Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid)
... Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid) Lab #9: Molecular Biology ...
... Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid) Lab #9: Molecular Biology ...
A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
... (tRNAs), and small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). rRNAs and tRNAs participate in protein assembly whereas snRNAs aid in a process called splicing —the process of editing of mRNA before it can be used as a template for protein synthesis. ...
... (tRNAs), and small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). rRNAs and tRNAs participate in protein assembly whereas snRNAs aid in a process called splicing —the process of editing of mRNA before it can be used as a template for protein synthesis. ...
Chapter 12 Molecular Genetics Identifying the Substance of Genes I
... 1. Prokaryotic – singular chromosome, circular 2. Eukaryotic – 1000x more DNA as prokaryotes, DNA in the nucleus, multiple chromosomes. Each species has a characteristic chromosome number. Contain both DNA and protein. Chromatin is tightly coiled around proteins (histones) – they form a bead-like st ...
... 1. Prokaryotic – singular chromosome, circular 2. Eukaryotic – 1000x more DNA as prokaryotes, DNA in the nucleus, multiple chromosomes. Each species has a characteristic chromosome number. Contain both DNA and protein. Chromatin is tightly coiled around proteins (histones) – they form a bead-like st ...
Genetics Test 1 Review
... What kind of cells are produced by somatic cell division? How many daughter cells are produced? Are daughter cells haploid or diploid? Explain what this means. Are daughter cells genetically identical or different? Explain why. ...
... What kind of cells are produced by somatic cell division? How many daughter cells are produced? Are daughter cells haploid or diploid? Explain what this means. Are daughter cells genetically identical or different? Explain why. ...
MBP 1022, LECTURE 1 – Oct 27, 2000
... Based on DNA sequence similarity Archaea are more related to humans than bacteria. ...
... Based on DNA sequence similarity Archaea are more related to humans than bacteria. ...
Name
... 41) A biologist identifies the DNA sequence, or gene, that codes for a protein that stops the production of eggs in mosquitoes. She labels this gene Sequence 1. During her investigation of the replication, transcription , and translation of the gene, she observes mosquitoes in which the protein code ...
... 41) A biologist identifies the DNA sequence, or gene, that codes for a protein that stops the production of eggs in mosquitoes. She labels this gene Sequence 1. During her investigation of the replication, transcription , and translation of the gene, she observes mosquitoes in which the protein code ...
Ch. 15 Genetic Code and Translation & Protein Structure
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter14/animations.html ...
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter14/animations.html ...
Topic: Genetic Mutations
... Substitution (point) mutation = when one base is replaced with another Results in transcription and translation of a different amino acid than expected. Sickle Cell Anemia disease where substitution occurs on one base ...
... Substitution (point) mutation = when one base is replaced with another Results in transcription and translation of a different amino acid than expected. Sickle Cell Anemia disease where substitution occurs on one base ...
E. coli DNA Gyrase Cleavage Assay Kit
... for 1 hour in Assay Buffer in the presence of CFX. 0.2 % SDS and 0.1 mg/ml Proteinase K are added before a further incubation at 37 C for 30 minutes. gyrase ...
... for 1 hour in Assay Buffer in the presence of CFX. 0.2 % SDS and 0.1 mg/ml Proteinase K are added before a further incubation at 37 C for 30 minutes. gyrase ...
PDF
... cancer results from the continuing expression of inappropriate embryonic gene sequences; and that oncogenic viruses use embryonic regulatory sequences involved in cell differentiation to accomplish the replication of viral gene sequences. The exact mechanism of interaction with cellular embryonic se ...
... cancer results from the continuing expression of inappropriate embryonic gene sequences; and that oncogenic viruses use embryonic regulatory sequences involved in cell differentiation to accomplish the replication of viral gene sequences. The exact mechanism of interaction with cellular embryonic se ...
Recitation Section 7 Answer Key Molecular Biology—DNA as
... Some of the examples of the various types of information encoded in DNA are: where replication begins; when a given gene would be expressed; amino acid sequence of a gene; cellular address of a protein; and information for properly segregating the chromosomes during cell division. 7. How is it poss ...
... Some of the examples of the various types of information encoded in DNA are: where replication begins; when a given gene would be expressed; amino acid sequence of a gene; cellular address of a protein; and information for properly segregating the chromosomes during cell division. 7. How is it poss ...
Chapter Objectives: Chapters 18~19: Genetics of
... 3. The control of gene expression enables individual bacteria to adjust their metabolism to environmental change C. The Structure of Chromatin 1. Chromatin structure is based on successive levels of DNA packing D. Genome Organization at the DNA Level 1. Repetitive DNA and othe noncoding sequences ac ...
... 3. The control of gene expression enables individual bacteria to adjust their metabolism to environmental change C. The Structure of Chromatin 1. Chromatin structure is based on successive levels of DNA packing D. Genome Organization at the DNA Level 1. Repetitive DNA and othe noncoding sequences ac ...
EXAM #3 - life.illinois.edu
... of the protein or one could construct a variant that contains a His-tag on the N or Cterminus to aid in purification on a nickel column (or both). c. (2 Points). Describe one potential problem with your answer to part (b). Answer: Expression of the protein from the T7 promoter might result in inclus ...
... of the protein or one could construct a variant that contains a His-tag on the N or Cterminus to aid in purification on a nickel column (or both). c. (2 Points). Describe one potential problem with your answer to part (b). Answer: Expression of the protein from the T7 promoter might result in inclus ...
Mrs Single`s Genetics Powerpoint
... Each cell splits into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell has the haploid number of chromosomes, but each chromosome is made of two chromatids. A new spindle forms and chromosomes are arranged on the equator Chromatids separate to the cell ends Each daughter cell splits into two to finally form f ...
... Each cell splits into two daughter cells. Each daughter cell has the haploid number of chromosomes, but each chromosome is made of two chromatids. A new spindle forms and chromosomes are arranged on the equator Chromatids separate to the cell ends Each daughter cell splits into two to finally form f ...
Biology_EOC_Review_Spring_2010
... 6. Where is the most energy in this pyramid? Where is the least energy? 7. What happens to energy as it moves through the food chain/web? 8. Assume there are 10,000 kcal of energy in the leaves? Estimate the amount of energy in each of the other levels of the energy pyramid. ...
... 6. Where is the most energy in this pyramid? Where is the least energy? 7. What happens to energy as it moves through the food chain/web? 8. Assume there are 10,000 kcal of energy in the leaves? Estimate the amount of energy in each of the other levels of the energy pyramid. ...
Williams Bio 93 Final Exam Fall 2014 Answer Key 1
... 37. In order to determine how long the NPC1 mRNA remain in the cell, researchers next blocked new mRNA production using the drug Actinomycin D (Act-D). Where should Act-D bind in order to block mRNA production? A. DNA polymerase B. Ribosomes C. General transcription factors D. Restriction enzyme Onl ...
... 37. In order to determine how long the NPC1 mRNA remain in the cell, researchers next blocked new mRNA production using the drug Actinomycin D (Act-D). Where should Act-D bind in order to block mRNA production? A. DNA polymerase B. Ribosomes C. General transcription factors D. Restriction enzyme Onl ...
QPX methods 117KB Aug 15 2012 08:14:13 PM
... Temperature (mucus and cell) –hypothesis? We hypothesize that altered biochemical pathways will be associated with changes in temperature? Specifically we are interested in virulence factors, mucus production, cell growth and responses to heat stress. HELP! Virulence factors and QPX and methods to i ...
... Temperature (mucus and cell) –hypothesis? We hypothesize that altered biochemical pathways will be associated with changes in temperature? Specifically we are interested in virulence factors, mucus production, cell growth and responses to heat stress. HELP! Virulence factors and QPX and methods to i ...
Chapter 13 - Angelfire
... trait. What is the presumed genotype of the cat? Explain. • Suppose you want to produce a plant that has red flowers and speckled leaves. You have two offspring, each having one of the desired traits. How would you proceed? • Why is inbreeding rarely a problem among animals in the ...
... trait. What is the presumed genotype of the cat? Explain. • Suppose you want to produce a plant that has red flowers and speckled leaves. You have two offspring, each having one of the desired traits. How would you proceed? • Why is inbreeding rarely a problem among animals in the ...
Slide 1
... A. encode transcription factors that control the expression of genes responsible for specific anatomical structures. B. are found only in Drosophila and other arthropods. C. encode proteins that form anatomical structures in the fly. D. are responsible for patterning during plant development. ...
... A. encode transcription factors that control the expression of genes responsible for specific anatomical structures. B. are found only in Drosophila and other arthropods. C. encode proteins that form anatomical structures in the fly. D. are responsible for patterning during plant development. ...
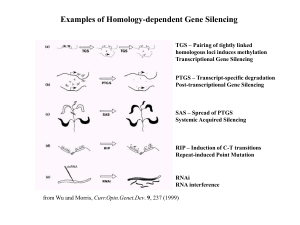
Nature Rev.Genet
... Transfer a mixture with siRNA, target mRNA fused with EGFP, and control RFP construct to a glass slide ...
... Transfer a mixture with siRNA, target mRNA fused with EGFP, and control RFP construct to a glass slide ...
BSC 1010 Exam 3 Study Guide
... • DNA to RNA • type of RNA produced: • Where in cell: • When during cell cycle: • How (what enzymes, structures are involved): • DNA coding strand vs. template strand • RNA polymerases • Transcriptional Unit (on the DNA) 1. Promoter 2. Coding region 3. Terminator sequence • Post-Transcriptional modi ...
... • DNA to RNA • type of RNA produced: • Where in cell: • When during cell cycle: • How (what enzymes, structures are involved): • DNA coding strand vs. template strand • RNA polymerases • Transcriptional Unit (on the DNA) 1. Promoter 2. Coding region 3. Terminator sequence • Post-Transcriptional modi ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.