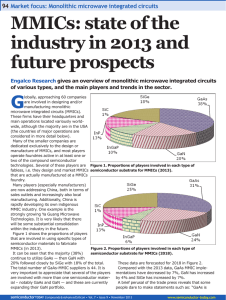
Part I
... The solutions to this equation are damped harmonic oscillations. The system will be underdamped for R2 < 4L/C, and overdamped for ...
... The solutions to this equation are damped harmonic oscillations. The system will be underdamped for R2 < 4L/C, and overdamped for ...
Ch19circuits - Mother Seton
... The safest plugs are those with three prongs; they have a separate ground line. Here is an example of household wiring – colors can vary, though! Be sure you know which is the hot wire before you do anything. ...
... The safest plugs are those with three prongs; they have a separate ground line. Here is an example of household wiring – colors can vary, though! Be sure you know which is the hot wire before you do anything. ...
v R + v C + v L
... unlike resistance, which is a property of the resistor independent of circuit frequency. • decreases as frequency increases. • at very high frequencies, XC approaches 0 and the capacitor acts like a wire. ...
... unlike resistance, which is a property of the resistor independent of circuit frequency. • decreases as frequency increases. • at very high frequencies, XC approaches 0 and the capacitor acts like a wire. ...
Describing Motion Verbally with Speed and Velocity
... across this 3 resistor must be __18__ V. This provides sufficient evidence to conclude that the voltage drop across the 6 resistor is __18__ V and the voltage drop across the 9 resistor is __18__ V. Therefore, the current in the 6 resistor is __3__ Amperes and the current in the 9 resistor ...
... across this 3 resistor must be __18__ V. This provides sufficient evidence to conclude that the voltage drop across the 6 resistor is __18__ V and the voltage drop across the 9 resistor is __18__ V. Therefore, the current in the 6 resistor is __3__ Amperes and the current in the 9 resistor ...
- Premier University of Technology
... Threshold voltage-effects of ion implantation. short channel and narrow width. The MOS transistor in dynamic operation, small signal model for low. medium and high frequencies. Charge coupled devices (CCD). EEE 6402: Compound Semiconductor Devices 3 Credits Introduction to GaAs device technology. Ga ...
... Threshold voltage-effects of ion implantation. short channel and narrow width. The MOS transistor in dynamic operation, small signal model for low. medium and high frequencies. Charge coupled devices (CCD). EEE 6402: Compound Semiconductor Devices 3 Credits Introduction to GaAs device technology. Ga ...
Undriven RLC Circuit - TSG@MIT Physics
... Consider the RLC circuit of fig. 2 below. The capacitor has an initial charge Q 0 (it was charged by a battery no longer in the circuit), but it can’t go anywhere because the switch is open. When the switch is closed, the positive charge will flow off the top plate of the capacitor, through the resi ...
... Consider the RLC circuit of fig. 2 below. The capacitor has an initial charge Q 0 (it was charged by a battery no longer in the circuit), but it can’t go anywhere because the switch is open. When the switch is closed, the positive charge will flow off the top plate of the capacitor, through the resi ...
Column Fixed Pattern Noise Suppression with STI profile control in
... condition, the column fixed pattern noise is to be screened out in wafer level by algorithm that compares averaging code of every column data with neighboring line (line averaging and line by line comparison) and calculated standard deviation of line averaging. From those pixel probe test and transi ...
... condition, the column fixed pattern noise is to be screened out in wafer level by algorithm that compares averaging code of every column data with neighboring line (line averaging and line by line comparison) and calculated standard deviation of line averaging. From those pixel probe test and transi ...
Integrated circuit

An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small plate (""chip"") of semiconductor material, normally silicon. This can be made much smaller than a discrete circuit made from independent electronic components. ICs can be made very compact, having up to several billion transistors and other electronic components in an area the size of a fingernail. The width of each conducting line in a circuit can be made smaller and smaller as the technology advances; in 2008 it dropped below 100 nanometers, and has now been reduced to tens of nanometers.ICs were made possible by experimental discoveries showing that semiconductor devices could perform the functions of vacuum tubes and by mid-20th-century technology advancements in semiconductor device fabrication. The integration of large numbers of tiny transistors into a small chip was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits using discrete electronic components. The integrated circuit's mass production capability, reliability and building-block approach to circuit design ensured the rapid adoption of standardized integrated circuits in place of designs using discrete transistors.ICs have two main advantages over discrete circuits: cost and performance. Cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC's components switch quickly and consume little power (compared to their discrete counterparts) as a result of the small size and close proximity of the components. As of 2012, typical chip areas range from a few square millimeters to around 450 mm2, with up to 9 million transistors per mm2.Integrated circuits are used in virtually all electronic equipment today and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones, and other digital home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the low cost of integrated circuits.