AG1 INVESTIGATOR Name Miyuki Yamamoto Address
... Dedkov, E.I., Borisov, A.B., Wernig, A., and Carlson, B.M. (2003). Aging of skeletal muscle does not affect the response of satellite cells to denervation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51(7), 853-863. Keller, C., Hansen, M.S., Coffin, C.M., and Capecchi, M.R. (2004). Pax3:Fkhr interferes with embryonic P ...
... Dedkov, E.I., Borisov, A.B., Wernig, A., and Carlson, B.M. (2003). Aging of skeletal muscle does not affect the response of satellite cells to denervation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51(7), 853-863. Keller, C., Hansen, M.S., Coffin, C.M., and Capecchi, M.R. (2004). Pax3:Fkhr interferes with embryonic P ...
PBS: What Darwin Never Knew Name: Biology Date: Period: 1
... 15. Without ___________________, everything would stay the same, generation after generation. We can now find the genes that are responsible for evolutionary change. 16. Humans have _______________ genes. The same numbers as a chicken and less that an ear of corn. Many of our key genes are similar t ...
... 15. Without ___________________, everything would stay the same, generation after generation. We can now find the genes that are responsible for evolutionary change. 16. Humans have _______________ genes. The same numbers as a chicken and less that an ear of corn. Many of our key genes are similar t ...
Phylum Porifera
... • Animals are the most physically diverse kingdom but share common characteristics. • Most animals reproduce sexually. ...
... • Animals are the most physically diverse kingdom but share common characteristics. • Most animals reproduce sexually. ...
Evolution
... Divergent evolution (diversification of an ancestral group into 2 or more species in different habitats) Covergent evolution (common selection pressures bring about similar adaptations; analogous structures) Coevolution (describes cases where two or more species reciprocally affect each other’s evol ...
... Divergent evolution (diversification of an ancestral group into 2 or more species in different habitats) Covergent evolution (common selection pressures bring about similar adaptations; analogous structures) Coevolution (describes cases where two or more species reciprocally affect each other’s evol ...
Extended phenotype redux
... he idea of the extended phenotype (EP), which was first proposed by the British evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins to explain how and why organisms—or, more fundamentally, their genes—are able to manipulate their environment (Dawkins, 1982), has been the focus of intense debate and much research ...
... he idea of the extended phenotype (EP), which was first proposed by the British evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins to explain how and why organisms—or, more fundamentally, their genes—are able to manipulate their environment (Dawkins, 1982), has been the focus of intense debate and much research ...
perspectives - Biology Learning Center
... are certainly others. Evolution has generated our planet’s biodiversity, and over the past century scientists have become able to explain the mechanisms by which changes in animal body structure can be produced, inherited and selected. Genetics is crucial to this understanding. The MODERN SYNTHESIS ...
... are certainly others. Evolution has generated our planet’s biodiversity, and over the past century scientists have become able to explain the mechanisms by which changes in animal body structure can be produced, inherited and selected. Genetics is crucial to this understanding. The MODERN SYNTHESIS ...
Ever-changing Populations
... larger over time. What type example of speciation is this? A. Stabilizing B. Disruptive C. Directional ...
... larger over time. What type example of speciation is this? A. Stabilizing B. Disruptive C. Directional ...
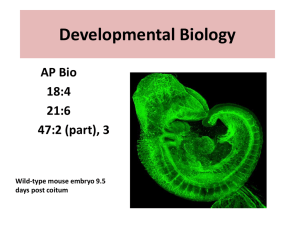
Developmental Biology
... • Their fate is determined largely by their position but they do have signaling. • Homeotic genes control organ identity (ABC model) but genes are called Mad-box genes instead of Hox genes ...
... • Their fate is determined largely by their position but they do have signaling. • Homeotic genes control organ identity (ABC model) but genes are called Mad-box genes instead of Hox genes ...
Modern Evolutionary Theory - bayo2pisay
... to another? http://4.bp.blogspot.com/EmedhzGoq4U/Tl14PpYybRI/AAAAAAAAgT0/nzHhIdibNw8/s800/101%2Bdalmatians%2Bposter.jpg ...
... to another? http://4.bp.blogspot.com/EmedhzGoq4U/Tl14PpYybRI/AAAAAAAAgT0/nzHhIdibNw8/s800/101%2Bdalmatians%2Bposter.jpg ...
The Impotence of Darwinism
... just a few million years, nearly all the animal phyla make their first appearance. "The term ‘explosion' should not be taken too literally, but in terms of evolution it is still very dramatic. What it means is rapid diversification of animal life. ‘Rapid' in this case means a few million years, rath ...
... just a few million years, nearly all the animal phyla make their first appearance. "The term ‘explosion' should not be taken too literally, but in terms of evolution it is still very dramatic. What it means is rapid diversification of animal life. ‘Rapid' in this case means a few million years, rath ...
Evolvability of physiological and biochemical traits: evolutionary
... features that comparative physiologists have discovered? Network properties enable evolvability The flowering of interactomics, network biology, and systems biology has revealed how single-nucleotide substitutions (and/or much larger mutations; see below) may in principle yield transformations of la ...
... features that comparative physiologists have discovered? Network properties enable evolvability The flowering of interactomics, network biology, and systems biology has revealed how single-nucleotide substitutions (and/or much larger mutations; see below) may in principle yield transformations of la ...
Okami Study Guide
... good qualities while downplaying the bad; vulnerability to the fundamental attribution error (FAE), the tendency to attribute another person’s behavior to that person’s inner dispositions and character traits while downplaying the possibility that situational factors may have played a large role in ...
... good qualities while downplaying the bad; vulnerability to the fundamental attribution error (FAE), the tendency to attribute another person’s behavior to that person’s inner dispositions and character traits while downplaying the possibility that situational factors may have played a large role in ...
Natural Selection and Evolution
... Natural Selection and Evolution - Ideas the textbook reviewers looked for: Modern ideas about evolution (including natural selection and common descent) provide a scientific explanation for the history of life on earth depicted in the fossil record and in the similarities evident within the diversit ...
... Natural Selection and Evolution - Ideas the textbook reviewers looked for: Modern ideas about evolution (including natural selection and common descent) provide a scientific explanation for the history of life on earth depicted in the fossil record and in the similarities evident within the diversit ...
Slide 1
... likely to survive and reproduce. This means that their genes are less likely to be passed to the next generation. Given enough time, a species will gradually evolve. ...
... likely to survive and reproduce. This means that their genes are less likely to be passed to the next generation. Given enough time, a species will gradually evolve. ...
ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... Scientists generally agree about the taxonomic classification of 36 animal phyla -They do disagree, however, about how these are interrelated Traditional reconstructions lump together phyla that share major features of body plan New reconstructions employ molecular comparisons of rRNA and other ge ...
... Scientists generally agree about the taxonomic classification of 36 animal phyla -They do disagree, however, about how these are interrelated Traditional reconstructions lump together phyla that share major features of body plan New reconstructions employ molecular comparisons of rRNA and other ge ...
Developmental Biology
... • Their fate is determined largely by their position but they do have signaling. • Homeotic genes control organ identity (ABC model) but genes are called Mad-box genes instead of Hox genes ...
... • Their fate is determined largely by their position but they do have signaling. • Homeotic genes control organ identity (ABC model) but genes are called Mad-box genes instead of Hox genes ...
AnimalDevelopment32_33_34
... Some animals develop directly into adults (vertebrates) All animals have Homeoboxes (genes that regulate development), most have Hox genes that regulate body development ...
... Some animals develop directly into adults (vertebrates) All animals have Homeoboxes (genes that regulate development), most have Hox genes that regulate body development ...
Unit 7: Evolution - Blue Valley Schools
... that humans and bats have fairly similar skeletal structures, while whales have diverged considerably in the shapes and proportions of their bones. However, analysis of several genes in these species suggests that all three diverged from a common ancestor at about the same time. Which of the followi ...
... that humans and bats have fairly similar skeletal structures, while whales have diverged considerably in the shapes and proportions of their bones. However, analysis of several genes in these species suggests that all three diverged from a common ancestor at about the same time. Which of the followi ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... fundamental tenet of molecular biology is that genes are coded sequences of the DNA molecule in the chromosome and that a gene codes for a precise sequence of amino acids in a protein. Mutations alter DNA chemically, leading to modified or new proteins. Over evolutionary time, proteins have had hist ...
... fundamental tenet of molecular biology is that genes are coded sequences of the DNA molecule in the chromosome and that a gene codes for a precise sequence of amino acids in a protein. Mutations alter DNA chemically, leading to modified or new proteins. Over evolutionary time, proteins have had hist ...
CLADISTICS: UNRAVELING EVOLUTION
... Plants—eukaryotes, photosynthetic, sporic life cycles Fungi—eukaryotes, simple multicellular, non-motile, zygotic life cycles Animals—eukaryotes, consumers, gametic life cycles How are these organisms related? What was the path of evolution to each? What did the ancestors look like? How do we figure ...
... Plants—eukaryotes, photosynthetic, sporic life cycles Fungi—eukaryotes, simple multicellular, non-motile, zygotic life cycles Animals—eukaryotes, consumers, gametic life cycles How are these organisms related? What was the path of evolution to each? What did the ancestors look like? How do we figure ...
Document
... When two different species share a common ancestor, but have different characteristics from one another. Exmple; Darwin finches. Convergent evolution When two different species do not share a common ancesstor, but have developed similar characteristics through adaptation to similar environmental con ...
... When two different species share a common ancestor, but have different characteristics from one another. Exmple; Darwin finches. Convergent evolution When two different species do not share a common ancesstor, but have developed similar characteristics through adaptation to similar environmental con ...
Evolution - MrOwdijWiki
... biology and scientific principles • In order to be respectful to all people’s beliefs and ideas • I would also ask you to stick to the principals of biology ...
... biology and scientific principles • In order to be respectful to all people’s beliefs and ideas • I would also ask you to stick to the principals of biology ...
SR 47(8) 35-37
... could also leave an imprint on the genetic material in eggs and sperm, short-circuiting the evolutionary process and passing along new traits observed even in a single generation. Epigenetics examines the inheritance of characteristics that are not set out in the DNA sequence. A renowned science wri ...
... could also leave an imprint on the genetic material in eggs and sperm, short-circuiting the evolutionary process and passing along new traits observed even in a single generation. Epigenetics examines the inheritance of characteristics that are not set out in the DNA sequence. A renowned science wri ...