Chromosomal changes associated with changes in development
... To illustrate the principles of Ig gene rearrangement we will consider only the heavy chain genes (Fig. 3). The first stage of rearrangement brings together one of the several hundred variable genes (VH), one of the 'diversity' segments (DH) and one of the junction segments (JH), see review by Marcu ...
... To illustrate the principles of Ig gene rearrangement we will consider only the heavy chain genes (Fig. 3). The first stage of rearrangement brings together one of the several hundred variable genes (VH), one of the 'diversity' segments (DH) and one of the junction segments (JH), see review by Marcu ...
File - Molecular Biology 2
... DNA samples but not from others, which means that the presence or absence of the amplified fragment is polymorphic in the population of organisms. In most organisms it is usually straightforward to identify a large number of RAPDs that can serve as genetic markers for many different kinds of genetic ...
... DNA samples but not from others, which means that the presence or absence of the amplified fragment is polymorphic in the population of organisms. In most organisms it is usually straightforward to identify a large number of RAPDs that can serve as genetic markers for many different kinds of genetic ...
Chapter 5 Gases - LCMR School District
... most base triplets (codons) code for amino acids; the genetic code consists of all sixty-four codons • Ribosomes, which consist of two subunits of rRNA and proteins, assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains • A tRNA has an anticodon complementary to an mRNA codon, and it has a binding site for t ...
... most base triplets (codons) code for amino acids; the genetic code consists of all sixty-four codons • Ribosomes, which consist of two subunits of rRNA and proteins, assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains • A tRNA has an anticodon complementary to an mRNA codon, and it has a binding site for t ...
DNA Analysis
... Some Phraseology • Recall from general biology the heirarchy of structure of DNA: – Humans carry 2 copies of the DNA in their cells (diploid). The exception is sperm and eggs which contain one copy (haploid) – The DNA is organized into chromosomes – long strands of DNA – On the chromosomes, genes ( ...
... Some Phraseology • Recall from general biology the heirarchy of structure of DNA: – Humans carry 2 copies of the DNA in their cells (diploid). The exception is sperm and eggs which contain one copy (haploid) – The DNA is organized into chromosomes – long strands of DNA – On the chromosomes, genes ( ...
Recombination in Bacteria Overview This module looks at how the
... F factor did in Hfr cells. In a lysogenic infection by lambda, the DNA integrates into a very specific spot in the host chromosome. The integrated viral DNA can remain integrated for long periods of time, without disturbing the cell. Under the appropriate conditions (the regulation of this is very c ...
... F factor did in Hfr cells. In a lysogenic infection by lambda, the DNA integrates into a very specific spot in the host chromosome. The integrated viral DNA can remain integrated for long periods of time, without disturbing the cell. Under the appropriate conditions (the regulation of this is very c ...
Request Form - Exeter Clinical Laboratory International
... conserves precious fetal samples and/or is appropriate for cases where fetal DNA is of insufficient quality or quantity for exome sequencing. This strategy is most likely to yield a diagnosis for unrelated couples with multiple affected fetuses but has been successful for couples with a single affec ...
... conserves precious fetal samples and/or is appropriate for cases where fetal DNA is of insufficient quality or quantity for exome sequencing. This strategy is most likely to yield a diagnosis for unrelated couples with multiple affected fetuses but has been successful for couples with a single affec ...
Shotgun DNA sequencing using cloned DNase I
... In order to clone the DNase I-generated fragments synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide " l i n k e r s " were attached to the flush ends using T4 DNA ligase. BamHI linkers were chosen because the bovine mtDNA EcoRI fragment was known to contain no BamHI sites [14]. ...
... In order to clone the DNase I-generated fragments synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide " l i n k e r s " were attached to the flush ends using T4 DNA ligase. BamHI linkers were chosen because the bovine mtDNA EcoRI fragment was known to contain no BamHI sites [14]. ...
Complications to Mendel: Gene Interactions Lecture starts on next
... Two genes independently controlling the synthesis of two different pigments; each gene has two alleles showing complete dominance ...
... Two genes independently controlling the synthesis of two different pigments; each gene has two alleles showing complete dominance ...
5.6 Mutations
... Usually occurs between two nonhomologous chromosomes. Result is a fusion protein with an altered function ...
... Usually occurs between two nonhomologous chromosomes. Result is a fusion protein with an altered function ...
1 Generating a Synthetic Genome by Whole Genome Assembly
... Chemical synthesis of life in the laboratory has been a standing challenge to synthetic organic chemistry since Wöhler’s synthesis of urea in 1828 (1) and the doctrine of spontaneous generation was put to rest by Pasteur in 1864, (an address delivered by Louis Pasteur at the "Sorbonne Scientific So ...
... Chemical synthesis of life in the laboratory has been a standing challenge to synthetic organic chemistry since Wöhler’s synthesis of urea in 1828 (1) and the doctrine of spontaneous generation was put to rest by Pasteur in 1864, (an address delivered by Louis Pasteur at the "Sorbonne Scientific So ...
Document
... P1 Artificial Chromosome (PAC)- One type of vector used to clone DNA fragments (100- to 300-kb insert size; average, 150 kb) in Escherichia coli cells. Based on bacteriophage (a virus) P1 genome. Proteomics-The study of the full set of proteins encoded by a genome. Yeast Artificial Chromosome (YAC)- ...
... P1 Artificial Chromosome (PAC)- One type of vector used to clone DNA fragments (100- to 300-kb insert size; average, 150 kb) in Escherichia coli cells. Based on bacteriophage (a virus) P1 genome. Proteomics-The study of the full set of proteins encoded by a genome. Yeast Artificial Chromosome (YAC)- ...
Zebrafish - yourgenome
... What is a model organism? • Non-human species widely studied to understand human disease. • Model organisms are used when experimentation using humans is unfeasible or unethical. • Can you think of a model organism? ...
... What is a model organism? • Non-human species widely studied to understand human disease. • Model organisms are used when experimentation using humans is unfeasible or unethical. • Can you think of a model organism? ...
Protein Nucleic Acid Interactions
... b. Hormone receptor • Pseudosymmetric homo or heterodimer • 2 Zn coordinating modules – 1 Zn stabilizes DNA recognition helix, other Zn involved in dimer formation ...
... b. Hormone receptor • Pseudosymmetric homo or heterodimer • 2 Zn coordinating modules – 1 Zn stabilizes DNA recognition helix, other Zn involved in dimer formation ...
BMC Genomics - LCBB
... This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
... This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
Chemistry 100 Exam 3 Part 2
... in our skin by changing configurations and releasing the UV energy as heat. Damage has still been done, but less than with a sunburn. 3. Antioxidants (such as Vitamins E and C) are brought in to deactivate free radicals before they can damage the DNA. Some are oxidized themselves, others disrupt oxi ...
... in our skin by changing configurations and releasing the UV energy as heat. Damage has still been done, but less than with a sunburn. 3. Antioxidants (such as Vitamins E and C) are brought in to deactivate free radicals before they can damage the DNA. Some are oxidized themselves, others disrupt oxi ...
Genome Analysis Excerpt from Chapter 11
... There are several classes of sequences (transposable elements) that can move from one genome location to another, thus affecting gene content. Highly repetitive sequences in the genome are derived from such classes of sequences that move (transpose) from one genome location to another. These sequenc ...
... There are several classes of sequences (transposable elements) that can move from one genome location to another, thus affecting gene content. Highly repetitive sequences in the genome are derived from such classes of sequences that move (transpose) from one genome location to another. These sequenc ...
Document
... chondrial DNA in 1997, then the entire mitochondrial genomes of several Genes from the past modern humans interbred with Neandertals as Neandertals—and found them to be dis- Then in May 2010 came the Neandertals’ they left Africa in the past 100,000 years. Thus tinct from those of living people. So ...
... chondrial DNA in 1997, then the entire mitochondrial genomes of several Genes from the past modern humans interbred with Neandertals as Neandertals—and found them to be dis- Then in May 2010 came the Neandertals’ they left Africa in the past 100,000 years. Thus tinct from those of living people. So ...
Leukaemia Section t(9;12)(q34;p13) ETV6/ABL1 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... The SH2 and SH3 domains are involved in proteinprotein interactions, which regulate the tyrosine kinase activity; they are necessary for signal transduction function. The ABL1 protein has also three nuclear localization signal domains and three DNA binding regions and an F-actin binding domain. ...
... The SH2 and SH3 domains are involved in proteinprotein interactions, which regulate the tyrosine kinase activity; they are necessary for signal transduction function. The ABL1 protein has also three nuclear localization signal domains and three DNA binding regions and an F-actin binding domain. ...
epigenetics
... Activity: Analyzing Amino Acid Sequences to Determine Evolutionary Relationships ...
... Activity: Analyzing Amino Acid Sequences to Determine Evolutionary Relationships ...
Heredity Unit Plan
... 3. Why are the products of mitosis and meiosis different? 4. Make a monohybrid punnett square using whichever trait you would like. Use that trait and another to make a dihybrid cross. Find the genotypic and phenotypic ratios in both problems. 5. What is the difference between polygenic and single g ...
... 3. Why are the products of mitosis and meiosis different? 4. Make a monohybrid punnett square using whichever trait you would like. Use that trait and another to make a dihybrid cross. Find the genotypic and phenotypic ratios in both problems. 5. What is the difference between polygenic and single g ...
Founder Effect for Ullrich-Type CMD in French Canadians
... transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) on chromosome 7 that, when mutant, causes cystic fibrosis. First gene replacement therapy. T cells of a four-year old girl were exposed outside of her body to retroviruses containing an RNA copy of a normal ADA gene. This allowed her immune system t ...
... transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) on chromosome 7 that, when mutant, causes cystic fibrosis. First gene replacement therapy. T cells of a four-year old girl were exposed outside of her body to retroviruses containing an RNA copy of a normal ADA gene. This allowed her immune system t ...
Unoshan_project
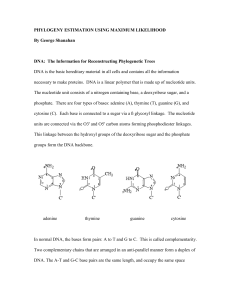
... their common ancestor. Its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) characterize a phylogenetic tree. Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in that node. Maximum Likelihood is a method for the inference of phylogeny. It evaluates a hypothesis ...
... their common ancestor. Its topology (form) and its length (sum of its branch lengths) characterize a phylogenetic tree. Each node of a tree is an estimation of the ancestor of the elements included in that node. Maximum Likelihood is a method for the inference of phylogeny. It evaluates a hypothesis ...
Journal of Biotechnology
... Bacillus subtilis DSM10T was calculated as being 3098 and their identity was 92.25%. The 3,980,199 bp genome of DSM7T contains numerous genomic islands (GI) detected by different methods. Many of them were located in vicinity of tRNA, glnA, and glmS gene copies. In contrast to FZB42, but similar to ...
... Bacillus subtilis DSM10T was calculated as being 3098 and their identity was 92.25%. The 3,980,199 bp genome of DSM7T contains numerous genomic islands (GI) detected by different methods. Many of them were located in vicinity of tRNA, glnA, and glmS gene copies. In contrast to FZB42, but similar to ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... representative of the import set (figs. 1b and 2 and supplementary fig. S1, Supplementary Material online). In fact, most of the genes reported by NS as acquired at the origins of a MAL are present in very few species in Archaea and Bacteria. More precisely, 52% (1,171/2,264 import clusters) are rep ...
... representative of the import set (figs. 1b and 2 and supplementary fig. S1, Supplementary Material online). In fact, most of the genes reported by NS as acquired at the origins of a MAL are present in very few species in Archaea and Bacteria. More precisely, 52% (1,171/2,264 import clusters) are rep ...
The history of gene duplication Phylogenies are not just useful for
... When biologists began sequencing genomes they were surprised to find that many genes have closely related genes within the very same genome. We now understand that during evolution genes often duplicate – an ancestral genome with one copy gives rise to a descendant genome with two copies of a partic ...
... When biologists began sequencing genomes they were surprised to find that many genes have closely related genes within the very same genome. We now understand that during evolution genes often duplicate – an ancestral genome with one copy gives rise to a descendant genome with two copies of a partic ...