J factor. In particular, non-negligible writhe, depending on its sign, will couple differently with the ...
DNA is - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... __________ in humans, but beneficial in some ___________. Triploid (___) or tetraploid (___) plants are often ________________ than diploid plants. ...
... __________ in humans, but beneficial in some ___________. Triploid (___) or tetraploid (___) plants are often ________________ than diploid plants. ...
Quiz 22
... (c) Because the cytoplasm of many cells of D is formed by repeated divisions (1) of the cytoplasm of the same one cell C (1). (d) Sheep X (1) because the body characteristics of Dolly is determined by its genetic material (1) which is derived from and identical to that in the body cell of sheep X. ( ...
... (c) Because the cytoplasm of many cells of D is formed by repeated divisions (1) of the cytoplasm of the same one cell C (1). (d) Sheep X (1) because the body characteristics of Dolly is determined by its genetic material (1) which is derived from and identical to that in the body cell of sheep X. ( ...
File - Zachary Carscaddon
... 1. In theory, scientists can remove any gene from any living organism for insertion into any other living organism. ...
... 1. In theory, scientists can remove any gene from any living organism for insertion into any other living organism. ...
Leukaemia Section t(19;21)(q13.4;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Clinics and pathology Disease Acute non lymphocytic leukemia (ANLL) secondary to toxic exposure. Note Only one case, but with features identical to 2 other cases: one case of t(1;21)(p36;q22), and one case of t(18;21)(q21;q22). ...
... Clinics and pathology Disease Acute non lymphocytic leukemia (ANLL) secondary to toxic exposure. Note Only one case, but with features identical to 2 other cases: one case of t(1;21)(p36;q22), and one case of t(18;21)(q21;q22). ...