Series and Parallel Circuits
... • Series Circuits are the simplest to work with. • Here we have three resistors of different resistances. They share a single connection point. When added together the total resistance is 90-Ohms. ...
... • Series Circuits are the simplest to work with. • Here we have three resistors of different resistances. They share a single connection point. When added together the total resistance is 90-Ohms. ...
Pre-Lab: (Total 10 Points)
... Fuel cells are used for direction conversion of the energy of combustion reactions to ______________. A fuel cell is a ______________ in which electricity is generated by a combustion reaction. A fuel cell provides a ______________ voltage that can be used to power motors, lights or any number of el ...
... Fuel cells are used for direction conversion of the energy of combustion reactions to ______________. A fuel cell is a ______________ in which electricity is generated by a combustion reaction. A fuel cell provides a ______________ voltage that can be used to power motors, lights or any number of el ...
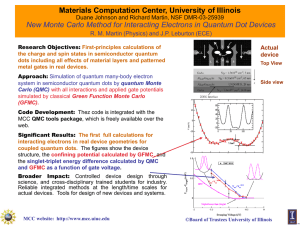
A Double Grounded Transformerless Photovoltaic Array String
... A new photovoltaic (PV) array power converter circuit is presented. The salient features of this inverter are: transformerless topology, grounded PV array, and only film capacitors. The motivations are to reduce cost, eliminate leakage ground currents, and improve reliability. The use of Silicon Car ...
... A new photovoltaic (PV) array power converter circuit is presented. The salient features of this inverter are: transformerless topology, grounded PV array, and only film capacitors. The motivations are to reduce cost, eliminate leakage ground currents, and improve reliability. The use of Silicon Car ...
EPAD® Technology (Electrically Programmable Analog Device)
... Hence the EPAD® (Electrically Programmable Analog Device) Technology was developed specifically by Advanced Linear Devices to address this need. EPAD is a new class of analog device, like the operational amplifier and the A/D converter. It is a unique CMOS-based device which, when used in combinatio ...
... Hence the EPAD® (Electrically Programmable Analog Device) Technology was developed specifically by Advanced Linear Devices to address this need. EPAD is a new class of analog device, like the operational amplifier and the A/D converter. It is a unique CMOS-based device which, when used in combinatio ...
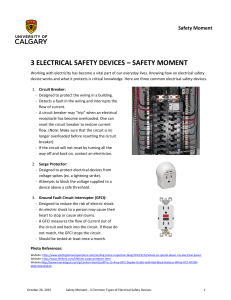
3 ELECTRICAL SAFETY DEVICES – SAFETY MOMENT
... Working with electricity has become a vital part of our everyday lives. Knowing how an electrical safety device works and what it protects is critical knowledge. Here are three common electrical safety devices. 1. Circuit Breaker: - Designed to protect the wiring in a building. - Detects a fault in ...
... Working with electricity has become a vital part of our everyday lives. Knowing how an electrical safety device works and what it protects is critical knowledge. Here are three common electrical safety devices. 1. Circuit Breaker: - Designed to protect the wiring in a building. - Detects a fault in ...
In a series circuit, every device must function for the circuit to be
... voltage across the components is shared The voltage of series circuit is equal to the voltage source, for example if you have a 12 volt battery, then the voltage is 12 volts. Remember with series circuit, there is voltage drop across each resistor. To find voltage drop use ohm’s law. ...
... voltage across the components is shared The voltage of series circuit is equal to the voltage source, for example if you have a 12 volt battery, then the voltage is 12 volts. Remember with series circuit, there is voltage drop across each resistor. To find voltage drop use ohm’s law. ...
1. Current which keeps on reversing it`s direction is called
... the other one is called neutral. The difference in potential between: A hot wire and the neutral is ___________ volts Two hot wires is .................... ___________ volts Between the neutral & the ground is ____ volts ...
... the other one is called neutral. The difference in potential between: A hot wire and the neutral is ___________ volts Two hot wires is .................... ___________ volts Between the neutral & the ground is ____ volts ...
Integrated circuit

An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small plate (""chip"") of semiconductor material, normally silicon. This can be made much smaller than a discrete circuit made from independent electronic components. ICs can be made very compact, having up to several billion transistors and other electronic components in an area the size of a fingernail. The width of each conducting line in a circuit can be made smaller and smaller as the technology advances; in 2008 it dropped below 100 nanometers, and has now been reduced to tens of nanometers.ICs were made possible by experimental discoveries showing that semiconductor devices could perform the functions of vacuum tubes and by mid-20th-century technology advancements in semiconductor device fabrication. The integration of large numbers of tiny transistors into a small chip was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits using discrete electronic components. The integrated circuit's mass production capability, reliability and building-block approach to circuit design ensured the rapid adoption of standardized integrated circuits in place of designs using discrete transistors.ICs have two main advantages over discrete circuits: cost and performance. Cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC's components switch quickly and consume little power (compared to their discrete counterparts) as a result of the small size and close proximity of the components. As of 2012, typical chip areas range from a few square millimeters to around 450 mm2, with up to 9 million transistors per mm2.Integrated circuits are used in virtually all electronic equipment today and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones, and other digital home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the low cost of integrated circuits.
















![1E6 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING [5 credits]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008172045_1-b416785fd6305cc783c87ea745442b53-300x300.png)