Uracil (U) - Cloudfront.net
... The amino acids link together to form a polypeptide chain of the protein. The tRNA has a sequence of three nucleotides called the anticodon, because they bind to the codon of the mRNA ...
... The amino acids link together to form a polypeptide chain of the protein. The tRNA has a sequence of three nucleotides called the anticodon, because they bind to the codon of the mRNA ...
Non-coding RNA
... Non-coding RNA genes exhibit similar levels of conservation as the protein-coding genes at ...
... Non-coding RNA genes exhibit similar levels of conservation as the protein-coding genes at ...
Transcription_12_Teacher
... and the passage of mRNA into the cytoplasm Genes may play roles in multiple proteins, introns may enable a gene to be diverse in function May increase recombination of genetic material (easier to cut and paste) ...
... and the passage of mRNA into the cytoplasm Genes may play roles in multiple proteins, introns may enable a gene to be diverse in function May increase recombination of genetic material (easier to cut and paste) ...
Protein Synthesis Digital Guide
... 4B Investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules 6A Identify components of DNA and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6B Recognize that components ...
... 4B Investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules 6A Identify components of DNA and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6B Recognize that components ...
apbio ch 17 test
... C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. E) The polypeptide enters the E site. 17) What are polyribosomes? A) groups of ribosomes reading a single mRNA simultaneously B) ribosomes containing mor ...
... C) The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site and is released. D) The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome via a tunnel. E) The polypeptide enters the E site. 17) What are polyribosomes? A) groups of ribosomes reading a single mRNA simultaneously B) ribosomes containing mor ...
RNA
... mRNA (messenger RNA) tRNA (transfer RNA) rRNA (ribosomal RNA) Transcription produces three general classes* of RNA, each of which plays a role in translation (protein synthesis) * actually, there are many more classes of small RNA molecules that perform important functions in the cell, including gen ...
... mRNA (messenger RNA) tRNA (transfer RNA) rRNA (ribosomal RNA) Transcription produces three general classes* of RNA, each of which plays a role in translation (protein synthesis) * actually, there are many more classes of small RNA molecules that perform important functions in the cell, including gen ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
Controlling the Code: molecules at work
... then that the repressor is released from the operator and no longer blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter. This allows transcription to begin. ...
... then that the repressor is released from the operator and no longer blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter. This allows transcription to begin. ...
Wavelet Analysis of Gene Expression (WAGE)
... Human Chromosomes and Genes WAGE model-based approach re-organizes gene expression values according to their chromosomal position and then searches for spatial clusters of activity ...
... Human Chromosomes and Genes WAGE model-based approach re-organizes gene expression values according to their chromosomal position and then searches for spatial clusters of activity ...
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: THE GENETIC CODE
... 1. The table below (taken from the Chemguide page) shows the three-base combinations used to code for the various amino acids in messenger RNA chains. ...
... 1. The table below (taken from the Chemguide page) shows the three-base combinations used to code for the various amino acids in messenger RNA chains. ...
DNA and RNA Chapter 12
... Mendel/flower images from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.html Blood cell by Riedell ...
... Mendel/flower images from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookTOC.html Blood cell by Riedell ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA Replication
... • Chargraff’s Rule: for any given species the % of Ts will by equivalent of the % of As while the % of Cs will be equivalent to the % of Gs ...
... • Chargraff’s Rule: for any given species the % of Ts will by equivalent of the % of As while the % of Cs will be equivalent to the % of Gs ...
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
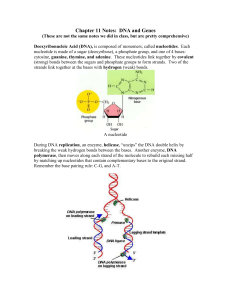
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is also single stranded, like mRNA, but it is held together in a “hairpin” or “T” shape by hydrogen bonds. It carries a specific amino acid on one end based on a series of three bases on the other end called an anti-codon. There are only 20 amino acids that make up all of the pro ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is also single stranded, like mRNA, but it is held together in a “hairpin” or “T” shape by hydrogen bonds. It carries a specific amino acid on one end based on a series of three bases on the other end called an anti-codon. There are only 20 amino acids that make up all of the pro ...
Protein Synthesis
... • The tRNA having the anticodon “UAC” will bring the first amino acid to the ribosome to begin the formation of the protein. • The ribosome slides to the next codon on the mRNA. The complementary tRNA anticodon brings the second amino acid to the protein strand. ...
... • The tRNA having the anticodon “UAC” will bring the first amino acid to the ribosome to begin the formation of the protein. • The ribosome slides to the next codon on the mRNA. The complementary tRNA anticodon brings the second amino acid to the protein strand. ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... • RNA polymerase binds to DNA promoter • DNA strands unwind & separate • RNA polymerase adds free RNA nucleotides to complement 1 strand of DNA bases. ...
... • RNA polymerase binds to DNA promoter • DNA strands unwind & separate • RNA polymerase adds free RNA nucleotides to complement 1 strand of DNA bases. ...
Differences between DNA and RNA • Ribonucleic acid is similar to
... those hydroxyl groups have been removed. ...
... those hydroxyl groups have been removed. ...
Nucleic acid recognition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Case
... Part (2) Recognition of the 3' pre-mRNA splice site. Almost all human genes contain intervening noncoding introns that must be removed by pre-mRNA splicing. The 3' splice site is marked by consensus sequences, yet variations of these sequences allow specific splice site regulation. Structures of the ...
... Part (2) Recognition of the 3' pre-mRNA splice site. Almost all human genes contain intervening noncoding introns that must be removed by pre-mRNA splicing. The 3' splice site is marked by consensus sequences, yet variations of these sequences allow specific splice site regulation. Structures of the ...
RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA)
... • Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome • Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals • One of these active processes is protein synthesis, ...
... • Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome • Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals • One of these active processes is protein synthesis, ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code. Codons are three-nucleotide sequences that specify which amino acids (61 codons) will be added to the growing polypeptide. Codons can also signal when translation terminates (3 codons). The codon for methionine (AUG) acts as a ...
... The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code. Codons are three-nucleotide sequences that specify which amino acids (61 codons) will be added to the growing polypeptide. Codons can also signal when translation terminates (3 codons). The codon for methionine (AUG) acts as a ...
Protein Synthesis & Mutation
... Genetic code & codons • Redundant – multiple codons specify same AA • Unambiguous - NO codon specifies more than one AA • Ancient – ALL organisms have same genetic code – AUG = Methionine whether you’re a redwood or a fruitfly ...
... Genetic code & codons • Redundant – multiple codons specify same AA • Unambiguous - NO codon specifies more than one AA • Ancient – ALL organisms have same genetic code – AUG = Methionine whether you’re a redwood or a fruitfly ...
Unit 9 Completed Vocabulary - WAHS
... chromatin – granular material visible within the nucleus; consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins. histone – globular protein molecule around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin. replication – copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA. DNA polymerase – enzyme that “proofreads” n ...
... chromatin – granular material visible within the nucleus; consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins. histone – globular protein molecule around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin. replication – copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA. DNA polymerase – enzyme that “proofreads” n ...
I - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... A student used the firefly luciferase as a reporter gene to demonstrate the promoter function of X gene. She isolated the X gene promoter with 982 bp in front of the start site of transcription (+1). To define the sequence involved in the regulation of X gene, she made a series deletions containing ...
... A student used the firefly luciferase as a reporter gene to demonstrate the promoter function of X gene. She isolated the X gene promoter with 982 bp in front of the start site of transcription (+1). To define the sequence involved in the regulation of X gene, she made a series deletions containing ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.