A programme for the construction of a lambda phage
... time required for RNA polymerase to reach the gene from its promoter /?R , 7000 base-pairs away. The product of Q activates transcription initiated at P'R to traverse the late genes, whose products are responsible for DNA encapsidation and cell lysis. The Q protein acts as an antiterminator, employi ...
... time required for RNA polymerase to reach the gene from its promoter /?R , 7000 base-pairs away. The product of Q activates transcription initiated at P'R to traverse the late genes, whose products are responsible for DNA encapsidation and cell lysis. The Q protein acts as an antiterminator, employi ...
041610_gene Regulation
... 1. Read and understand lecture .ppt files and animations 2. Review these materials and use audio file of lectures to self-clarify doubts 3. If you still do not understand, seek help from preceptors, TA and me ...
... 1. Read and understand lecture .ppt files and animations 2. Review these materials and use audio file of lectures to self-clarify doubts 3. If you still do not understand, seek help from preceptors, TA and me ...
Symposium Poster - uospur
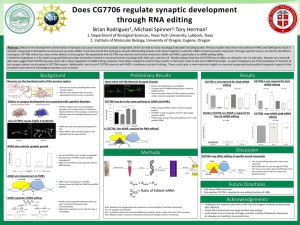
... Abstract: Defects in the development and formation of synapses can cause neuronal and synaptic overgrowth, which can lead to many neurological disorders including autism. Previous studies have shown that defective FMR1 and ADAR genes result in synaptic overgrowth in Drosophila neuromuscular junction ...
... Abstract: Defects in the development and formation of synapses can cause neuronal and synaptic overgrowth, which can lead to many neurological disorders including autism. Previous studies have shown that defective FMR1 and ADAR genes result in synaptic overgrowth in Drosophila neuromuscular junction ...
Document
... Transcription of the lacZYA genes is controlled by a regulator protein synthesized by the lacI gene. The lac genes are controlled by negative regulation: they are transcribed unless turned off by the regulator protein. The repressor is a tetramer of identical subunits of 38 kD each. There are ...
... Transcription of the lacZYA genes is controlled by a regulator protein synthesized by the lacI gene. The lac genes are controlled by negative regulation: they are transcribed unless turned off by the regulator protein. The repressor is a tetramer of identical subunits of 38 kD each. There are ...
The trp Operon - aandersonbiology
... is a region of a chromosome or DNA to which the repressor binds when the operon is turned off and not producing a protein product. The area of the operon called the promoter indicates to the enzyme, RNA polymerase, where to bind to make mRNA during the process of transcription. The repressor is a pr ...
... is a region of a chromosome or DNA to which the repressor binds when the operon is turned off and not producing a protein product. The area of the operon called the promoter indicates to the enzyme, RNA polymerase, where to bind to make mRNA during the process of transcription. The repressor is a pr ...
pdf
... 1. The natural inducer (or antirepressor), is allolactose, an analog of lactose. It is made as a metabolic by-product of the reaction catalyzed by β-galactosidase. Usually this enzyme catalyzes the cleavage of lactose to galactose + glucose, but occasionally it will catalyze an isomerization to form ...
... 1. The natural inducer (or antirepressor), is allolactose, an analog of lactose. It is made as a metabolic by-product of the reaction catalyzed by β-galactosidase. Usually this enzyme catalyzes the cleavage of lactose to galactose + glucose, but occasionally it will catalyze an isomerization to form ...
Targets for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment
... back into the chromosome (Alitalo et al.). As a result. 50 or ...
... back into the chromosome (Alitalo et al.). As a result. 50 or ...
Genetics Workbook
... 3. How many potential mRNA sequences code for the polypeptide Ser-Arg-Gly-Thr-Phe? 4. The following true breeding individuals: AAbbCCDDee * aabbccDDEE were crossed to yield the F1 progeny. Upon self-fertilization of the F1 generation, what is the probability of producing an F2 individual that is phe ...
... 3. How many potential mRNA sequences code for the polypeptide Ser-Arg-Gly-Thr-Phe? 4. The following true breeding individuals: AAbbCCDDee * aabbccDDEE were crossed to yield the F1 progeny. Upon self-fertilization of the F1 generation, what is the probability of producing an F2 individual that is phe ...
DNA THIS ONE
... 2. RNA and DNA are both types of Nucleic Acids. What are the 3 main differences between RNA and DNA? ...
... 2. RNA and DNA are both types of Nucleic Acids. What are the 3 main differences between RNA and DNA? ...
Departamento de Clínica Médica
... different pattern of Bmal1 expression, which was higher at ZT11 (P=0.02), and of Cry1, Cry2 and Rorα expression, which were higher at ZT3 and ZT11 (P=0.008). In the PVN of CG, Per1 showed higher expression in the afternoon and in the night (P=0.002), while Per2, Per3, Cry2, and Rorα had higher expre ...
... different pattern of Bmal1 expression, which was higher at ZT11 (P=0.02), and of Cry1, Cry2 and Rorα expression, which were higher at ZT3 and ZT11 (P=0.008). In the PVN of CG, Per1 showed higher expression in the afternoon and in the night (P=0.002), while Per2, Per3, Cry2, and Rorα had higher expre ...
Interdependence, Reflexivity, Fidelity, Impedance Matching
... activation of the amino acid’s α-carboxyl group by reaction with ATP. In cells, activation and aminoacylation require a separate enzyme for each amino acid. These assignment catalysts, called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRS), were first clearly identified by Berg and Ofe ...
... activation of the amino acid’s α-carboxyl group by reaction with ATP. In cells, activation and aminoacylation require a separate enzyme for each amino acid. These assignment catalysts, called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRS), were first clearly identified by Berg and Ofe ...
Gen660_Lecture1B_sequencing_2014
... Phylogenomics: Using Whole-genome information to reconstruct the Tree of Life Several approaches: 1. Concatonate many gene sequences and treat as one Use a ‘super matrix’ of variable sequence characters 2. Construct many separate trees, one for each gene, and then compare Often construct a ‘super t ...
... Phylogenomics: Using Whole-genome information to reconstruct the Tree of Life Several approaches: 1. Concatonate many gene sequences and treat as one Use a ‘super matrix’ of variable sequence characters 2. Construct many separate trees, one for each gene, and then compare Often construct a ‘super t ...
Interdependence, Reflexivity, Fidelity, Impedance Matching
... activation of the amino acid’s α-carboxyl group by reaction with ATP. In cells, activation and aminoacylation require a separate enzyme for each amino acid. These assignment catalysts, called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRS), were first clearly identified by Berg and Ofe ...
... activation of the amino acid’s α-carboxyl group by reaction with ATP. In cells, activation and aminoacylation require a separate enzyme for each amino acid. These assignment catalysts, called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRS), were first clearly identified by Berg and Ofe ...
Data Supplement
... agarose (20 ml) was added and incubated over night at 4°C. Pellets were washed three times with IP buffer prior to isolation for real-time PCR. The primers used to assess NFATc1 binding to the Rcan1.4 promoter amplified a 65 bp fragment between –282 and –217 in a region with the highest conservation ...
... agarose (20 ml) was added and incubated over night at 4°C. Pellets were washed three times with IP buffer prior to isolation for real-time PCR. The primers used to assess NFATc1 binding to the Rcan1.4 promoter amplified a 65 bp fragment between –282 and –217 in a region with the highest conservation ...
Monoallelic Expression and Dominance
... S haplotype by allowing pollen of the recessive genotype to elude the S haplotype-specific stigmatic surveillance mediated by SRK. In fact, “pollenrecessive” alleles attain high frequencies in populations (Uyenoyama, 2000). Elucidation of the molecular basis of S haplotype recessiveness in pollen is ...
... S haplotype by allowing pollen of the recessive genotype to elude the S haplotype-specific stigmatic surveillance mediated by SRK. In fact, “pollenrecessive” alleles attain high frequencies in populations (Uyenoyama, 2000). Elucidation of the molecular basis of S haplotype recessiveness in pollen is ...
Kanr T-DNA Supplemental Figure 1. Transgenic complementation of
... are grey-shaded. The boxed sequences indicate the region with low amino acid similarity between the two proteins. The BCCP1 and BCCP2 cDNAs coding for this region were PCR amplified and cloned into an expression vector. Using the expressed peptides, BCCP1- and BCCP2-specific antisera were generated. ...
... are grey-shaded. The boxed sequences indicate the region with low amino acid similarity between the two proteins. The BCCP1 and BCCP2 cDNAs coding for this region were PCR amplified and cloned into an expression vector. Using the expressed peptides, BCCP1- and BCCP2-specific antisera were generated. ...
Supplementary Material Legends
... border genomic DNA-T-DNA fusion site was known (Suppl. Info. 1). In these cases, it was assumed that the T-DNA insertion had happened without DNA sequence deletion and sequence feature analysis for the “unknown” side was started at the nucleotide directly adjacent to the known genomic DNA-T-DNA fusi ...
... border genomic DNA-T-DNA fusion site was known (Suppl. Info. 1). In these cases, it was assumed that the T-DNA insertion had happened without DNA sequence deletion and sequence feature analysis for the “unknown” side was started at the nucleotide directly adjacent to the known genomic DNA-T-DNA fusi ...
Organizing Protein Synthesis - Dallastown Area School District Moodle
... 11) During ___________________________________________________________, parental strands of DNA separate, serve as a template, and produce DNA molecules that have one strand of parental DNA and one strand of new DNA. 12) _________________________is the process through which mRNA is decoded and forms ...
... 11) During ___________________________________________________________, parental strands of DNA separate, serve as a template, and produce DNA molecules that have one strand of parental DNA and one strand of new DNA. 12) _________________________is the process through which mRNA is decoded and forms ...
Chromatin Remodeling - Molecular Pharmacology
... investigations reporting altered gene expression in response to different types of psychiatric medications (e.g., antidepressants and antipsychotics) and drugs of abuse (e.g., psychostimulants and opiates), demonstrating the plasticity of neural systems at a molecular level (Duman et al., 1997; Duma ...
... investigations reporting altered gene expression in response to different types of psychiatric medications (e.g., antidepressants and antipsychotics) and drugs of abuse (e.g., psychostimulants and opiates), demonstrating the plasticity of neural systems at a molecular level (Duman et al., 1997; Duma ...
Leukaemia Section t(3;8)(q26;q24) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... transcribed in different isoform which may have different oncogenic effect. Protein 1051 amino acids; 118335 Da. Nuclear location, contains 10 C2H2-type zinc fingers. ...
... transcribed in different isoform which may have different oncogenic effect. Protein 1051 amino acids; 118335 Da. Nuclear location, contains 10 C2H2-type zinc fingers. ...
PPR2263, a DYW-Subgroup Pentatricopeptide
... the PPR proteins are predicted to be targeted to either mitochondria or chloroplasts, whereas no clear prediction is made for the rest. In addition to numerous experimental localizations in plastids and mitochondria, nuclear (Ding et al., 2006) or dual localization to mitochondria and nuclei (Hamman ...
... the PPR proteins are predicted to be targeted to either mitochondria or chloroplasts, whereas no clear prediction is made for the rest. In addition to numerous experimental localizations in plastids and mitochondria, nuclear (Ding et al., 2006) or dual localization to mitochondria and nuclei (Hamman ...
S1 Appendix.
... Extracting feature information from input files We extract the information of a given genomic feature from the full-genome sequence (.fa or equivalent) and annotation (.gff3 or equivalent) files. First, GRS extracts the name and length of each chromosome from the sequence file. It creates a list for ...
... Extracting feature information from input files We extract the information of a given genomic feature from the full-genome sequence (.fa or equivalent) and annotation (.gff3 or equivalent) files. First, GRS extracts the name and length of each chromosome from the sequence file. It creates a list for ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... Both oligonucleotides are designed such that the first four bases create 5’ overhangs compatible with Bbs I (TCCC for the sense strand and AAAC for the antisense strand). In the sense strand, the 5’ overhang is followed by an A (transcription initiation point of the human H1 promoter), then the targ ...
... Both oligonucleotides are designed such that the first four bases create 5’ overhangs compatible with Bbs I (TCCC for the sense strand and AAAC for the antisense strand). In the sense strand, the 5’ overhang is followed by an A (transcription initiation point of the human H1 promoter), then the targ ...
Genetics Project
... 1. What is the structure of DNA? How does the structure allow the DNA to be replicated easily? 2. What are the base-pairing rules for DNA? a. Explain how the base-pairing rules allow DNA to make two exact copies of itself. 3. Explain the role that enzymes play in replication. 4. What is a mutation? ...
... 1. What is the structure of DNA? How does the structure allow the DNA to be replicated easily? 2. What are the base-pairing rules for DNA? a. Explain how the base-pairing rules allow DNA to make two exact copies of itself. 3. Explain the role that enzymes play in replication. 4. What is a mutation? ...
GENE EXPRESSION
... enes are transcribed into RNA, which, for the most part, is then translated into protein. Control mechanisms are exercised along the way. Without some control of gene expression, an Escherichia coli cell, for example, would produce all its proteins in large quantities all the time, and all the cells ...
... enes are transcribed into RNA, which, for the most part, is then translated into protein. Control mechanisms are exercised along the way. Without some control of gene expression, an Escherichia coli cell, for example, would produce all its proteins in large quantities all the time, and all the cells ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.