Blood Vessels of the Fetal Pig Dissection
... f. The costocervical veins also branch off the superior vena cava and extend back toward the spinal column. g. Note the coronary veins on the surface of the fetal pig heart. h. Find the intercostal veins that drain the tissue along each rib. i. The hemiazygous vein receives blood from the left inter ...
... f. The costocervical veins also branch off the superior vena cava and extend back toward the spinal column. g. Note the coronary veins on the surface of the fetal pig heart. h. Find the intercostal veins that drain the tissue along each rib. i. The hemiazygous vein receives blood from the left inter ...
The Human Heart Essay Research Paper Biology
... the right ventricle. It forms a small part of the left side of the anterior surface of the heart and a large portion of the posterior surface. It also forms the apex of the heart because it extends beyond the right ventricle. Its walls are nearly twice as thick as those of the right ventricle. They ...
... the right ventricle. It forms a small part of the left side of the anterior surface of the heart and a large portion of the posterior surface. It also forms the apex of the heart because it extends beyond the right ventricle. Its walls are nearly twice as thick as those of the right ventricle. They ...
Heart size Blood Volume and Flow
... calculate how often their heart beats at rest and after exercising. A pulse of 60 beats a minute means the heart is pumping 60 times a minute, every minute. 5. Ask students to estimate how much blood (how many bottles) is in their bodies. 6. Say that a child’s body contains about 4 liters (~4 quarts ...
... calculate how often their heart beats at rest and after exercising. A pulse of 60 beats a minute means the heart is pumping 60 times a minute, every minute. 5. Ask students to estimate how much blood (how many bottles) is in their bodies. 6. Say that a child’s body contains about 4 liters (~4 quarts ...
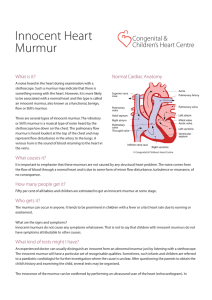
Innocent Heart Murmur - Congenital and Children`s Heart Centre
... stethoscope. Such a murmur may indicate that there is something wrong with the heart. However, it is more likely to be associated with a normal heart and this type is called an innocent murmur, also known as a functional, benign, flow or Still’s murmur. There are several types of innocent murmur. Th ...
... stethoscope. Such a murmur may indicate that there is something wrong with the heart. However, it is more likely to be associated with a normal heart and this type is called an innocent murmur, also known as a functional, benign, flow or Still’s murmur. There are several types of innocent murmur. Th ...
06 Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]
... introduction of a contrast medium into a particular bronchus usually under fluoroscopic control. The contrast media are nonirritating and sufficiently radiopaque to allow good visualization of the bronchi. After the radiographic examination is completed, the patient is asked to cough and expectorate ...
... introduction of a contrast medium into a particular bronchus usually under fluoroscopic control. The contrast media are nonirritating and sufficiently radiopaque to allow good visualization of the bronchi. After the radiographic examination is completed, the patient is asked to cough and expectorate ...
Palpation of the apical impulse
... 2. Right border: does not exceed the right border of the sternum. 3. Upper border: 3d ...
... 2. Right border: does not exceed the right border of the sternum. 3. Upper border: 3d ...
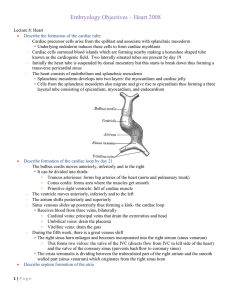
Embryology_Objectives heart 2008
... Each AV orifice is now surrounded by mesenchymal tissue. Valves form and remain attached to the ventricle wall by muscular cords The muscle tissue in the cords degenerates and is replaced by dens connective tissue Valves are connective tissue covered by endocardium They are connected to a ...
... Each AV orifice is now surrounded by mesenchymal tissue. Valves form and remain attached to the ventricle wall by muscular cords The muscle tissue in the cords degenerates and is replaced by dens connective tissue Valves are connective tissue covered by endocardium They are connected to a ...
heart
... expelled into the pulmonary trunk to be conveyed to the lungs. As it circulates through the pulmonary capillaries the blood is brought into close relationship with the inspired air and it gives off some of its carbon dioxide and acquires a fresh supply of oxygen. This oxygenated blood is returned by ...
... expelled into the pulmonary trunk to be conveyed to the lungs. As it circulates through the pulmonary capillaries the blood is brought into close relationship with the inspired air and it gives off some of its carbon dioxide and acquires a fresh supply of oxygen. This oxygenated blood is returned by ...
HEART ANATOMY RESUMED - Sinoe Medical Association
... embryonic heart. Sinus Venarum: A smooth area in the Right Ventricle, remaining from the Right Horn of the embryonic Sinus Venosus. Cristae Terminalis: Ridge on superior anterior border, demarcating the embryonic heart (auricle) from the adult heart. It is at the border of the Right Auricle. ...
... embryonic heart. Sinus Venarum: A smooth area in the Right Ventricle, remaining from the Right Horn of the embryonic Sinus Venosus. Cristae Terminalis: Ridge on superior anterior border, demarcating the embryonic heart (auricle) from the adult heart. It is at the border of the Right Auricle. ...
Heart Anatomy
... o the left side of the heart is the systemic circuit pump o this is a long, high-resistance pathway through the entire body ...
... o the left side of the heart is the systemic circuit pump o this is a long, high-resistance pathway through the entire body ...
What is a fetal echocardiogram?
... see the main heart chambers, heart valves and main blood vessels directly attaching to the heart, and establish information about the heart rate and rhythm. We can establish, with a high degree of certainty, the presence of most congenital abnormalities of the heart. Limitations of the examination S ...
... see the main heart chambers, heart valves and main blood vessels directly attaching to the heart, and establish information about the heart rate and rhythm. We can establish, with a high degree of certainty, the presence of most congenital abnormalities of the heart. Limitations of the examination S ...
Cardiovascular System
... blood collected in the right atrium to flow into the right ventricle Mitral Valve: The mitral valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle. It opens to allow the oxygenated blood collected in the left atrium to flow into the left ventricle Pulmonary Valve: The pulmonary valve separate ...
... blood collected in the right atrium to flow into the right ventricle Mitral Valve: The mitral valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle. It opens to allow the oxygenated blood collected in the left atrium to flow into the left ventricle Pulmonary Valve: The pulmonary valve separate ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Muscle impulses are distributed immediately and simultaneously throughout all fibers either of the atria or of the ventricles. ...
... Muscle impulses are distributed immediately and simultaneously throughout all fibers either of the atria or of the ventricles. ...
Ecological - WordPress.com
... Also called filum terminale- terminal part of spinalcord 32 Somaesthetic area Also called post- centra larea- center for pain touch temp. 33 Eighth cranial nerve Goes to ear 34 Fifth cranial nerve Goes to jaw muscle 35 Broca’s area Speech control center- present in frontal lobe 36 Cereellum Only par ...
... Also called filum terminale- terminal part of spinalcord 32 Somaesthetic area Also called post- centra larea- center for pain touch temp. 33 Eighth cranial nerve Goes to ear 34 Fifth cranial nerve Goes to jaw muscle 35 Broca’s area Speech control center- present in frontal lobe 36 Cereellum Only par ...
Heart
... Each is composed of three thin, pocketlike semilunar cusps. As blood is pumped into the arterial trunks, it pushes against the cusps, forcing the valves open. When ventricular contraction ceases, blood is prevented from flowing back into the ventricles from the arterial trunk by first entering the p ...
... Each is composed of three thin, pocketlike semilunar cusps. As blood is pumped into the arterial trunks, it pushes against the cusps, forcing the valves open. When ventricular contraction ceases, blood is prevented from flowing back into the ventricles from the arterial trunk by first entering the p ...
Pulmonary semilunar valve
... walls. The Left side has a thicker wall because it is the main pump having to move blood through the entire body. ...
... walls. The Left side has a thicker wall because it is the main pump having to move blood through the entire body. ...
Thorax Forum Questions 2010ish
... A catheter can be passed from the superior vena cava through the right atrium into the inferior vena cava 7. Explain why when a patient has angina pectoralis they experience pain radiating down their left arm. This is caused by referred pain; sensory cell bodies coming from the heart will synapse ne ...
... A catheter can be passed from the superior vena cava through the right atrium into the inferior vena cava 7. Explain why when a patient has angina pectoralis they experience pain radiating down their left arm. This is caused by referred pain; sensory cell bodies coming from the heart will synapse ne ...
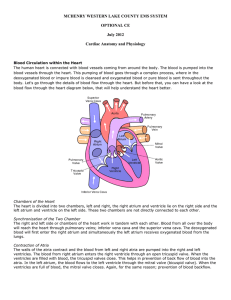
MCHENRY WESTERN LAKE COUNTY EMS SYSTEM OPTIONAL
... left atrium and ventricle on the left side. These two chambers are not directly connected to each other. Synchronization of the Two Chamber The right and left side or chambers of the heart work in tandem with each other. Blood from all over the body will reach the heart through pulmonary veins; infe ...
... left atrium and ventricle on the left side. These two chambers are not directly connected to each other. Synchronization of the Two Chamber The right and left side or chambers of the heart work in tandem with each other. Blood from all over the body will reach the heart through pulmonary veins; infe ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 21 Martini Lecture Outline
... Coronary sulcus separates the atria and the ventricles Anterior interventricular sulcus separates the left and right ventricles Posterior interventricular sulcus also separates the left and right ventricles ...
... Coronary sulcus separates the atria and the ventricles Anterior interventricular sulcus separates the left and right ventricles Posterior interventricular sulcus also separates the left and right ventricles ...
Slide ()
... Most commonly used modifications of the Fontan operation. A. Right atrial (RA) to pulmonary artery (PA) Fontan connection with the right atrial appendage directly sutured to the RPA in a patient with tricuspid and pulmonary atresia. The right ventricle (RV), left ventricle (LV), mitral valve (MV), r ...
... Most commonly used modifications of the Fontan operation. A. Right atrial (RA) to pulmonary artery (PA) Fontan connection with the right atrial appendage directly sutured to the RPA in a patient with tricuspid and pulmonary atresia. The right ventricle (RV), left ventricle (LV), mitral valve (MV), r ...
Gross anatomy of the heart
... chordae tendinae: slender, fibrous threads that arise from apices of the papillary muscles. These insert into the free edges and ventricular surfaces of the valve cusps. right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve: located between the right atrium and right ventricle. This valve blocks the reflux of bl ...
... chordae tendinae: slender, fibrous threads that arise from apices of the papillary muscles. These insert into the free edges and ventricular surfaces of the valve cusps. right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve: located between the right atrium and right ventricle. This valve blocks the reflux of bl ...
Internal Anatomy and Organization of the Heart
... Compare to the right ventricle, which has a thin wall since it only pumps blood through the pulmonary circuit Does not have a moderator band The AV valve has chordae tendineae connecting to the two cusps and to two papillary muscles ...
... Compare to the right ventricle, which has a thin wall since it only pumps blood through the pulmonary circuit Does not have a moderator band The AV valve has chordae tendineae connecting to the two cusps and to two papillary muscles ...
The Circulatory System:
... What are the Steps of Circulation? • 1. Blood returns to the right atrium through the inferior and superior vena cavae. • 2. Blood passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle • 3. Blood passes through the pulmonary semi-lunar valve into the pulmonary arteries • 4. Blood releases CO ...
... What are the Steps of Circulation? • 1. Blood returns to the right atrium through the inferior and superior vena cavae. • 2. Blood passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle • 3. Blood passes through the pulmonary semi-lunar valve into the pulmonary arteries • 4. Blood releases CO ...
Heart

The heart is a muscular organ in humans and other animals, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, and also assists in the removal of metabolic wastes. The heart is located in the middle compartment of the mediastinum in the chest.In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria; and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish in contrast have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.The heart pumps blood through both circulatory systems. Blood low in oxygen from the systemic circulation enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here it is pumped into the pulmonary circulation, through the lungs where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide. In addition the blood carries nutrients from the liver and gastrointestinal tract to various organs of the body, while transporting waste to the liver and kidneys. Normally with each heartbeat the right ventricle pumps the same amount of blood into the lungs as the left ventricle pumps to the body. Veins transport blood to the heart and carry deoxygenated blood - except for the pulmonary and portal veins. Arteries transport blood away from the heart, and apart from the pulmonary artery hold oxygenated blood. Their increased distance from the heart cause veins to have lower pressures than arteries. The heart contracts at a resting rate close to 72 beats per minute. Exercise temporarily increases the rate, but lowers resting heart rate in the long term, and is good for heart health.Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the most common cause of death globally as of 2008, accounting for 30% of deaths. Of these more than three quarters follow coronary artery disease and stroke. Risk factors include: smoking, being overweight, little exercise, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and poorly controlled diabetes, among others. Diagnosis of CVD is often done by listening to the heart-sounds with a stethoscope, ECG or by ultrasound. Specialists who focus on diseases of the heart are called cardiologists, although many specialties of medicine may be involved in treatment.


![06 Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000576414_1-742a4dc499e0753b1c920d47b2cac2b5-300x300.png)






![06 Radiological_Anatomy_of_Thorax_(2)[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000414327_1-04da754cadb08122653c700a0fc76def-300x300.png)