File - Biology withMrs. Ellsworth
... - each with unique shape and unique function - 20 different amino acids Proteins have many functions – proteins determine structure and function of organisms : -enzymes - regulate and speed up chemical reactions - very specific (one enzyme for each reaction) - structural proteins - contractile prote ...
... - each with unique shape and unique function - 20 different amino acids Proteins have many functions – proteins determine structure and function of organisms : -enzymes - regulate and speed up chemical reactions - very specific (one enzyme for each reaction) - structural proteins - contractile prote ...
8.5 Translation
... • The genetic code matches EACH codon to its amino acid or function. The genetic code matches each RNA codon with its amino acid or function. – three stop ...
... • The genetic code matches EACH codon to its amino acid or function. The genetic code matches each RNA codon with its amino acid or function. – three stop ...
Translation - St. Robert CHS
... • The third base in each codon may differ b/w two codons that code for the same a.a. – E.g, AAU and AAC both code for tyrosine. ...
... • The third base in each codon may differ b/w two codons that code for the same a.a. – E.g, AAU and AAC both code for tyrosine. ...
Transcription and Translation
... mutation is a substitution. For example, consider what happens if the codon UAC changes to UAA. UAC codes for tyrosine. UAA is a stop codon. By substituting a single nucleotide for another, the message changes from “add a tyrosine” to “stop adding nucleotides here.” This results in a shorter-than-no ...
... mutation is a substitution. For example, consider what happens if the codon UAC changes to UAA. UAC codes for tyrosine. UAA is a stop codon. By substituting a single nucleotide for another, the message changes from “add a tyrosine” to “stop adding nucleotides here.” This results in a shorter-than-no ...
mRNA
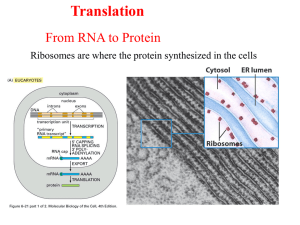
... nucleus to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) Protein is translated from the RNA at the cytoplasm at the ribosome ...
... nucleus to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) Protein is translated from the RNA at the cytoplasm at the ribosome ...
RNA - Gulf Coast State College
... • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
... • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
RNA - Gulf Coast State College
... • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
... • More than 1 triplet may code for the same amino acid. This is fine as long as no triplet can code for more than one a.acid. • Note that several codons can also act as start (AUG) or stop (UAA) signals. ...
The CENTRAL DOGMA in Biology
... occasionally sulphur. There are _____ different amino acids (the human body can make some amino acids, others must be obtained from food). Amino acids link to form polypeptide chains which make up the primary structure of a protein. A typical protein may contain ____________ or more amino acids. ...
... occasionally sulphur. There are _____ different amino acids (the human body can make some amino acids, others must be obtained from food). Amino acids link to form polypeptide chains which make up the primary structure of a protein. A typical protein may contain ____________ or more amino acids. ...
Objectives 2
... (DNA) is found in the cell nucleus and in the mitochondria and functions to store genetic information used for the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is found in the nucleus, in the cytosol, and in the mitochondria and has many functions: mRNA carries messages transcribed from ...
... (DNA) is found in the cell nucleus and in the mitochondria and functions to store genetic information used for the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is found in the nucleus, in the cytosol, and in the mitochondria and has many functions: mRNA carries messages transcribed from ...
Transcription and the control of gene expression
... FIGURE 6.14. In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase II is guided to the promoter by TFII accessory proteins. (A) TBP binds to the TATA box. (B) The complete transcription preinitiation complex. (C) Phosphorylated RNA polymerase is active. ...
... FIGURE 6.14. In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase II is guided to the promoter by TFII accessory proteins. (A) TBP binds to the TATA box. (B) The complete transcription preinitiation complex. (C) Phosphorylated RNA polymerase is active. ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... (a) Differential Removal of Introns This can produce variations in the mRNA produced. Different mRNA may have different introns removed. Differential removal of introns enables a gene to code for more than one different protein. An average human gene is thought to code for 3 different proteins. For ...
... (a) Differential Removal of Introns This can produce variations in the mRNA produced. Different mRNA may have different introns removed. Differential removal of introns enables a gene to code for more than one different protein. An average human gene is thought to code for 3 different proteins. For ...
April 3 lecture slides
... Structures like this involving DNA with bound activator proteins and RNA polymerase complex are names “enhanceosomes”. TBP stands for TATAbinding protein, a component of RNA polymerase II associated factor, TFIID ...
... Structures like this involving DNA with bound activator proteins and RNA polymerase complex are names “enhanceosomes”. TBP stands for TATAbinding protein, a component of RNA polymerase II associated factor, TFIID ...
2.7 DNA Transcription_translation
... The code is written using four “letters” (the bases: A, U, C, and G). ...
... The code is written using four “letters” (the bases: A, U, C, and G). ...
CHEM 642-09 Powerpoint
... first and second positions, and vary at the third position. Three codons do not specify any amino acid but act as termination sites (stop codons), signaling the end of the protein- coding sequence. One codon— AUG—acts both as an initiation codon, signaling the start of a protein-coding message, and ...
... first and second positions, and vary at the third position. Three codons do not specify any amino acid but act as termination sites (stop codons), signaling the end of the protein- coding sequence. One codon— AUG—acts both as an initiation codon, signaling the start of a protein-coding message, and ...
Group 6 - Purdue Genomics Wiki
... Bases: •START & STOP codons •High GC content •No repeats •Good E-value •Proper splice sites •Both program agreed •No mobile elements ...
... Bases: •START & STOP codons •High GC content •No repeats •Good E-value •Proper splice sites •Both program agreed •No mobile elements ...
Chapter 12. Protein biosynthesis (P215, sP875)
... mRNA in eukaryotes is usually monocistronic: one mRNA encodes only a single polypeptide chain. mRNA in prokaryotes usually encodes more than one polypeptide chain. This is called ...
... mRNA in eukaryotes is usually monocistronic: one mRNA encodes only a single polypeptide chain. mRNA in prokaryotes usually encodes more than one polypeptide chain. This is called ...
Unit 6 Protein Synthesis
... If instructions for cell division are affected, this can lead to cancer! Point Mutation A change in a single DNA base may or may not affect the AA sequence ...
... If instructions for cell division are affected, this can lead to cancer! Point Mutation A change in a single DNA base may or may not affect the AA sequence ...
Protein Synthesis
... • tRNA’s anticodon matches with mRNA’s codon to deliver the correct amino acid needed to make the protein. • The Ribosome positions the tRNA molecules close enough so that peptide bonds can form between the amino acids. ...
... • tRNA’s anticodon matches with mRNA’s codon to deliver the correct amino acid needed to make the protein. • The Ribosome positions the tRNA molecules close enough so that peptide bonds can form between the amino acids. ...
Repressor protein - Edwin C. Foreman High School
... Gene regulation in bacteria • Cells vary amount of specific enzymes by regulating gene transcription – turn genes on or turn genes off ...
... Gene regulation in bacteria • Cells vary amount of specific enzymes by regulating gene transcription – turn genes on or turn genes off ...
157KB - NZQA
... carries the amino acid to the ribosome and drops it off. The process of translation is explained by giving a substantially correct sequence of steps: ribosomes move along the mRNA from the start codon until the stop codons is reached. Each sequence of 3 bases (codon) on the mRNA is read by the r ...
... carries the amino acid to the ribosome and drops it off. The process of translation is explained by giving a substantially correct sequence of steps: ribosomes move along the mRNA from the start codon until the stop codons is reached. Each sequence of 3 bases (codon) on the mRNA is read by the r ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.