Objective - Central Magnet School
... extraction, PCR, and restriction analysis to identify single base pair differences in DNA • Explain how single base pair changes called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be identified through genetic testing and often correlate to specific diseases or traits. ...
... extraction, PCR, and restriction analysis to identify single base pair differences in DNA • Explain how single base pair changes called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be identified through genetic testing and often correlate to specific diseases or traits. ...
Biology B Final Review ANSWERS
... Describe the structure of DNA proposed by Watson and Crick. The structure was a double helix that twists as it goes Apply Chargaff ’s rule to decide how many guanine bases a length of DNA will have if it has 26 cytosine bases. Explain. It would 26 guanine bases since A=G ...
... Describe the structure of DNA proposed by Watson and Crick. The structure was a double helix that twists as it goes Apply Chargaff ’s rule to decide how many guanine bases a length of DNA will have if it has 26 cytosine bases. Explain. It would 26 guanine bases since A=G ...
Unit 4 ~ DNA Review
... That means that when it makes a copy, one half of the old strand is always kept in the new strand. This helps reduce the number of copy error ...
... That means that when it makes a copy, one half of the old strand is always kept in the new strand. This helps reduce the number of copy error ...
Mendelism
... she certainly didn't talk to Maurice [Wilkins] or to John Randall, then the professor at Kings". James Watson quoted in Nature, 302, 21 (April 1983): 653. There's a myth which is, you know, that Francis and I basically stole the structure from the people at King's. I was shown Rosalind Franklin's x- ...
... she certainly didn't talk to Maurice [Wilkins] or to John Randall, then the professor at Kings". James Watson quoted in Nature, 302, 21 (April 1983): 653. There's a myth which is, you know, that Francis and I basically stole the structure from the people at King's. I was shown Rosalind Franklin's x- ...
Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid)
... The Process of Heat Shock • Helps to increase the bacterial uptake of foreign DNA • Membrane becomes more permeable to DNA • Time is essential: -ice water bath (42ºC) for 50 sec. ice ...
... The Process of Heat Shock • Helps to increase the bacterial uptake of foreign DNA • Membrane becomes more permeable to DNA • Time is essential: -ice water bath (42ºC) for 50 sec. ice ...
AGO1-IP approach to small RNA target discovery in Arabidopsis
... A drawback of the method is its intrinsic reliance on sufficient VSR expression levels in the tissues of interest. This may partly explain its poor performances in roots (Figure S5), where the 35S promoter is reputed to be only weakly active in several cell layers. Constitutive VSR expression might ...
... A drawback of the method is its intrinsic reliance on sufficient VSR expression levels in the tissues of interest. This may partly explain its poor performances in roots (Figure S5), where the 35S promoter is reputed to be only weakly active in several cell layers. Constitutive VSR expression might ...
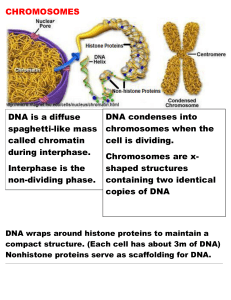
Chromosomes Notes
... spaghetti-like mass called chromatin during interphase. Interphase is the non-dividing phase. ...
... spaghetti-like mass called chromatin during interphase. Interphase is the non-dividing phase. ...
The Production of a
... A DNA fingerprint is the unique pattern that results from the DNA analysis of an individual ...
... A DNA fingerprint is the unique pattern that results from the DNA analysis of an individual ...
Slide 1
... Some viruses can hide their DNA or RNA inside the host cell for many years before they begin to kill cells! HIV retrovirus ( ) virus attacks white blood cells called T-cells. Destroys T-cells. Once no more Tcells then It causes the disease ...
... Some viruses can hide their DNA or RNA inside the host cell for many years before they begin to kill cells! HIV retrovirus ( ) virus attacks white blood cells called T-cells. Destroys T-cells. Once no more Tcells then It causes the disease ...
Replication is when DNA
... The single chromosome displayed here and those on the previous screen are shown in their most compacted state -- they're about to ______________________________, along with the cell, through the process of ________________________. o ...
... The single chromosome displayed here and those on the previous screen are shown in their most compacted state -- they're about to ______________________________, along with the cell, through the process of ________________________. o ...
Agilent 101: An Introduction to Microarrays and Genomics
... which holds all the instructions for making and controlling each structure and activity of the cell. These instructions are encoded in molecules of DNA that are analogous to paper tape. Taken as a whole, we call this DNA our genome. The instruction set for a single piece part is called a gene. As I ...
... which holds all the instructions for making and controlling each structure and activity of the cell. These instructions are encoded in molecules of DNA that are analogous to paper tape. Taken as a whole, we call this DNA our genome. The instruction set for a single piece part is called a gene. As I ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP): Variation between individuals in DNA fragment sizes cut by specific restriction enzymes; polymorphic sequences that result in RFLPs are used as markers on both physical maps and genetic linkage maps. RFLPs are usually caused by mutation at a cutting s ...
... Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP): Variation between individuals in DNA fragment sizes cut by specific restriction enzymes; polymorphic sequences that result in RFLPs are used as markers on both physical maps and genetic linkage maps. RFLPs are usually caused by mutation at a cutting s ...
Fig1 from Nature Rev Mol. Cell Biol (Nov2003) 4(11):865
... Prokaryotic IS elements (e.g. IS10, Ac/Ds, mariner) encode only transposase sequences ...
... Prokaryotic IS elements (e.g. IS10, Ac/Ds, mariner) encode only transposase sequences ...
File
... • Mutations in mtDNA provide information about the evolutionary path of animals and plant species ...
... • Mutations in mtDNA provide information about the evolutionary path of animals and plant species ...
Interspersed Repetitive Noncoding DNA
... – Submitting the work one has done for one class or project to a second class, or as a second project, without the prior informed consent of the relevant instructors; – Submitting work prepared in collaboration with another or other member(s) of a class, when collaborative work on a project has not ...
... – Submitting the work one has done for one class or project to a second class, or as a second project, without the prior informed consent of the relevant instructors; – Submitting work prepared in collaboration with another or other member(s) of a class, when collaborative work on a project has not ...
Supporting Information Khalil et al. 10.1073/pnas.0904715106
... assigned to each probe and recalculated the statistic. We took the value for each permutation as the maximum score obtained for any random region. We performed 1,000 permutations, and assigned a P value to each region, corrected for multiple testing, based on its rank within this distribution. All r ...
... assigned to each probe and recalculated the statistic. We took the value for each permutation as the maximum score obtained for any random region. We performed 1,000 permutations, and assigned a P value to each region, corrected for multiple testing, based on its rank within this distribution. All r ...
Control of Gene Activity
... molecules can vary, as well as their ability to bind ribosomes Some mRNA's may need additional changes before they are translated The initiation of translation of selected mRNAs can be blocked by regulatory proteins that bind to sequences or structures of the mRNA ...
... molecules can vary, as well as their ability to bind ribosomes Some mRNA's may need additional changes before they are translated The initiation of translation of selected mRNAs can be blocked by regulatory proteins that bind to sequences or structures of the mRNA ...
Mutation and DNA Repair
... the “p” is the connecting phosphate) gets methylated: a CH3 group is attached to the 5 position on the ring. When 5-methyl cytosine is spontaneously deaminated, it is converted to thymine, a standard DNA base. Replication leads to a base change: one daughter stays a C-G base pair while the other is ...
... the “p” is the connecting phosphate) gets methylated: a CH3 group is attached to the 5 position on the ring. When 5-methyl cytosine is spontaneously deaminated, it is converted to thymine, a standard DNA base. Replication leads to a base change: one daughter stays a C-G base pair while the other is ...
Mutations Worksheet
... During replication, transcription and translation there can be a mistake made in the bonding of complementary bases. These mistakes will lead to mutations. There are three main types of mutations: point mutations, insertion, and deletion mutations (the latter two are both frame shift mutations). In ...
... During replication, transcription and translation there can be a mistake made in the bonding of complementary bases. These mistakes will lead to mutations. There are three main types of mutations: point mutations, insertion, and deletion mutations (the latter two are both frame shift mutations). In ...
Regulating Gene Expression
... the longer there is for the necessary mutations to accumulate Viruses also play a role in the development of some cancers Retroviruses have oncogenes that can be donated to the host cell The viral DNA may also be inserted in such a way that it disrupts a tumor-supressing gene. ...
... the longer there is for the necessary mutations to accumulate Viruses also play a role in the development of some cancers Retroviruses have oncogenes that can be donated to the host cell The viral DNA may also be inserted in such a way that it disrupts a tumor-supressing gene. ...
013368718X_CH15_229-246.indd
... produced by recombinant viruses. 5. In DNA fingerprinting, an absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. 6. Prospective parents can find out if they carry the alleles for a genetic disease through genetic testing. ...
... produced by recombinant viruses. 5. In DNA fingerprinting, an absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. 6. Prospective parents can find out if they carry the alleles for a genetic disease through genetic testing. ...
Chapter 15 Study Guide
... Complete each statement by underlining the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 1. Cohen and Boyer revolutionized genetics by producing recombinant [DNA / RNA]. 2. In Cohen and Boyer’s 1973 experiment, genetically engineered [bacterial / human] cells produced frog rRNA. 3. Moving genes from one o ...
... Complete each statement by underlining the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 1. Cohen and Boyer revolutionized genetics by producing recombinant [DNA / RNA]. 2. In Cohen and Boyer’s 1973 experiment, genetically engineered [bacterial / human] cells produced frog rRNA. 3. Moving genes from one o ...
Chapter 9 I am - Mrs Smith`s Biology
... I am the number of chromosomes that are found in each new daughter cell compared to the original cell following mitosis ...
... I am the number of chromosomes that are found in each new daughter cell compared to the original cell following mitosis ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.