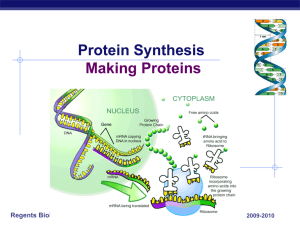
here - Biology 100
... Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells while aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria. e. Both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle release CO2 as “waste” products. ...
... Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells while aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria. e. Both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle release CO2 as “waste” products. ...
Prok transcription
... Transcription- synthesis of RNA from only one strand of a double stranded DNA helix DNARNA(Protein) Why is RNA an intermediate???? 1. Protect the DNA; limited access; 2. Gives regulatory opportunity (all cells have the same DNA but not the same genes are expressed) 3. In Eukaryotes the DNA i ...
... Transcription- synthesis of RNA from only one strand of a double stranded DNA helix DNARNA(Protein) Why is RNA an intermediate???? 1. Protect the DNA; limited access; 2. Gives regulatory opportunity (all cells have the same DNA but not the same genes are expressed) 3. In Eukaryotes the DNA i ...
UC Irvine FOCUS! 5 E Lesson Plan Title: Genetics Scavenger Hunt
... the replication of DNA” or simply “DNA->DNA->RNA->Protein”. This process is therefore broken down into 3 steps: Transcription, Translation, and Replication. By new knowledge of the RNA processing, a fourth step must be included, the splicing. Transcription is the process by which the information con ...
... the replication of DNA” or simply “DNA->DNA->RNA->Protein”. This process is therefore broken down into 3 steps: Transcription, Translation, and Replication. By new knowledge of the RNA processing, a fourth step must be included, the splicing. Transcription is the process by which the information con ...
Presentation title: Introduction to RNA
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
Unit #3 Retake Ticket Unit 3 Retake Ticket
... _____________ and its specific amino acid. The two amino acids shown in this diagram are _______________ and ____________. The amino acids bind with a ______________ bond and form a _____________, the final product. Through this process cells create enzymes, produce antibodies, and construct all of ...
... _____________ and its specific amino acid. The two amino acids shown in this diagram are _______________ and ____________. The amino acids bind with a ______________ bond and form a _____________, the final product. Through this process cells create enzymes, produce antibodies, and construct all of ...
Bioinformatics Protein Synthesis Amino Acid Table Amino Acids
... A cisITon is a distinct region of DNA that codes for a particular polypeptide. The term is used in the context of a protein which is made up of several subunits, each of which is coded by a different gene. An operon is a common form of gene organization in bacteria. ...
... A cisITon is a distinct region of DNA that codes for a particular polypeptide. The term is used in the context of a protein which is made up of several subunits, each of which is coded by a different gene. An operon is a common form of gene organization in bacteria. ...
Common Assessment Review
... Transcription- process by which RNA is made. Part of the nucleotide sequence of a DNA molecule is copied into RNA. Occurs in the nucleus Steps: DNA is unzipped in the nucleus by an enzyme - Another enzyme, RNA polymerase, bonds “free nucleotides” to the exposed bases - Adenine bonds with uracil (A ...
... Transcription- process by which RNA is made. Part of the nucleotide sequence of a DNA molecule is copied into RNA. Occurs in the nucleus Steps: DNA is unzipped in the nucleus by an enzyme - Another enzyme, RNA polymerase, bonds “free nucleotides” to the exposed bases - Adenine bonds with uracil (A ...
Transcriptional regulation is only half the story
... APEX method critically corrects for factors, such as efficiency of ionization, that influence the a priori probability of peptide detection. As a result, APEX provides reliable quantification of protein levels over five orders of magnitude. Vogel et al. analyzed about 200 sequence features as potent ...
... APEX method critically corrects for factors, such as efficiency of ionization, that influence the a priori probability of peptide detection. As a result, APEX provides reliable quantification of protein levels over five orders of magnitude. Vogel et al. analyzed about 200 sequence features as potent ...
Stages and mechanisms of translation, regulation of translat
... Initiator tRNA • First codon translated is usually AUG • The initiator tRNA recognizes initiation codons -Bacteria: N-formylmethionyl-tRNA -Eukaryotes: methionyl-tRNA ...
... Initiator tRNA • First codon translated is usually AUG • The initiator tRNA recognizes initiation codons -Bacteria: N-formylmethionyl-tRNA -Eukaryotes: methionyl-tRNA ...
Protein Synthesis Paper Lab
... the sequence of tRNA bases responsible for forming this protein? 9. A ribosome receives the following mRNA message: AAA CGA GAA GUU. a. What will be the sequence of tRNA bases matching up with the mRNA molecule? b. What will be the sequence of amino acids formed from this code? To review: You should ...
... the sequence of tRNA bases responsible for forming this protein? 9. A ribosome receives the following mRNA message: AAA CGA GAA GUU. a. What will be the sequence of tRNA bases matching up with the mRNA molecule? b. What will be the sequence of amino acids formed from this code? To review: You should ...
Chapter 19: Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... 7.) What is a promoter proximal element? How does it differ from the gene’s promoter? What is the benefit of the promoter proximal elements for gene expression? 8.) What are the steps for transcription initiation in eukaryotes? 9.) What is a transcriptional enhancer? How enhancers in the DNA work fr ...
... 7.) What is a promoter proximal element? How does it differ from the gene’s promoter? What is the benefit of the promoter proximal elements for gene expression? 8.) What are the steps for transcription initiation in eukaryotes? 9.) What is a transcriptional enhancer? How enhancers in the DNA work fr ...
Protein Synthesis
... the DNA and breaks the H-bonds between the bases of the two strands, separating them from one another Base pairing occurs between incoming RNA nucleotides and the DNA nucleotides of the gene (template) • recall RNA uses uracil instead of thymine ...
... the DNA and breaks the H-bonds between the bases of the two strands, separating them from one another Base pairing occurs between incoming RNA nucleotides and the DNA nucleotides of the gene (template) • recall RNA uses uracil instead of thymine ...
Transcription and Translation
... Transcription: chain termination • Most known about bacterial chain termination • Termination is signaled by a sequence that can form a hairpin loop. • The polymerase and the new RNA molecule are released upon formation of the loop. • Review the transcription animation. ...
... Transcription: chain termination • Most known about bacterial chain termination • Termination is signaled by a sequence that can form a hairpin loop. • The polymerase and the new RNA molecule are released upon formation of the loop. • Review the transcription animation. ...
RNA
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
NAME
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
Rice Krispie Treats
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
... 1. Check with the other groups in the class. What other variants of the gene exist? How similar or dissimilar were their DNA sequence? ...
Chapter 12 guided Notes 2
... 2. RNA polymerase builds a strand of mRNA using one strand of DNA as a template. 3. The DNA is transcribed into mRNA following the base pairing rules except uracil binds to adenine. The directions for making proteins are in the order of the four nitrogenous bases. This code is read three letters at ...
... 2. RNA polymerase builds a strand of mRNA using one strand of DNA as a template. 3. The DNA is transcribed into mRNA following the base pairing rules except uracil binds to adenine. The directions for making proteins are in the order of the four nitrogenous bases. This code is read three letters at ...
chapter13
... A regulon is a group of operons that are organized into a multigene system. Regulons are controlled by a single regulatory protein. ...
... A regulon is a group of operons that are organized into a multigene system. Regulons are controlled by a single regulatory protein. ...
Bio1A Unit 2 Study Guide Cell Cycle
... b. mRNA, Ribosome(rRNA), charge‐tRNAs c. rRNA is the enzyme 7. Be able to determine the anticodon sequence and amino acid of the tRNA for corresponding mRNA 8. Identify mutations and consequences to amino acid sequence and severity (and why) a. Silent, missense, nonsense, frameshift ...
... b. mRNA, Ribosome(rRNA), charge‐tRNAs c. rRNA is the enzyme 7. Be able to determine the anticodon sequence and amino acid of the tRNA for corresponding mRNA 8. Identify mutations and consequences to amino acid sequence and severity (and why) a. Silent, missense, nonsense, frameshift ...
Chapter 4: Cellular metabolism
... 3. Explain how DNA & RNA store and carry genetic information. 4. Explain how genetic information controls cellular processes. 5. How do DNA molecules replicate? ...
... 3. Explain how DNA & RNA store and carry genetic information. 4. Explain how genetic information controls cellular processes. 5. How do DNA molecules replicate? ...
Transcription and Translation Title: The Central Dogma: By Humans
... Start the activity by having one student assigned to the nucleus to represent the DNA. There is only one student with the notecard that contains the DNA code. This student can work together with multiple students representing mRNA in order to translate the code. An example code may be as follows: o ...
... Start the activity by having one student assigned to the nucleus to represent the DNA. There is only one student with the notecard that contains the DNA code. This student can work together with multiple students representing mRNA in order to translate the code. An example code may be as follows: o ...
Nucline RNA and Its Uses
... • It is conditionally translated into a protein. • Protein is only expressed when researcher-defined gene profiles are present in the cell. • It can be used to modify, tag, and even destroy cells that express the gene profile. • It is not siRNA (methylates target DNA) or antisense (blocks mRNA trans ...
... • It is conditionally translated into a protein. • Protein is only expressed when researcher-defined gene profiles are present in the cell. • It can be used to modify, tag, and even destroy cells that express the gene profile. • It is not siRNA (methylates target DNA) or antisense (blocks mRNA trans ...
Full file at http://TestbanksCafe.eu/Test-Bank-for-Introduction
... the formation of peptide bonds between an amino acid attached to a peptidyl-tRNA and an amino acid from an aminoacyl-tRNA? A) Reverse transcriptase B) DNA polymerase C) Peptidyl transferase D) DNA ligase E) β-galactosidase Answer: C 6) Addition of a poly(A) tail to an mRNA molecule ________. A) allo ...
... the formation of peptide bonds between an amino acid attached to a peptidyl-tRNA and an amino acid from an aminoacyl-tRNA? A) Reverse transcriptase B) DNA polymerase C) Peptidyl transferase D) DNA ligase E) β-galactosidase Answer: C 6) Addition of a poly(A) tail to an mRNA molecule ________. A) allo ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.