17_Learning_Objectives
... 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alterna ...
... 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. 18. Explain why, due to alterna ...
Variation, Genetics and Evolution
... characteristics which enable them to survive better. Over time this may result in entirely new species. There are different theories of evolution. Darwin’s theory is the most widely accepted. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: • interpret evidence relating to evoluti ...
... characteristics which enable them to survive better. Over time this may result in entirely new species. There are different theories of evolution. Darwin’s theory is the most widely accepted. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: • interpret evidence relating to evoluti ...
STANYSintro2005
... bases of introns than they do exons.” “Hemoglobin sequences show that seals are closer to weasels than they are to whales.” “Protein shapes determine their function, so small changes can make a big difference.” ...
... bases of introns than they do exons.” “Hemoglobin sequences show that seals are closer to weasels than they are to whales.” “Protein shapes determine their function, so small changes can make a big difference.” ...
25.6 - Laurel County Schools
... of the branches do not survive. • When tracing the evolutionary history of a species consider all the evidence. • There is no drive toward a particular outcome (phenotype – physical attributes due to genes) • Does the evolutionary history of horses really show an evolutionary trend toward large size ...
... of the branches do not survive. • When tracing the evolutionary history of a species consider all the evidence. • There is no drive toward a particular outcome (phenotype – physical attributes due to genes) • Does the evolutionary history of horses really show an evolutionary trend toward large size ...
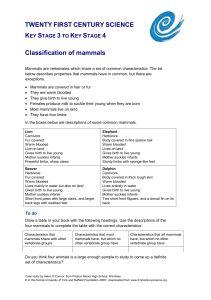
worksheet: classifying mammals
... characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes two different animals have in common, the more similar they are. ...
... characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes two different animals have in common, the more similar they are. ...
26LecturePresentation
... Concept 26.2: Phylogenies are inferred from morphological and molecular data • Homology - similarity due to shared ancestry • Analogy - similarity due to convergent evolution • Convergent evolution - similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar (analogous) adaptations in or ...
... Concept 26.2: Phylogenies are inferred from morphological and molecular data • Homology - similarity due to shared ancestry • Analogy - similarity due to convergent evolution • Convergent evolution - similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar (analogous) adaptations in or ...
15.11 Genes that control development play a major role in evolution
... In most cases, complex structures evolve by increments from simpler versions with the same basic functions. In the evolution of an eye or any other complex structure, behavior, or biochemical pathway, each step must – bring a selective advantage to the organism possessing it and – increase the o ...
... In most cases, complex structures evolve by increments from simpler versions with the same basic functions. In the evolution of an eye or any other complex structure, behavior, or biochemical pathway, each step must – bring a selective advantage to the organism possessing it and – increase the o ...
mutation-story-cystic
... increases her appetite, she is still unable to gain any. Maddy is only 3 years old and is already having a hard time doing little things. When she is walking around with her parents, she is constantly coughing with thick mucous, wheezing, and has a shortness of breath. She has bowel disturbances lik ...
... increases her appetite, she is still unable to gain any. Maddy is only 3 years old and is already having a hard time doing little things. When she is walking around with her parents, she is constantly coughing with thick mucous, wheezing, and has a shortness of breath. She has bowel disturbances lik ...
Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... Genetics Joins Evolutionary Theory Darwin developed his theory of evolution without knowing how heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. Researchers discovered that heritable traits are controlled by genes. Changes in genes and chromosomes gener ...
... Genetics Joins Evolutionary Theory Darwin developed his theory of evolution without knowing how heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. Researchers discovered that heritable traits are controlled by genes. Changes in genes and chromosomes gener ...
evolution and some ecobabble
... 1. mutations - mistake in replicating genetic information. e.g. single nucleotide deletion. A change in genetic instructions. -RANDOM (no matter how the env changes, will not determine type of mutation), whether beneficial or harmful depends on the environment. - only way that new alleles arize, i.e ...
... 1. mutations - mistake in replicating genetic information. e.g. single nucleotide deletion. A change in genetic instructions. -RANDOM (no matter how the env changes, will not determine type of mutation), whether beneficial or harmful depends on the environment. - only way that new alleles arize, i.e ...
The Return of Hopeful Monsters
... The mutant gene produces its effect . . . by changing the rates of partial processes of development. These might be rates of growth or differentiation, rates of production of stuffs necessary for differentiation, rates of reactions leading to definite physical or chemical situations at definite time ...
... The mutant gene produces its effect . . . by changing the rates of partial processes of development. These might be rates of growth or differentiation, rates of production of stuffs necessary for differentiation, rates of reactions leading to definite physical or chemical situations at definite time ...
The Return of Hopeful Monsters
... The mutant gene produces its effect . . . by changing the rates of partial processes of development. These might be rates of growth or differentiation, rates of production of stuffs necessary for differentiation, rates of reactions leading to definite physical or chemical situations at definite time ...
... The mutant gene produces its effect . . . by changing the rates of partial processes of development. These might be rates of growth or differentiation, rates of production of stuffs necessary for differentiation, rates of reactions leading to definite physical or chemical situations at definite time ...
Human evolution: Darwinism, genes and germs
... production of higher animals, directly follows. There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless fo ...
... production of higher animals, directly follows. There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless fo ...
The making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
... 15. How might these chromosomal alterations affect gene expression? (Hint: Watch the Gene Switch animation at http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/evolution/gene_switch.html.) Eukaryotic gene expression depends on enhancers and promoters, which are regulatory regions involved in transcription. These s ...
... 15. How might these chromosomal alterations affect gene expression? (Hint: Watch the Gene Switch animation at http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/evolution/gene_switch.html.) Eukaryotic gene expression depends on enhancers and promoters, which are regulatory regions involved in transcription. These s ...
Unit 8: Evolution - Sonoma Valley High School
... 6. Make of flow chart of the both the changes and causes of the changes in horses over the past 60 million years. 7. Explain how the following are used to support the theory of evolution: homology, development, and imperfect structures. After reading pg: 436-446: Define the following terms: speciati ...
... 6. Make of flow chart of the both the changes and causes of the changes in horses over the past 60 million years. 7. Explain how the following are used to support the theory of evolution: homology, development, and imperfect structures. After reading pg: 436-446: Define the following terms: speciati ...
introduction - University of Notre Dame
... accounts or saltationist models of evolution, the concern of Eldredge and Gould was rather to suggest an alternative naturalistic explanation that better fit the empirical geological evidence than the gradualist assumptions of the genetical theory of natural selection. The explanatory structure of t ...
... accounts or saltationist models of evolution, the concern of Eldredge and Gould was rather to suggest an alternative naturalistic explanation that better fit the empirical geological evidence than the gradualist assumptions of the genetical theory of natural selection. The explanatory structure of t ...
Patterns of Evolution
... • “Rapid” evolution after long periods of equilibrium – often occurs due to isolated populations, migrations, or mass extinctions ...
... • “Rapid” evolution after long periods of equilibrium – often occurs due to isolated populations, migrations, or mass extinctions ...
Document
... Some synonymous codons are favored over others e.g., yeast Leu codons: 6 possible codons/80% are UUG ...
... Some synonymous codons are favored over others e.g., yeast Leu codons: 6 possible codons/80% are UUG ...
Did Natural Selection Construct Metazoan Developmental
... bilaterian developmental architectures. We wish to know if the first appearances of the molecular, cellular, and systems-level features found in the ...
... bilaterian developmental architectures. We wish to know if the first appearances of the molecular, cellular, and systems-level features found in the ...
evolution - Big Picture
... Or a bumblebee, a frog, a mouse or a human being. Hox genes are found throughout the animal world. As new animals have evolved, their number and roles have changed slightly but they still perform basically the same function. There are many ways in which genes can take on new functions. The classical ...
... Or a bumblebee, a frog, a mouse or a human being. Hox genes are found throughout the animal world. As new animals have evolved, their number and roles have changed slightly but they still perform basically the same function. There are many ways in which genes can take on new functions. The classical ...
Evolutionary biology 2009 - (ecobio), rennes
... b) How do new species come into existence? There are different modes of speciation (e.g. allopatric, parapatric or sympatric) and a variety of mechanisms resulting in reproductive isolation. Speciation can be studied by making use of virtually all methods in evolutionary biology. c) How has sexual r ...
... b) How do new species come into existence? There are different modes of speciation (e.g. allopatric, parapatric or sympatric) and a variety of mechanisms resulting in reproductive isolation. Speciation can be studied by making use of virtually all methods in evolutionary biology. c) How has sexual r ...
Evolution: Medicine`s most basic science, Lancet, 2008
... as a machine designed by an engineer and manufactured from a blueprint. But there was no engineer and there is no master blueprint for the body. There is no single normal genome, there are just genes, some of which have been more successful than others in making bodies that survive to reproduce. Del ...
... as a machine designed by an engineer and manufactured from a blueprint. But there was no engineer and there is no master blueprint for the body. There is no single normal genome, there are just genes, some of which have been more successful than others in making bodies that survive to reproduce. Del ...
Die (Ir-)Rationalität religiöser Überzeugungen
... back, intestinal at front). Hence, change of species, common ancestry. Political relevance: (1) not ideas of God (2) ...if not even nature is stable? ...
... back, intestinal at front). Hence, change of species, common ancestry. Political relevance: (1) not ideas of God (2) ...if not even nature is stable? ...
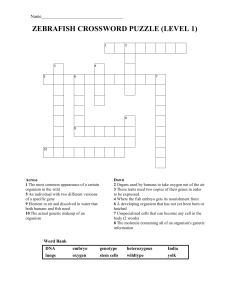
Zebrafish Crossword Puzzles
... 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance of a ce ...
... 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance of a ce ...