Introduction to Forensic Science
... Polygraphy—the use of the lie detector Anthropologist—study of human remains Serologist—deals with blood and other body fluids toxicologist—study of drugs and poisons Botanist—study of plants and plant residue ...
... Polygraphy—the use of the lie detector Anthropologist—study of human remains Serologist—deals with blood and other body fluids toxicologist—study of drugs and poisons Botanist—study of plants and plant residue ...
aquatic insects - UTas ePrints
... fish, wings are absent. They have also been lost from some species of more advanced orders of insects. Because of their rigid exoskeleton, insects cannot grow continuously but must shed their skeleton in a series of moults, the stage between moults being known as an instar. In the most primitive ins ...
... fish, wings are absent. They have also been lost from some species of more advanced orders of insects. Because of their rigid exoskeleton, insects cannot grow continuously but must shed their skeleton in a series of moults, the stage between moults being known as an instar. In the most primitive ins ...
Collecting and Identifying Insects
... o Environment (such as under a rock, on a flower, or in a stream) Keep the information with the insect; you will use it later to label your specimen. Store your insects in the freezer until you are ready to pin them. This keeps them fresh and flexible. ...
... o Environment (such as under a rock, on a flower, or in a stream) Keep the information with the insect; you will use it later to label your specimen. Store your insects in the freezer until you are ready to pin them. This keeps them fresh and flexible. ...
An Introduction to Forensic Science
... ground due to gravity. The skin will appear dark blue or purple in these lower areas close to the ground. ...
... ground due to gravity. The skin will appear dark blue or purple in these lower areas close to the ground. ...
An Introduction to Forensic Science
... ground due to gravity. The skin will appear dark blue or purple in these lower areas close to the ground. ...
... ground due to gravity. The skin will appear dark blue or purple in these lower areas close to the ground. ...
Think like an Entomologist… a scientist who studies insects
... Parasite: An organism that lives in or on another organism (the host) during some portion of its life cycle. Parasitoid: An animal that feeds in or on another living animal, consuming all or most of its tissues and eventually killing it. Pest: An organism that interferes with human activities, prope ...
... Parasite: An organism that lives in or on another organism (the host) during some portion of its life cycle. Parasitoid: An animal that feeds in or on another living animal, consuming all or most of its tissues and eventually killing it. Pest: An organism that interferes with human activities, prope ...
Chapter 1
... A medical examiner can often estimate the time of death by evaluating the stage of decomposition: Rigor mortis- immediately following death, when the body relaxes and then becomes rigid without the shortening of the muscles. Usually occurs within the first 24 hours and disappears within 36 hours. Li ...
... A medical examiner can often estimate the time of death by evaluating the stage of decomposition: Rigor mortis- immediately following death, when the body relaxes and then becomes rigid without the shortening of the muscles. Usually occurs within the first 24 hours and disappears within 36 hours. Li ...
Forensics - Salem Press
... Forensic anthropologists are most frequently called upon when human skeletal remains are found. Anthropologists use the remains to assist in identifying victims. They may also provide approximate dates and causes of death. Forensic entomology studies how insects colonize dead bodies. On the basis of ...
... Forensic anthropologists are most frequently called upon when human skeletal remains are found. Anthropologists use the remains to assist in identifying victims. They may also provide approximate dates and causes of death. Forensic entomology studies how insects colonize dead bodies. On the basis of ...
File
... flight, lay eggs on the surface of a water body and die, usually within a day but ranging from a few minutes to several days. The adults have no functioning mouthparts with which to feed, their only purpose is reproduction and dispersal. ...
... flight, lay eggs on the surface of a water body and die, usually within a day but ranging from a few minutes to several days. The adults have no functioning mouthparts with which to feed, their only purpose is reproduction and dispersal. ...
Insect Life Cycle
... specific to the type of insect. Each growth satge is called an instar. • After hatching from an egg, the insect is called the first instar. • After the first molt, the insect is called the second instar (and so on). ...
... specific to the type of insect. Each growth satge is called an instar. • After hatching from an egg, the insect is called the first instar. • After the first molt, the insect is called the second instar (and so on). ...
insects in the SEM
... The way insects sense touch is through stiff hairs that stick out from the armoured plates. When a hair touches against something it bends. That action pushes on a nerve cell at the base of the hair inside the armour plate, which in turn tells the insect brain what is going on. It works a little l ...
... The way insects sense touch is through stiff hairs that stick out from the armoured plates. When a hair touches against something it bends. That action pushes on a nerve cell at the base of the hair inside the armour plate, which in turn tells the insect brain what is going on. It works a little l ...
Unit 2 Study Outline
... • Forensic entomologists use insects as investigative aids • By examining insects, larvae or pupae associated with a corpse, knowing the life cycle of insects, and by using the existing environmental factors, forensic entomologists can estimate the time of death Jurisprudence: Attorneys for the pros ...
... • Forensic entomologists use insects as investigative aids • By examining insects, larvae or pupae associated with a corpse, knowing the life cycle of insects, and by using the existing environmental factors, forensic entomologists can estimate the time of death Jurisprudence: Attorneys for the pros ...
An Introduction to Forensic Science
... ground due to gravity. The skin will appear dark blue or purple in these lower areas close to the ground. ...
... ground due to gravity. The skin will appear dark blue or purple in these lower areas close to the ground. ...
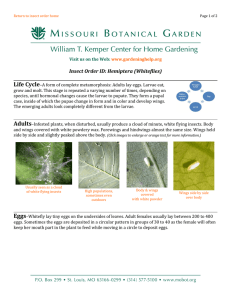
Insect Order ID: Hemiptera (Whiteflies)
... Life Cycle–A form of complete metamorphosis: Adults lay eggs. Larvae eat, grow and molt. This stage is repeated a varying number of times, depending on species, until hormonal changes cause the larvae to pupate. They form a pupal case, inside of which the pupae change in form and in color and develo ...
... Life Cycle–A form of complete metamorphosis: Adults lay eggs. Larvae eat, grow and molt. This stage is repeated a varying number of times, depending on species, until hormonal changes cause the larvae to pupate. They form a pupal case, inside of which the pupae change in form and in color and develo ...
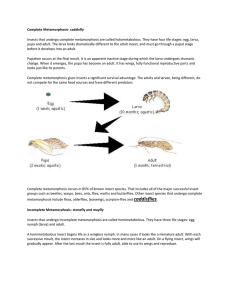
Insects that undergo complete metamorphosis are called
... pupa and adult. The larva looks dramatically different to the adult insect, and must go through a pupal stage before it develops into an adult. Pupation occurs at the final moult. It is an apparent inactive stage during which the larva undergoes dramatic change. When it emerges, the pupa has become ...
... pupa and adult. The larva looks dramatically different to the adult insect, and must go through a pupal stage before it develops into an adult. Pupation occurs at the final moult. It is an apparent inactive stage during which the larva undergoes dramatic change. When it emerges, the pupa has become ...
An Introduction to Forensic Science I
... How does the decomposition rate compare in: – sunshine vs shade? – In cool weather vs hot weather? – In a shallow grave vs on the ground? – In water? – Inside a car? – What effect do other variables have—humidity, insect activity, clothing, body weight, & so on? ...
... How does the decomposition rate compare in: – sunshine vs shade? – In cool weather vs hot weather? – In a shallow grave vs on the ground? – In water? – Inside a car? – What effect do other variables have—humidity, insect activity, clothing, body weight, & so on? ...
an introduction to the saps forensics laboratory
... The known (control) sample is material collected from a known source. Examples of control samples are: Blood collected by pathologist from the deceased body. Buccal epithelial cells collected by authorized person from suspect or victim. Test cartridge and projectile fired from firearm during examina ...
... The known (control) sample is material collected from a known source. Examples of control samples are: Blood collected by pathologist from the deceased body. Buccal epithelial cells collected by authorized person from suspect or victim. Test cartridge and projectile fired from firearm during examina ...
an intro to forensics ppt
... It is important to realize that the forensic scientist must pull from a wide array of knowledge and specialists to competently do his or her job. Forensics is more of a team effort than one would imagine. (Forget CSI, folks…….the real world is nothing like that.) A death that is unexpected or is tho ...
... It is important to realize that the forensic scientist must pull from a wide array of knowledge and specialists to competently do his or her job. Forensics is more of a team effort than one would imagine. (Forget CSI, folks…….the real world is nothing like that.) A death that is unexpected or is tho ...
File
... sucking blood. Fleas are external parasites, living by hematophagy off the blood of mammals and birds. ...
... sucking blood. Fleas are external parasites, living by hematophagy off the blood of mammals and birds. ...
Definition Page - The Curriculum Corner
... to walk and climb; all insects have three sets (six) of legs coming from their thorax ...
... to walk and climb; all insects have three sets (six) of legs coming from their thorax ...
Exam Review
... What does the V-pattern tell us? Briefly explain the different V-patterns and what they indicate. Compare and contrast low and high explosions. Compare and contrast primary and secondary explosions. Give examples of each. Compare and contrast rifled and smooth barrels. What is the most useful tool t ...
... What does the V-pattern tell us? Briefly explain the different V-patterns and what they indicate. Compare and contrast low and high explosions. Compare and contrast primary and secondary explosions. Give examples of each. Compare and contrast rifled and smooth barrels. What is the most useful tool t ...
What is Forensic Science? - Forensic science is science applied to
... race and skeletal injury Example: a female’s pelvis will differ from that of a male because of childbirth capabilities. Forensic Entomologist- responsible for the study of insects and their relation to criminal investigations. Ex: When a person dies their decomposing body attracts insects that lay ...
... race and skeletal injury Example: a female’s pelvis will differ from that of a male because of childbirth capabilities. Forensic Entomologist- responsible for the study of insects and their relation to criminal investigations. Ex: When a person dies their decomposing body attracts insects that lay ...