2009 - Barley World
... 32. In the case of a codominant molecular marker, the expected phenotypic ratio in the F2 progeny of the cross between two completely inbred lines will be a. 1:1 b. 1:2:1 c. 3:1 d. 9:3:3:1 33. The highest temperature steps in a PCR reaction are necessary for a. denaturation of the DNA. b. primer an ...
... 32. In the case of a codominant molecular marker, the expected phenotypic ratio in the F2 progeny of the cross between two completely inbred lines will be a. 1:1 b. 1:2:1 c. 3:1 d. 9:3:3:1 33. The highest temperature steps in a PCR reaction are necessary for a. denaturation of the DNA. b. primer an ...
Supplementary Methods
... Data analysis. Flow cytometry graphs were analyzed computationally using FACSDiva (Beckton Dickinson, FACSArray; DGC screen) or ModFit (LSR; phospho screen) software. To control for differences in culture conditions between batches of culture plates and for the well-dependent drift caused by the ins ...
... Data analysis. Flow cytometry graphs were analyzed computationally using FACSDiva (Beckton Dickinson, FACSArray; DGC screen) or ModFit (LSR; phospho screen) software. To control for differences in culture conditions between batches of culture plates and for the well-dependent drift caused by the ins ...
RNA polymerase
... 2. The first tRNA molecule (carrying the amino acid methionine) binds to the codon AUG (start codon). 3. A second tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid arrives at the codon adjacent to the first tRNA. 4. Enzymes catalyze the formation of a peptide bond that joins the amino acid carried by the first t ...
... 2. The first tRNA molecule (carrying the amino acid methionine) binds to the codon AUG (start codon). 3. A second tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid arrives at the codon adjacent to the first tRNA. 4. Enzymes catalyze the formation of a peptide bond that joins the amino acid carried by the first t ...
PowerPoint® slides
... LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. University will not be liable for any costs, damages, fees or other liability, nor for any direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages (including lost profits) with respect to any claims by ...
... LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. University will not be liable for any costs, damages, fees or other liability, nor for any direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages (including lost profits) with respect to any claims by ...
Document
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 5 kb and 3.1 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this clone was 720 nucleotides in length. A synthetic oligonucleotide that corresponded to amino acids 3 through 11 of this protein was produced and labeled; it hybridized to the 5 kb, ...
... and a clone derived from that library hybridized to the 5 kb and 3.1 kb restriction fragments only. When sequenced, this clone was 720 nucleotides in length. A synthetic oligonucleotide that corresponded to amino acids 3 through 11 of this protein was produced and labeled; it hybridized to the 5 kb, ...
Chapter 23 – Cancer Genetics
... – Enzymes that activate/inactivate other proteins by adding phosphate groups to them – Only functional when associated with a cyclin protein • Concentration of cyclins change throughout cell cycle; CDK concentration remains constant • Cyclin type determines which proteins will be phosphorylated ...
... – Enzymes that activate/inactivate other proteins by adding phosphate groups to them – Only functional when associated with a cyclin protein • Concentration of cyclins change throughout cell cycle; CDK concentration remains constant • Cyclin type determines which proteins will be phosphorylated ...
Biotechnology
... nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or "jumping genes") are small pieces of DNA that encode enzymes th ...
... nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or "jumping genes") are small pieces of DNA that encode enzymes th ...
Chapter 7: Getting into genes Name
... diagram to illustrate your answer. into single nucleotides. Diagram should show the two strands either before or after unzipping and indicate part of double helix shape. The codes for bases are not required. (b) What happens to the ‘unzipped’ DNA (b) It is copied when free nucleotides from molecule ...
... diagram to illustrate your answer. into single nucleotides. Diagram should show the two strands either before or after unzipping and indicate part of double helix shape. The codes for bases are not required. (b) What happens to the ‘unzipped’ DNA (b) It is copied when free nucleotides from molecule ...
Gene Regulation in Cells
... exact mix of proteins in a cell determines its cell fate (what kind of cell it is, for example making a neuron different from a skin cell). Therefore, gene regulation links genotype (genetic information) and phenotype (observable characteristics). The proteins that control gene regulation are transc ...
... exact mix of proteins in a cell determines its cell fate (what kind of cell it is, for example making a neuron different from a skin cell). Therefore, gene regulation links genotype (genetic information) and phenotype (observable characteristics). The proteins that control gene regulation are transc ...
Genetics and Evolution Question sheet Answer Key
... - The number of times an allele occurs within a gene pool compared to the number of times other alleles for the same gene occur 7) What is the relative frequency of the hair colour allele in this class? 8) How else can we view evolutionary change? Give an example. ...
... - The number of times an allele occurs within a gene pool compared to the number of times other alleles for the same gene occur 7) What is the relative frequency of the hair colour allele in this class? 8) How else can we view evolutionary change? Give an example. ...
Introduction To Databases – Day2
... In many cases a motif consists of distinct subparts that are highly conserved in the sequences, while the regions between these subparts have little in common. If we have a database of these patterns, we can assign potential function to a novel protein by finding one or more known motifs… ...
... In many cases a motif consists of distinct subparts that are highly conserved in the sequences, while the regions between these subparts have little in common. If we have a database of these patterns, we can assign potential function to a novel protein by finding one or more known motifs… ...
Science 9 Unit A 3.0
... the same trait (for example, leg length in a fly) • These pairs of genes are always found at the same position on a chromosome • However, the code for each gene in the pair may be different ...
... the same trait (for example, leg length in a fly) • These pairs of genes are always found at the same position on a chromosome • However, the code for each gene in the pair may be different ...
Gene Cloning 2
... backbone bonds of both DNA strands, creating single-stranded ends, sticky ends. – These extensions will form hydrogen-bonded base pairs with complementary single-stranded stretches on other DNA molecules cut with the same restriction enzyme ...
... backbone bonds of both DNA strands, creating single-stranded ends, sticky ends. – These extensions will form hydrogen-bonded base pairs with complementary single-stranded stretches on other DNA molecules cut with the same restriction enzyme ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... Genomic Library cDNA Library Either a genomic or cDNA library Neither a genomic nor cDNA library ...
... Genomic Library cDNA Library Either a genomic or cDNA library Neither a genomic nor cDNA library ...
Identify the three parts of cell theory All living things are made of
... How many nitrogen base pairs? ...
... How many nitrogen base pairs? ...
DNA Replication - The Biology Corner
... 2. DNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides and binds the sugars and phosphates. DNA polymerase travels from the 3' to the 5' end. The DNA is called the template strand. 3. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides on the other side of the ladder. Traveling in the opposite direction. 4. ...
... 2. DNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides and binds the sugars and phosphates. DNA polymerase travels from the 3' to the 5' end. The DNA is called the template strand. 3. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides on the other side of the ladder. Traveling in the opposite direction. 4. ...
In meiosis, what is the difference between metaphase 1 and
... 6. Explain what is meant by crossing-over (recombination). Be sure and mention at what time it is taking place within the cell. An exchange of corresponding segments between two homologous chromosomes at the chiasma. Occurs during prophase I of meiosis. ...
... 6. Explain what is meant by crossing-over (recombination). Be sure and mention at what time it is taking place within the cell. An exchange of corresponding segments between two homologous chromosomes at the chiasma. Occurs during prophase I of meiosis. ...
My Genetic Profile Worksheet
... • Each DNA cluster will be strongly attracted to any cDNA made from complimentary mRNA strands. For example: DNA strands with the base sequence TTCAGGCAG will be attracted to any cDNA strands with the sequence AAGTCCGTC. In other words each DNA cluster will be attracted to cDNA that were made using ...
... • Each DNA cluster will be strongly attracted to any cDNA made from complimentary mRNA strands. For example: DNA strands with the base sequence TTCAGGCAG will be attracted to any cDNA strands with the sequence AAGTCCGTC. In other words each DNA cluster will be attracted to cDNA that were made using ...
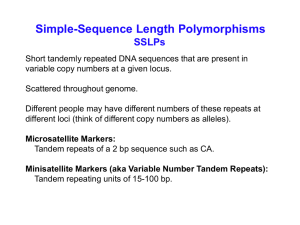
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
Human Heredity - mccombsscience
... By using tools that cut, separate, and then replicate DNA base by base, scientists can now read the base sequences in DNA from any cell ...
... By using tools that cut, separate, and then replicate DNA base by base, scientists can now read the base sequences in DNA from any cell ...
Genome Annotation - Virginia Commonwealth University
... includes regions preceding and following the coding region (leader and trailer) as well as intervening sequences (introns) Entire DNA sequence including exons, introns, and noncoding transcription-control regions ...
... includes regions preceding and following the coding region (leader and trailer) as well as intervening sequences (introns) Entire DNA sequence including exons, introns, and noncoding transcription-control regions ...
New Title
... b. The ribosome releases the completed protein chain. c. Messenger RNA enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. d. DNA “unzips” to direct the production of a strand of messenger RNA. 10. Circle the letter of the last step in protein synthesis. a. Transfer RNA carries amino acids to the ribos ...
... b. The ribosome releases the completed protein chain. c. Messenger RNA enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. d. DNA “unzips” to direct the production of a strand of messenger RNA. 10. Circle the letter of the last step in protein synthesis. a. Transfer RNA carries amino acids to the ribos ...