Primary Circuits workshop
... (Physicist-led activity) This activity models electrical circuits using pupils to represent charges/electrons travelling around a (~10ft x 10ft) rectangular circuit marked out using tape on the floor. Each child is given one or more sweets, representing energy, by a pupil representing the ‘battery’ ...
... (Physicist-led activity) This activity models electrical circuits using pupils to represent charges/electrons travelling around a (~10ft x 10ft) rectangular circuit marked out using tape on the floor. Each child is given one or more sweets, representing energy, by a pupil representing the ‘battery’ ...
Section H4: High-Frequency Transistor Models
... So far, we’ve been concentrating on the capacitors that are external to the transistor in an amplifier circuit and provide coupling or bypass functions. These components are treated as series capacitances and determine the low frequency response of the amplifier, which may be found by the method of ...
... So far, we’ve been concentrating on the capacitors that are external to the transistor in an amplifier circuit and provide coupling or bypass functions. These components are treated as series capacitances and determine the low frequency response of the amplifier, which may be found by the method of ...
A Fast Concurrent Power-Thermal Model for Sub-100nm
... temperature makes the thermal profile estimation of highperformance ICs a key issue to compute the total power dissipated in next-generations. In this paper we present accurate and compact analytical models to estimate the static power dissipation and the temperature of operation of CMOS gates. The ...
... temperature makes the thermal profile estimation of highperformance ICs a key issue to compute the total power dissipated in next-generations. In this paper we present accurate and compact analytical models to estimate the static power dissipation and the temperature of operation of CMOS gates. The ...
Fundamentals of Linear Electronics Integrated & Discrete
... – Are 4-layer silicon semiconductors. – Use low input power to control large load currents. – Are very common in industrial power & motor control. – Are inherently nonlinear devices. – Have two states: ON and OFF. • Unijunction transistors (UJTs) are not thyristors, but are commonly used with SCRs. ...
... – Are 4-layer silicon semiconductors. – Use low input power to control large load currents. – Are very common in industrial power & motor control. – Are inherently nonlinear devices. – Have two states: ON and OFF. • Unijunction transistors (UJTs) are not thyristors, but are commonly used with SCRs. ...
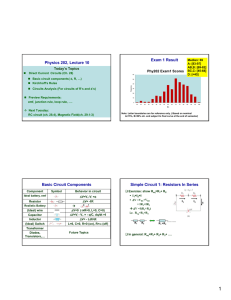
Physics 202, Lecture 10 Exam 1 Result Basic Circuit Components
... In general: 1/Req=1/R1+ 1/R2+ 1/R3+ …. ...
... In general: 1/Req=1/R1+ 1/R2+ 1/R3+ …. ...
Power supply of industrial enterprises Laboratory work Open
... In the substation to switch off fault transformer when relay protection responses high-frequency communication bus is used to deliver switching off signal to circuit breakers on supplying substations 1 and 2. As a communication bus power line 154 kV with high frequency filters, communication condens ...
... In the substation to switch off fault transformer when relay protection responses high-frequency communication bus is used to deliver switching off signal to circuit breakers on supplying substations 1 and 2. As a communication bus power line 154 kV with high frequency filters, communication condens ...
Integrated circuit

An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small plate (""chip"") of semiconductor material, normally silicon. This can be made much smaller than a discrete circuit made from independent electronic components. ICs can be made very compact, having up to several billion transistors and other electronic components in an area the size of a fingernail. The width of each conducting line in a circuit can be made smaller and smaller as the technology advances; in 2008 it dropped below 100 nanometers, and has now been reduced to tens of nanometers.ICs were made possible by experimental discoveries showing that semiconductor devices could perform the functions of vacuum tubes and by mid-20th-century technology advancements in semiconductor device fabrication. The integration of large numbers of tiny transistors into a small chip was an enormous improvement over the manual assembly of circuits using discrete electronic components. The integrated circuit's mass production capability, reliability and building-block approach to circuit design ensured the rapid adoption of standardized integrated circuits in place of designs using discrete transistors.ICs have two main advantages over discrete circuits: cost and performance. Cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC's components switch quickly and consume little power (compared to their discrete counterparts) as a result of the small size and close proximity of the components. As of 2012, typical chip areas range from a few square millimeters to around 450 mm2, with up to 9 million transistors per mm2.Integrated circuits are used in virtually all electronic equipment today and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones, and other digital home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the low cost of integrated circuits.