Part 1: External Anatomy of Heart 5. Insert your index finger into the
... Part 3: Tracing the Flow of blood Right heart Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium (chamber) through the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava .It passes through the tricuspid valve and enters the right ventricle (chamber). Blood leaves through the semilunar valve and goes into the Pulmona ...
... Part 3: Tracing the Flow of blood Right heart Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium (chamber) through the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava .It passes through the tricuspid valve and enters the right ventricle (chamber). Blood leaves through the semilunar valve and goes into the Pulmona ...
Throat, Thorax, and Visceral Conditions
... – 1-7 connect costal cartilage to bone – 8-10 connect to costal cartilage of superior ribs – 11-12 known as floating ribs as they don’t attach anteriorly to any surface ...
... – 1-7 connect costal cartilage to bone – 8-10 connect to costal cartilage of superior ribs – 11-12 known as floating ribs as they don’t attach anteriorly to any surface ...
The anatomy of the heart - Bloomsburg University of
... A chamber of the heart, on the upper right side of the heart. It receives blood from the vena cava and pumps it into the right ventricle. The opening on the right atrium is called the coronary sinus. It drains the myocardium (muscular tissue of the heart). ...
... A chamber of the heart, on the upper right side of the heart. It receives blood from the vena cava and pumps it into the right ventricle. The opening on the right atrium is called the coronary sinus. It drains the myocardium (muscular tissue of the heart). ...
BIOL 218 F 2011 Lecture Outline Ch 21
... Papillary muscles and chordae tendineae prevent valve inversion when the ventricles contract ...
... Papillary muscles and chordae tendineae prevent valve inversion when the ventricles contract ...
Blood Flow - WBR Teacher Moodle
... oxygenated blood through the mitral valve into the right ventricle. ...
... oxygenated blood through the mitral valve into the right ventricle. ...
Heart and Circulation PPT File
... The Heart • A pump that pushes blood around the body • Located in the mediastinum (between the 2 lungs – slightly more on the left) • About the size of closed human fist • Enclosed by a membrane – pericardium (holds the heart in place, but also allows it to move as it beats, prevents it from overst ...
... The Heart • A pump that pushes blood around the body • Located in the mediastinum (between the 2 lungs – slightly more on the left) • About the size of closed human fist • Enclosed by a membrane – pericardium (holds the heart in place, but also allows it to move as it beats, prevents it from overst ...
HEART internal structure
... that of the right side, and its margins are more deeply indented. It is directed forward and toward the right and overlaps the root of the pulmonary artery. 35 ...
... that of the right side, and its margins are more deeply indented. It is directed forward and toward the right and overlaps the root of the pulmonary artery. 35 ...
The Cardiovascular System
... that allow for gas and nutrient exchange between the endothelial cells. ► Oxygen and nutrient rich blood cells will give away their nutrients and oxygen while picking up NH3 and CO2. ...
... that allow for gas and nutrient exchange between the endothelial cells. ► Oxygen and nutrient rich blood cells will give away their nutrients and oxygen while picking up NH3 and CO2. ...
The Cardiovascular System
... that allow for gas and nutrient exchange between the endothelial cells. ► Oxygen and nutrient rich blood cells will give away their nutrients and oxygen while picking up NH3 and CO2. ...
... that allow for gas and nutrient exchange between the endothelial cells. ► Oxygen and nutrient rich blood cells will give away their nutrients and oxygen while picking up NH3 and CO2. ...
Document
... brachiocephalic artery and the thoracic portions of the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries; the brachiocephalic veins and the upper half of the superior vena cava; the vagus, cardiac, phrenic and left recurrent laryngeal nerves; the trachea, oesophagus, and thoracic duct; the remains o ...
... brachiocephalic artery and the thoracic portions of the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries; the brachiocephalic veins and the upper half of the superior vena cava; the vagus, cardiac, phrenic and left recurrent laryngeal nerves; the trachea, oesophagus, and thoracic duct; the remains o ...
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System
... Major function is transportation Using blood as transport vehicle, system carries oxygen, nutrients, cell wastes, hormones, and many other substances vital to homeostasis to and from cells The force to move blood around the body provided by beating heart Heart located in body thorax flanked by lungs ...
... Major function is transportation Using blood as transport vehicle, system carries oxygen, nutrients, cell wastes, hormones, and many other substances vital to homeostasis to and from cells The force to move blood around the body provided by beating heart Heart located in body thorax flanked by lungs ...
Anatomy 3: heart, pericardium, coronary vessels
... Thebesian vv- small vv that dump directly back into heart Coronary sinus: o Posterior coronary sulcus (AV groove)- b/n LA and LV o Opens into RA b/n IVC and tricuspid valve o Valve ...
... Thebesian vv- small vv that dump directly back into heart Coronary sinus: o Posterior coronary sulcus (AV groove)- b/n LA and LV o Opens into RA b/n IVC and tricuspid valve o Valve ...
Slide 1
... The walls of the left ventricle are three times thicker than those of the right ventricle. (The left intraventricular blood pressure is six times higher than that inside the right ventricle.) ...
... The walls of the left ventricle are three times thicker than those of the right ventricle. (The left intraventricular blood pressure is six times higher than that inside the right ventricle.) ...
Task 2 – Cardiovascular
... Pulmonary Circulation Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium via the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. From the right atrium, the deoxygenated blood drains into the right ventricle through the right atrioventricular valve. This valve is also referred to as the tricuspid valve becaus ...
... Pulmonary Circulation Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium via the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. From the right atrium, the deoxygenated blood drains into the right ventricle through the right atrioventricular valve. This valve is also referred to as the tricuspid valve becaus ...
final review sheet - Science with Shust
... 71. The structures of the heart that are located superiorly and are the receiving chambers for blood are the ____________. The structures of the heart that are located inferiorly and are discharging chambers of the heart are the ________________. 72. The mitral valve prevents blood from flowing from ...
... 71. The structures of the heart that are located superiorly and are the receiving chambers for blood are the ____________. The structures of the heart that are located inferiorly and are discharging chambers of the heart are the ________________. 72. The mitral valve prevents blood from flowing from ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Powerpoint
... blood vessel you will see. This is the aorta. The aorta takes oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body. ...
... blood vessel you will see. This is the aorta. The aorta takes oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body. ...
Presentation
... Caused by aging, some medications, or diseases that cause damage to hearts electrical system ...
... Caused by aging, some medications, or diseases that cause damage to hearts electrical system ...
Rat Dissection-Circulation
... (the broad, dorsal end). The apex is usually free within the pericardium, and the base contains the great vessels and the attachment of the pericardium. The pericardium or pericardial sac is a double-layered closed sac that surrounds the heart and anchors it. 5. The aorta and pulmonary artery are th ...
... (the broad, dorsal end). The apex is usually free within the pericardium, and the base contains the great vessels and the attachment of the pericardium. The pericardium or pericardial sac is a double-layered closed sac that surrounds the heart and anchors it. 5. The aorta and pulmonary artery are th ...
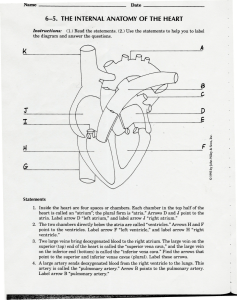
6-5. THE INTERNAL`ANATOMYOF THE HEART
... 6. Two small veins bring oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium. These veins are called "pulmonary veins." Find the arrow that points to the pulmonary veins. Label that arrow "pulmonary veins." 7. The bicuspid valve lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle. When it opens, blo ...
... 6. Two small veins bring oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium. These veins are called "pulmonary veins." Find the arrow that points to the pulmonary veins. Label that arrow "pulmonary veins." 7. The bicuspid valve lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle. When it opens, blo ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... a. Blood entering the ______________atrium flows through the tricuspid valve and into the ________________________________. From there, the deoxygenated blood flows past the ________________________________________________ valve and into enters the lungs. b. Oxygenated blood leaves the lungs through ...
... a. Blood entering the ______________atrium flows through the tricuspid valve and into the ________________________________. From there, the deoxygenated blood flows past the ________________________________________________ valve and into enters the lungs. b. Oxygenated blood leaves the lungs through ...
Flow of Blood and Vessel Structure and Location
... the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it branches off into two smaller arteries (the common iliacs). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation Pulmonary Artery – The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the hear ...
... the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it branches off into two smaller arteries (the common iliacs). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation Pulmonary Artery – The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the hear ...
ABC Anatomy coloring book By: Britney Rac
... Aorta is the largest artery in the body, the aorta arises from the left ventricle of the heart, goes up (ascends) a little ways, bends over (arches), then goes down (descends) through the chest and through the abdomen to where ends by dividing into two arteries called the common iliac arteries that ...
... Aorta is the largest artery in the body, the aorta arises from the left ventricle of the heart, goes up (ascends) a little ways, bends over (arches), then goes down (descends) through the chest and through the abdomen to where ends by dividing into two arteries called the common iliac arteries that ...
The cardiac cycle - Websupport1
... Blood flow through the heart • Right atria –receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava and pumps it to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve • Right ventricle –receives blood from right atrium and pumps it toto the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary semilunar valve • Pulmonar ...
... Blood flow through the heart • Right atria –receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava and pumps it to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve • Right ventricle –receives blood from right atrium and pumps it toto the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary semilunar valve • Pulmonar ...
Heart Dissection Lab
... i. On the left side of the heart, the pulmonary vein(s) empty into the left atrium. Depending on how your specimen has been cut, you may find 1-4 pulmonary veins. 4. Once you have identified all the external structures of the heart, you will need to make 2 incisions to examine the internal anatomy ...
... i. On the left side of the heart, the pulmonary vein(s) empty into the left atrium. Depending on how your specimen has been cut, you may find 1-4 pulmonary veins. 4. Once you have identified all the external structures of the heart, you will need to make 2 incisions to examine the internal anatomy ...
Heart

The heart is a muscular organ in humans and other animals, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, and also assists in the removal of metabolic wastes. The heart is located in the middle compartment of the mediastinum in the chest.In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria; and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish in contrast have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.The heart pumps blood through both circulatory systems. Blood low in oxygen from the systemic circulation enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here it is pumped into the pulmonary circulation, through the lungs where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide. In addition the blood carries nutrients from the liver and gastrointestinal tract to various organs of the body, while transporting waste to the liver and kidneys. Normally with each heartbeat the right ventricle pumps the same amount of blood into the lungs as the left ventricle pumps to the body. Veins transport blood to the heart and carry deoxygenated blood - except for the pulmonary and portal veins. Arteries transport blood away from the heart, and apart from the pulmonary artery hold oxygenated blood. Their increased distance from the heart cause veins to have lower pressures than arteries. The heart contracts at a resting rate close to 72 beats per minute. Exercise temporarily increases the rate, but lowers resting heart rate in the long term, and is good for heart health.Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the most common cause of death globally as of 2008, accounting for 30% of deaths. Of these more than three quarters follow coronary artery disease and stroke. Risk factors include: smoking, being overweight, little exercise, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and poorly controlled diabetes, among others. Diagnosis of CVD is often done by listening to the heart-sounds with a stethoscope, ECG or by ultrasound. Specialists who focus on diseases of the heart are called cardiologists, although many specialties of medicine may be involved in treatment.