Protein Synthesis - MsJacksonsBiologyWiki
... 1. Enzyme binds to DNA, unzips it 2. mRNA copy is made from DNA template ...
... 1. Enzyme binds to DNA, unzips it 2. mRNA copy is made from DNA template ...
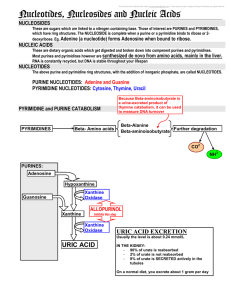
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portions of genes which encode protens; - INTRONS are portions of the gene which are not encoded into proteins - PROMOTER regions are near the transcription start of the gene, and this is where RNA polymerase binds to ...
... A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portions of genes which encode protens; - INTRONS are portions of the gene which are not encoded into proteins - PROMOTER regions are near the transcription start of the gene, and this is where RNA polymerase binds to ...
Chapter 11 - Evangel University
... • Trp operon codes for a leader sequence (trpL) & 5 polypeptides • The 5 proteins make up 4 different enzymes that catalyze the multistep process that converts chorisimate to tryptophan ...
... • Trp operon codes for a leader sequence (trpL) & 5 polypeptides • The 5 proteins make up 4 different enzymes that catalyze the multistep process that converts chorisimate to tryptophan ...
Protein Synthesis Poster
... second amino acid. Its anticodon links up with the second codon on the mRNA. A peptide bond joins the two amino acids to start the formation of a polypeptide chain. The process continues and amino acids are assembled in the correct sequence in a long chain to make the protein. ...
... second amino acid. Its anticodon links up with the second codon on the mRNA. A peptide bond joins the two amino acids to start the formation of a polypeptide chain. The process continues and amino acids are assembled in the correct sequence in a long chain to make the protein. ...
Revision - Mr C Biology
... second amino acid. Its anticodon links up with the second codon on the mRNA. A peptide bond joins the two amino acids to start the formation of a polypeptide chain. The process continues and amino acids are assembled in the correct sequence in a long chain to make the protein. ...
... second amino acid. Its anticodon links up with the second codon on the mRNA. A peptide bond joins the two amino acids to start the formation of a polypeptide chain. The process continues and amino acids are assembled in the correct sequence in a long chain to make the protein. ...
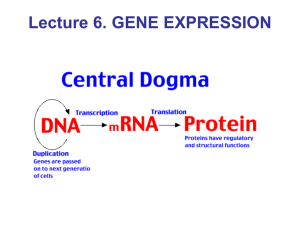
Gene Expression
... mRNA is going to copy the DNA code in the gene DNA is split – only one strand is read – the template strand The DNA strand that is not read is the nontemplate strand Three DNA nucleotides are a triplet. There are 64 possible triplets that code for the 20 different amino acids. RNA polymerase makes t ...
... mRNA is going to copy the DNA code in the gene DNA is split – only one strand is read – the template strand The DNA strand that is not read is the nontemplate strand Three DNA nucleotides are a triplet. There are 64 possible triplets that code for the 20 different amino acids. RNA polymerase makes t ...
Multiple Choice
... ____11. Which of the following is NOT a gene mutation? a. inversion c. deletion b. insertion d. substitution ____12. Which of the following statements is true? a. A promoter determines whether a gene is expressed. b. An expressed gene is turned off. c. Proteins that bind to regulatory sites on DNA d ...
... ____11. Which of the following is NOT a gene mutation? a. inversion c. deletion b. insertion d. substitution ____12. Which of the following statements is true? a. A promoter determines whether a gene is expressed. b. An expressed gene is turned off. c. Proteins that bind to regulatory sites on DNA d ...
Slide 1
... fit through nuclear membrane, so it needs to send a “messenger” RNA (mRNA) to the ribosomes to make proteins. DNA is very important and must be kept protected! ...
... fit through nuclear membrane, so it needs to send a “messenger” RNA (mRNA) to the ribosomes to make proteins. DNA is very important and must be kept protected! ...
DNA.Protein.Synthesis Notes
... Elongation adds amino acids to the polypeptide chain until a stop codon terminates translation – Once initiation is complete amino acids are added one by one to the first amino acid – The mRNA moves a codon at a time • A tRNA with a complementary anticodon pairs with each codon, adding its amino ac ...
... Elongation adds amino acids to the polypeptide chain until a stop codon terminates translation – Once initiation is complete amino acids are added one by one to the first amino acid – The mRNA moves a codon at a time • A tRNA with a complementary anticodon pairs with each codon, adding its amino ac ...
Steps in gene expression: comparison of
... separated from protein, denatured to separate the strands, and electrophoresed. The resulting gel is analyzed by autoradiography, which detects only labeled strands and reveals fragments extending from the labeled end to the site of cleavage by DNase I. ...
... separated from protein, denatured to separate the strands, and electrophoresed. The resulting gel is analyzed by autoradiography, which detects only labeled strands and reveals fragments extending from the labeled end to the site of cleavage by DNase I. ...
Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation)
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Translation is performed by the ribosome – the protein builder of the cell. • The ribosome consists of two smaller parts – the 60S and the 40S subunits. (The number refers to the size and the S is for the “sedimentation rate” of the molecule when placed in a centrifuge.) • The ribosome recognizes ...
... • Translation is performed by the ribosome – the protein builder of the cell. • The ribosome consists of two smaller parts – the 60S and the 40S subunits. (The number refers to the size and the S is for the “sedimentation rate” of the molecule when placed in a centrifuge.) • The ribosome recognizes ...
Transcription & Translation PowerPoint
... Which of the following reactions occurs when a dipeptide is formed from amino acids? A. Hydrolysis B. Denaturation C. Condensation D. Oxidation ...
... Which of the following reactions occurs when a dipeptide is formed from amino acids? A. Hydrolysis B. Denaturation C. Condensation D. Oxidation ...
Welcome to Mrs. Gomez-Buckley General Biology Class (Room 615)
... DNA opens up and messenger RNA (mRNA) copies message mRNA is edited – some parts taken out (introns) mRNA goes out of nucleus to ribosome mRNA attaches to ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) picks up an amino acid tRNA attaches to mRNA matching complementary base pairs at opposite end from amin ...
... DNA opens up and messenger RNA (mRNA) copies message mRNA is edited – some parts taken out (introns) mRNA goes out of nucleus to ribosome mRNA attaches to ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) picks up an amino acid tRNA attaches to mRNA matching complementary base pairs at opposite end from amin ...
doc14873 - Mrothery.co.uk
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
Slide 1
... A gene is the same as a segment of DNA that after transcription and translation gives rise to a specific protein (polypeptide chain). You may also see the word cistron used. It is in practice the same as gene. ...
... A gene is the same as a segment of DNA that after transcription and translation gives rise to a specific protein (polypeptide chain). You may also see the word cistron used. It is in practice the same as gene. ...
Transcription and the Central Dogma
... How were they discovered? RNA-DNA hybrids weren’t colinear- loops of DNA extend out where there is no RNA to base pair with it. RNA = red. ...
... How were they discovered? RNA-DNA hybrids weren’t colinear- loops of DNA extend out where there is no RNA to base pair with it. RNA = red. ...
How does DNA store and transmit cell information?
... the same as mRNA except the Ts are replaced with Us ...
... the same as mRNA except the Ts are replaced with Us ...
DNA Quiz #1 - Houston ISD
... 12. ____________ is complementary to the original DNA strand? 13. The mRNA carries information from the nucleus to a _________. 14. What is the correct base pairing of RNA? ___=___ ___=___ 15. Translation takes place in the ________________. 16. Replication, transcription, and translation are the st ...
... 12. ____________ is complementary to the original DNA strand? 13. The mRNA carries information from the nucleus to a _________. 14. What is the correct base pairing of RNA? ___=___ ___=___ 15. Translation takes place in the ________________. 16. Replication, transcription, and translation are the st ...
Notes Protein Synthesis
... RNA SPLICING • In eukaryotes… • Large portions of mRNA do not code for parts of a protein • Introns – noncoding segments • Exons – coding segments • snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) combine with proteins to make spliceosome • Spliceosomes cut at ends of introns and rejoins remaining exons ...
... RNA SPLICING • In eukaryotes… • Large portions of mRNA do not code for parts of a protein • Introns – noncoding segments • Exons – coding segments • snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) combine with proteins to make spliceosome • Spliceosomes cut at ends of introns and rejoins remaining exons ...
401Lecture5sp2013post
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.